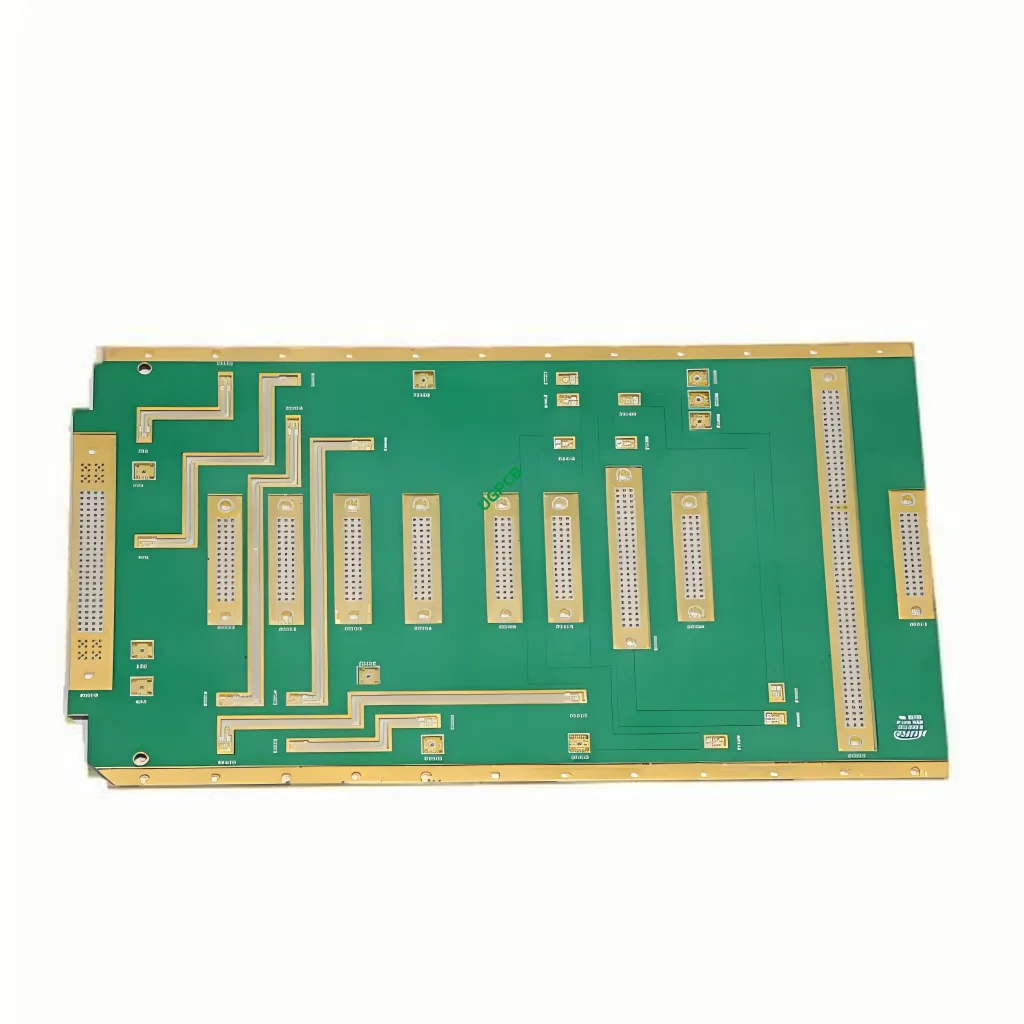
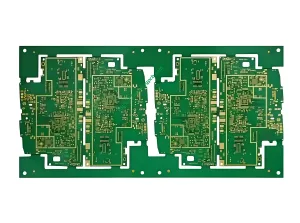
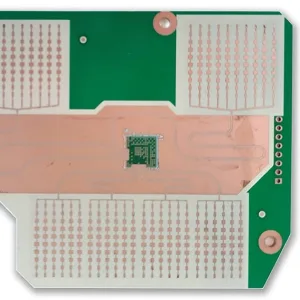
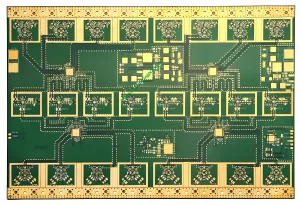
Overview of Microwave Hybrid PCB
Microwave Hybrid PCB, also known as Hybrid Printed Circuit Board, is a specialized type of circuit board designed for high-frequency applications. It combines the benefits of traditional FR4 material and advanced materials like Teflon and ceramic to meet stringent performance requirements in various industries.
Definition and Design Considerations
A Hybrid PCB integrates different substrate materials within a single board. This design approach allows for optimizing dielectric constants (ranging from 2.2 ل 16) and tailoring the board’s properties for specific high-frequency needs. Key design considerations include material selection, layer stack-up, and impedance control to ensure signal integrity and minimize losses.
Working Principle and Applications
The working principle revolves around managing electromagnetic waves at microwave frequencies efficiently. By using a combination of low and high dielectric constant materials, Hybrid PCBs can achieve better impedance matching, reduced signal loss, and enhanced overall performance. They are widely used in telecommunications, أنظمة الرادار, satellite communications, and other high-frequency microwave applications.
Classification and Materials
Types:
- 2-Layer to Multi-Layer Hybrid PCBs: Depending on complexity, these boards can range from two layers up to multiple layers, accommodating intricate circuit designs.
- Thickness Variants: Available in thicknesses from 0.1mm to 12mm, providing flexibility for different application requirements.
Core Materials:
- Teflon: Known for its low dielectric constant and loss tangent, making it ideal for high-frequency applications.
- Ceramic + FR4: Combines the thermal stability of ceramic with the mechanical robustness of FR4, offering a balanced solution for many designs.
Performance and Structure
Hybrid PCBs excel in high-frequency performance due to their carefully selected materials and precise manufacturing processes. They feature controlled copper thickness (from 0.5oz to 3oz), which directly impacts current-carrying capacity and heat dissipation. The surface technology options, including Silver, ذهب, and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives), further enhance solderability and corrosion resistance.
Characteristics and Production Process
Key characteristics of Microwave Hybrid PCBs include:
- Enhanced signal integrity through optimized dielectric constants.
- Superior thermal management capabilities.
- Customizable to meet specific application needs regarding frequency range, power handling, and environmental conditions.
The production process involves several stages:
- Material Selection: Choosing appropriate core and prepreg materials based on design specifications.
- Lamination: Combining layers under pressure and heat to form a solid board structure.
- النقش: Removing unwanted copper to create the desired circuit pattern.
- Surface Finishing: Applying the chosen surface treatment to protect against oxidation and improve solderability.
- ضمان الجودة: Ensuring the final product meets IPC6012 Class 2 or 3 المعايير, guaranteeing reliability and performance.
Use Scenarios
Microwave Hybrid PCBs are essential in scenarios where conventional PCBs cannot provide the necessary performance levels. These include but are not limited to:
- Telecommunication infrastructure, such as base stations and antennas.
- Aerospace and defense systems requiring reliable high-frequency operation.
- Medical equipment utilizing microwave technology for diagnostics or treatment.
- High-speed data communication networks and servers.
في ملخص, Microwave Hybrid PCBs represent a sophisticated solution for demanding high-frequency applications, combining advanced materials and precise engineering to deliver exceptional performance and reliability.
 شعار UGPCB
شعار UGPCB