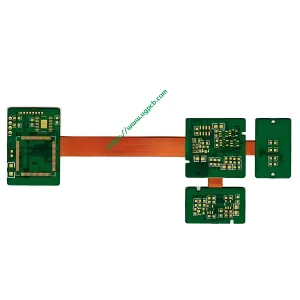
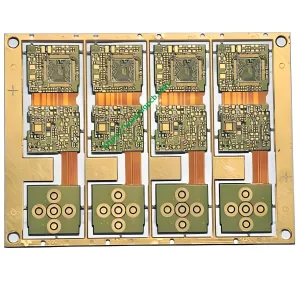
Promotion of R-FPCB Technology
The application of R-FPCB for high-density interconnect structure (IDH) to automotive PCB has greatly promoted the rapid development of R-FPCB technology. Al mismo tiempo, with the development and improvement of PCB technology, R-FPCB has been developed and researched extensively and has been widely used. The global supply of R-FPCB is expected to increase substantially in the future. The durability and flexibility of R-FPCB also make it more suitable for applications in the automotive electronics field, gradually eroding the market share of rigid PCBs.
Advantages of R-FPCB in Electronics
PCB manufacturers are aware that R-FPCB is light, thin, and compact, and is particularly suitable for the latest portable electronics and automotive electronics—these end products are currently boosting the output of R-FPCB. Por lo tanto, industry insiders expect that R-FPCB will surpass other types of PCBs in the next few years.
Manufacturing Threshold and Automotive Electronics Demand
Although R-FPCB products are good, the manufacturing threshold is somewhat high. Among all types of PCBs, R-FPCB has the strongest resistance to harsh application environments, so it is favored by automotive electronics manufacturers. R-FPCB combines the durability of a rigid PCB with the adaptability of a flexible PCB. PCB companies are increasing the proportion of such PCBs in overall production to take full advantage of the great opportunities that continue to grow in demand. Reducing the assembly size and weight of electronic products, avoiding wiring errors, increasing assembly flexibility, improving reliability, and achieving three-dimensional assembly under different assembly conditions is an inevitable demand for the increasing development of electronic products. Interconnection technologies that can meet the needs of three-dimensional assembly, such as being light and flexible, have been increasingly widely used and valued in the automotive electronics industry.
Continuous Development of R-FPCB
With the continuous expansion of the R-FPCB application field, the flexible circuit board itself is also constantly developing, such as from single-sided flexible board to double-sided, multicapa, and even rigid-flexible board, etc.. Fine line width/pitch, surface technology applications, and the material characteristics of the flexible substrate itself put forward more stringent requirements for the production of flexible boards, such as substrate treatment, layer alignment, dimensional stability control, and decontamination. The reliability of small hole metallization and electroplating, as well as surface protective coating, etc., should be highly valued.
HDI R-FPCB
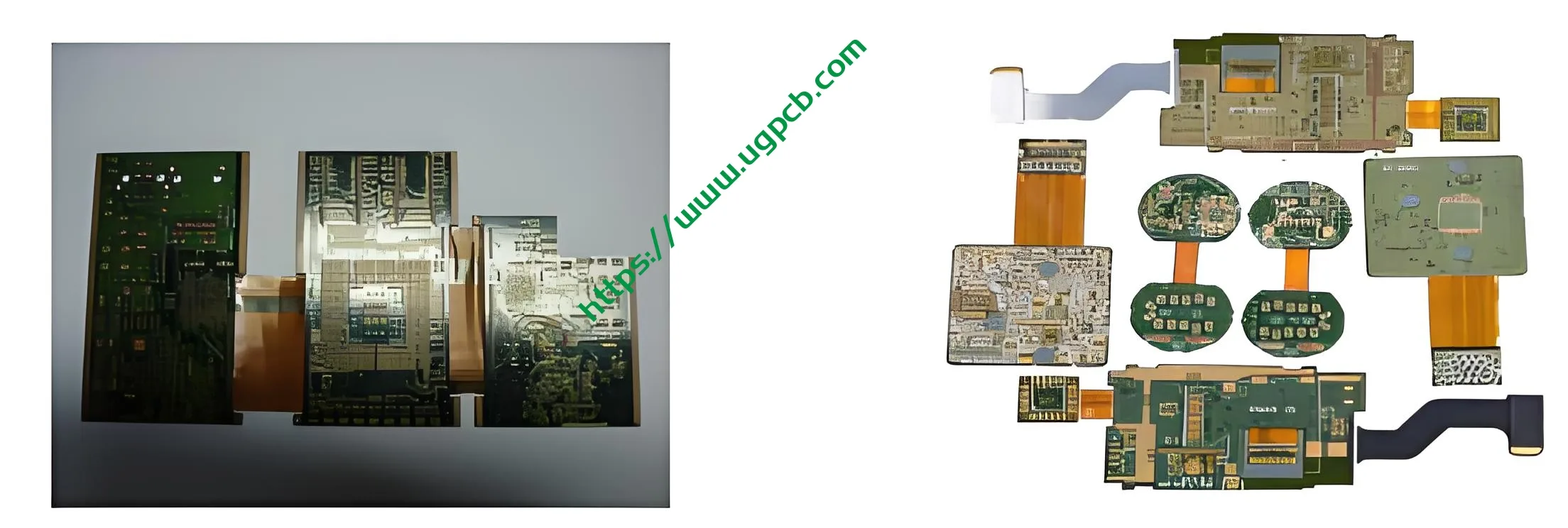

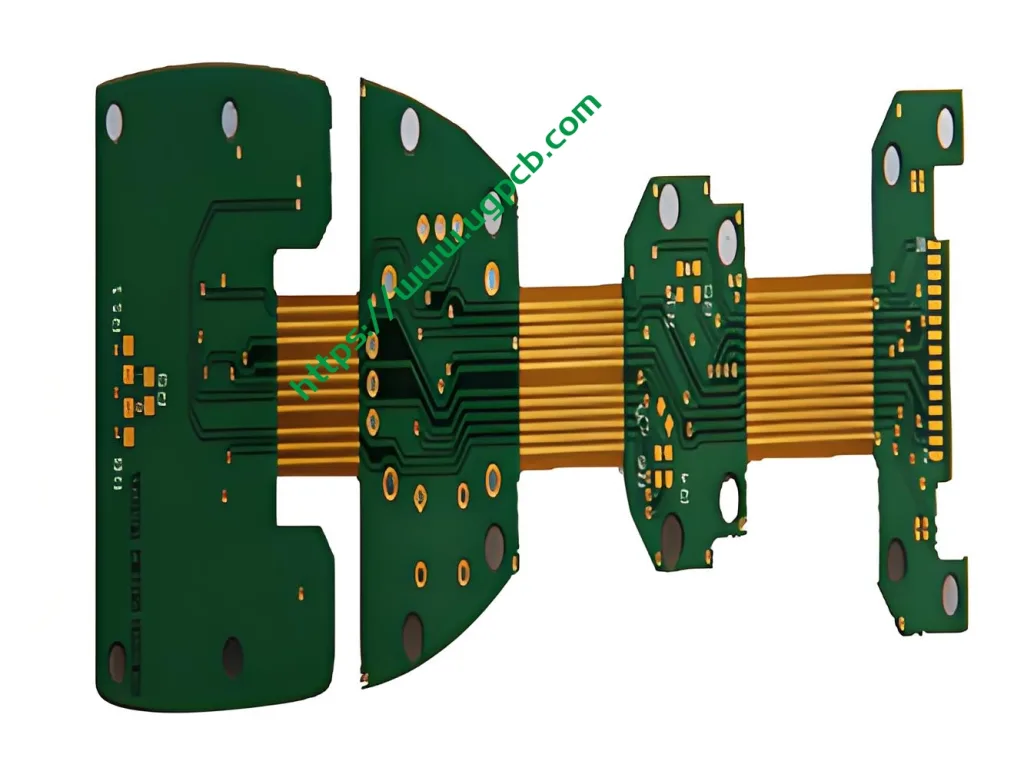
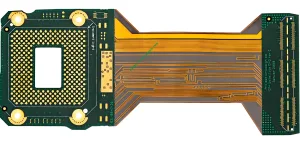
HDI R-FPCB (High-Density Interconnect Rigid-Flex PCB)
R-FPCB Design and Production Process
R-FPCB refers to a PCB that contains one or more rigid areas and one or more flexible areas on a PCB. It can be divided into different types such as flexible boards with reinforced layers and rigid-flex combined multilayer PCB boards.
