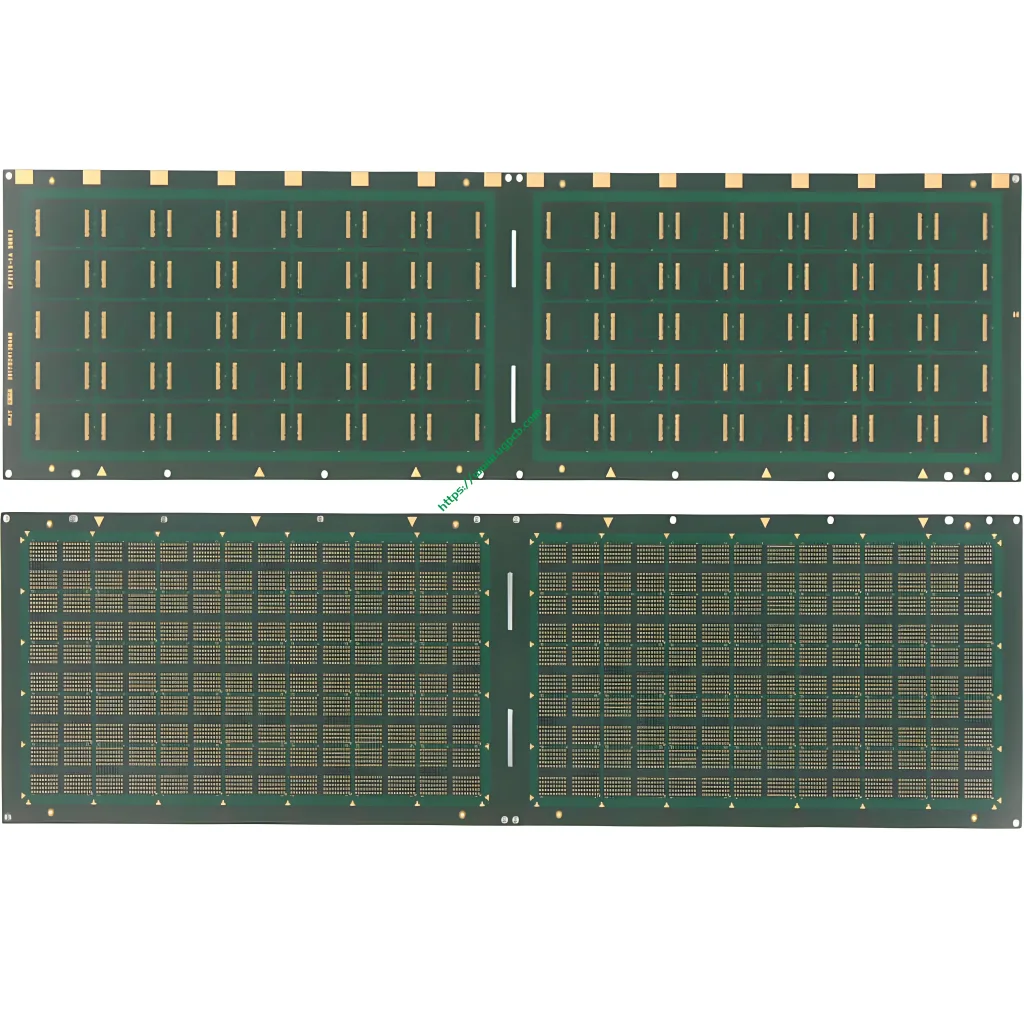
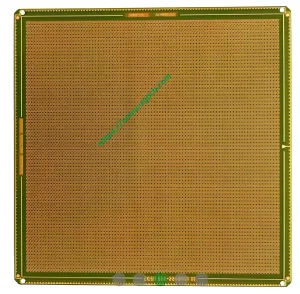
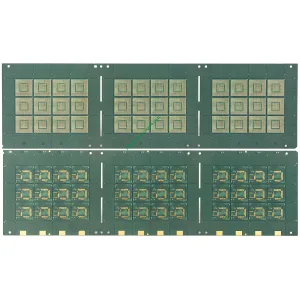
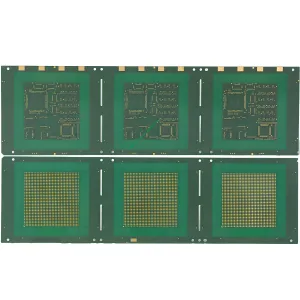
Characteristics of UGPCB DDR Package Carrier
High-Density Junction Structure
The UGPCB DDR package carrier features a high-density junction structure. This includes hole filling electroplating and hole stacking structure, contributing to its robust design.
Surface Treatment Methods
The carrier employs various surface treatment methods to enhance its performance and reliability.
Sheet and Surface Flatness Requirements
The UGPCB DDR package carrier adheres to strict sheet and surface flatness requirements to ensure proper functioning and integration into electronic devices.
Resin Filling
Resin filling is another critical aspect of the UGPCB DDR package carrier, contributing to its structural integrity and durability.
Application Process of UGPCB DDR Package Carrier
The application process of the UGPCB DDR package carrier involves semi-addition method and laser drilling techniques, ensuring precise and reliable manufacturing.
Application of UGPCB DDR Package Carrier
Smart Phones, Ordinateurs, IoT Products, and Message Electronics
The UGPCB DDR package carrier is widely applied in smart phones, ordinateurs, Internet des objets (IdO) produits, and message electronic products, underscoring its versatility and importance in modern electronics.
