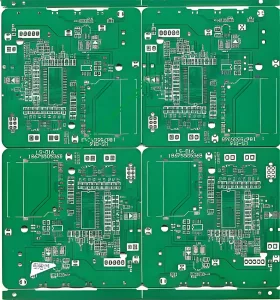
What is a 2 Layer PCB/Double-Sided PCB?
2 Layer PCBs are the most common type of PCB. Plus, 2 layer PCBs are also known as double-sided PCBs because they have components on both sides of the board. The 2-layer pcb fabrication is by bonding two layers of copper together with a dielectric material in between. And the dielectric material can be either an FR-42 or an FR-44.
How Does a Double-Layer PCB Work?
PCB Prototyping
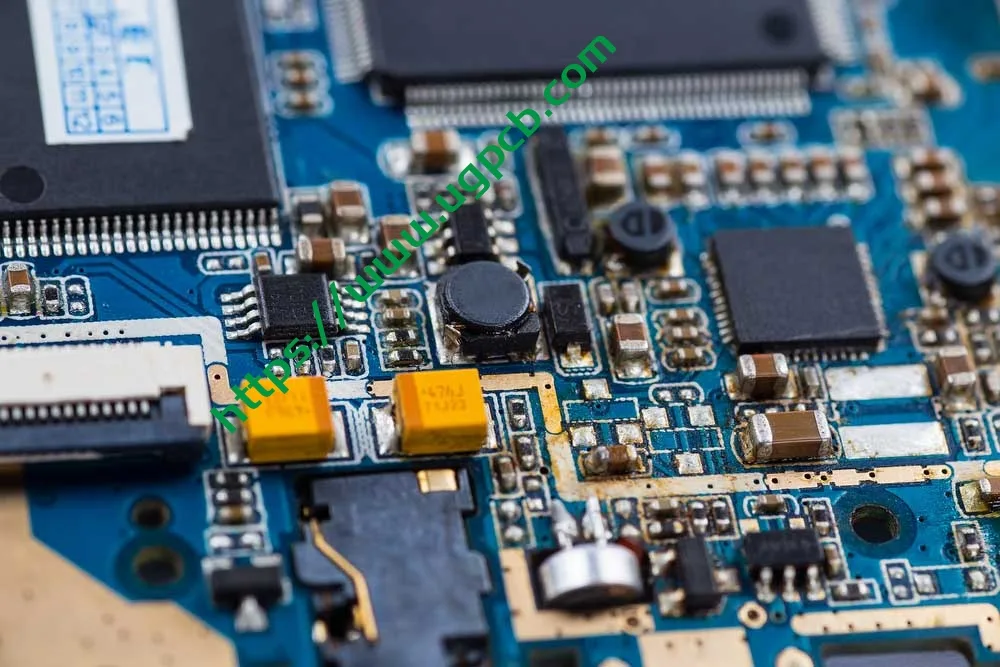
UN 2 layer PCB works by having electrical signals routed between the two layers of copper. These signals can be either digital or analog. Plus, the dielectric material in the middle of the board helps to keep these signals from interfering with each other.
2 Layer PCB Specifications
2 Layer PCB Thickness
UN 2 layer PCB can be anywhere from 0.010” to 0.060” thick. The thickness of the board will depend on the dielectric material that you use and the size of the components mounted on the board. Aussi, the thicker the board, the better it is at reducing crosstalk between the signal traces.
Layer Configuration
- Couche 1 (Couche supérieure): A signal layer.
- Inner Layer: A copper layer where most of the vias get located. Vias are the tiny little holes that connect the top and bottom layers together, allowing for electrical signals to flow from one layer to another.
- Couche 2 (Couche inférieure): Another signal layer.
- Ground Plane: Helps reduce noise in electrical signals and provides a place for the electrical signals to return. It also helps to distribute heat better and can be used as a power or ground layer.
- Couche de puissance: Used to distribute power to the different parts of the board and can be used as a return path for the ground signals.
- Prepreg Layer: A thin layer of dielectric material that provides insulation between the copper layers and support for the copper layers. The dielectric constant of the prepreg layer is 2.2, which is lower than the FR-408 dielectric constant.
- Solder Mask Layer: A thin layer of material that covers the exposed copper and protects it from oxidation and corrosion.
- Silkscreen Layer: A thin layer of material used to print the legends on the board, the board’s name, and part numbers.
How to Make a 2-Layer PCB/Double-Sided Circuit Board
To make a 2 couche PCB, you need to start with a substrate, the most common of which is FR-4. Once you have your substrate, you need to add the copper in layers.

- Couche de signal: The first layer added, where it will carry the electrical signals.
- Couche terrestre: The second layer added, where the electrical signals will return to it.
- Prepreg Layer: An insulating material that provides insulation between the layers.
- Masque de soudure: A thin layer of green or black plastic that helps to protect the copper from short circuits and corrosion.
- Silkscreen: A white or yellow printing on the PCB that shows the name of the components and their values.
2 Layer PCB Price
The price of a 2-layer PCB will vary depending on the size of the board, the complexity of the design, and the quantity that you order. Plus, 2-layer PCBs are typically more expensive than single-sided board because they require more materials and labor to manufacture. The cost of a 2 layer PCB can range from 1000 per square foot. Donc, if you need a 2-layer PCB that is 2 feet by 2 feet, it would cost between 4000.
 LOGO UGPCB
LOGO UGPCB