Material Selection of R-FPCB
When considering the design and production process of an R-FPCB, it is very important to make adequate preparations, but this requires a certain degree of professional knowledge and an understanding of the characteristics of the required materials. The materials selected for R-FPCB directly affect the subsequent production process and its performance.
Flexible Substrate Material
ipcb selects DuPont’s (AP no adhesive series) polyimide flexible substrate. Polyimide is a material with good flexibility, excellent electrical properties, y resistencia al calor, but it has larger hygroscopicity and is not resistant to strong alkali. The reason why the base material without an adhesive layer is selected is that the adhesive between the dielectric layer and the copper foil is mostly acrylic, polyester, modified epoxy resin, y otros materiales. Modified epoxy resin adhesives and polyester adhesives have good flexibility but poor heat resistance. Although acrylic adhesives are satisfactory in terms of heat resistance, dielectric properties, and flexibility, they need to be considered. The glass transition temperature (tg) and pressing temperature are relatively high (around 185°C). Actualmente, many factories use Japanese (epoxy resin series) substrates and adhesives to produce R-FPCB.
Rigid PCB Material
There are also certain requirements for the choice of rigid PCB. ipcb first chose the lower cost epoxy glue board, but due to the smooth surface, it could not stick firmly, so FR-4.G200 and other substrates with a certain thickness were chosen. Sin embargo, due to the difference between the FR-4.G200 core material and the PI resin system, Tg and CTE were not compatible. After thermal shock, the rigid-flex joint part warped seriously and could not meet the requirements, so the rigidity of the PI resin series was finally selected. This material can be laminated with P95 base material or simply laminated with P95 prepreg. De este modo, the rigid-flex PCB board of the matching resin system can be laminated to avoid warping deformation after thermal shock. Actualmente, many PCB substrate manufacturers have developed and produced some rigid PCB materials specifically for R-FPCB.
Adhesive for Flex-Rigid Transition
For the adhesive part between the flexible PCB board and the hard PCB board, it is best to use No flow (low flow) Prepreg for pressing, because its small fluidity is very helpful for the soft and hard transition area. The transition area needs to be reworked due to glue overflow or functionality being affected. Actualmente, many companies that produce PCB raw materials have developed this kind of PP film, and there are many specifications that can meet the structural requirements. Además, for customers with ROHS, Tg alta, Impedancia, and other requirements, it is also necessary to pay attention to whether the characteristics of the raw material can meet the final requirements, such as the thickness specification of the PCB material, the dielectric constant, the TG value, and the environmental protection requirements.
 UGPCB LOGO
UGPCB LOGO