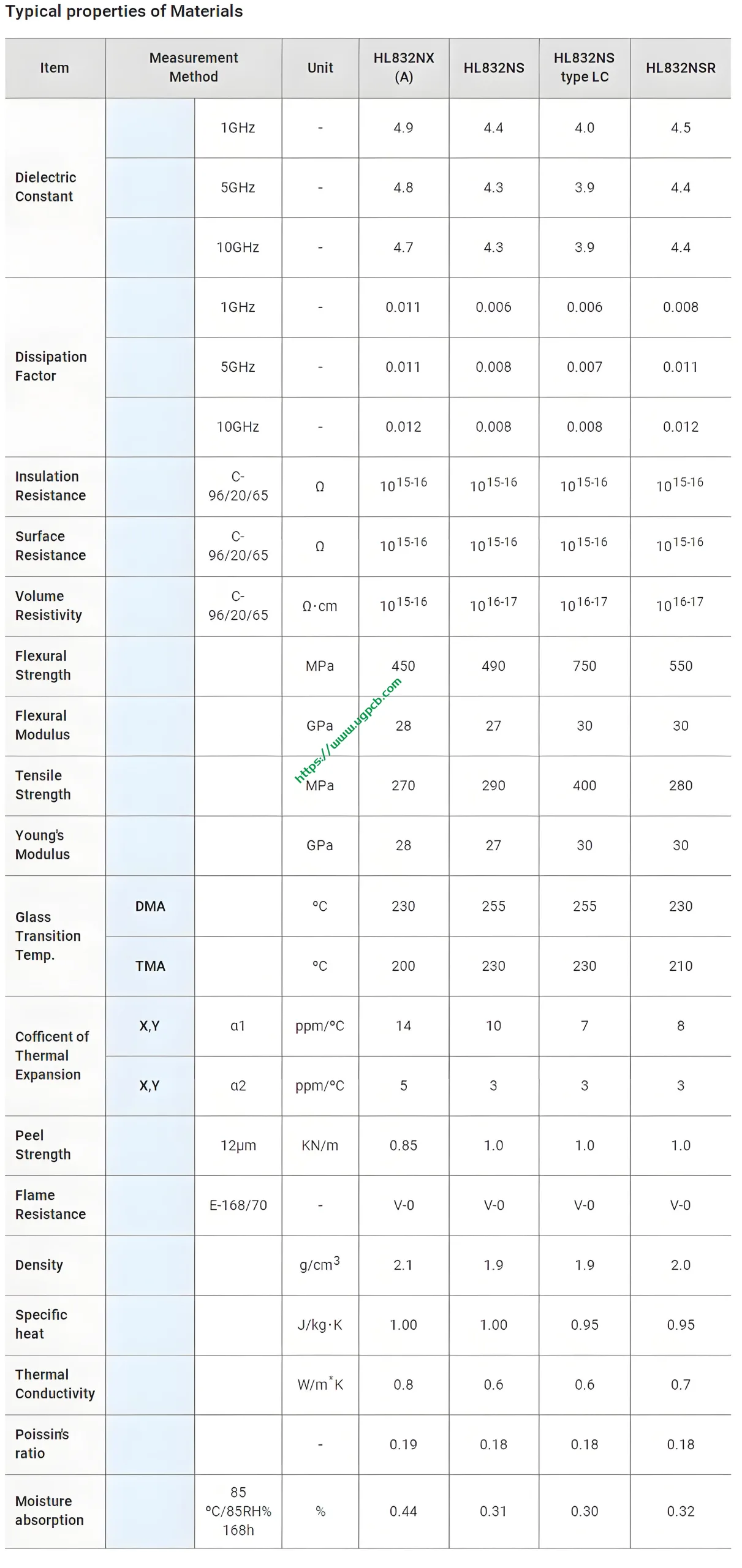
Typical Properties of Materials Used in UGPCB DDR Package Carrier
DDR Memory Overview
The full name of DDR memory is DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM). DDR SDRAM was first proposed by Samsung in 1996 and is an upgraded version of SDRAM, also known as “SDRAM II.” DDR is the mainstream memory specification at the beginning of the 21st century, supported by all major chipset manufacturers.
DDR Operating Frequencies and Data Transmission
As of 2017, DDR operating frequencies are mainly 100MHz, 133MHz, and 166MHz. DDR memory has the characteristics of double rate data transmission, adopting the method of operating frequency*2 in identification (par ex., DDR200, DDR266, DDR333, DDR400). DDR can perform data processing on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, doubling the data transmission rate compared to SDR (Single Data Rate) SDRAM.
DDR SDRAM Module Specifications
Compared to the SDRAM module, the DDR SDRAM module uses a 184-pin, 4-6 layer printed circuit board, with the electrical interface changed from “LVTTL” à “SSTL2.” DDR SDRAM is named based on data transfer volume (par ex., PC1600 and PC2100), differing from SDRAM’s clock frequency-based naming (par ex., PC100 and PC133). DDR200 in DDR SDRAM is equivalent to PC1600, with a data transfer volume of 1600MB/s, and DDR266 is equivalent to PC2100.
CAS Latency in DDR SDRAM
DDR SDRAM’s signal delay time (CL; CAS Latency) differs based on the Joint Electronic Engineering Design and Development Association (JEDEC) specifications. DDR SDRAM has two CAS delays: 2ns and 2.5ns. Faster CL=2 plus PC 2100 specification DDR SDRAM is called DDR 266A, while slower CL=2.5 plus PC 2100 specification DDR SDRAM is called DDR 266B.
 LOGO UGPCB
LOGO UGPCB