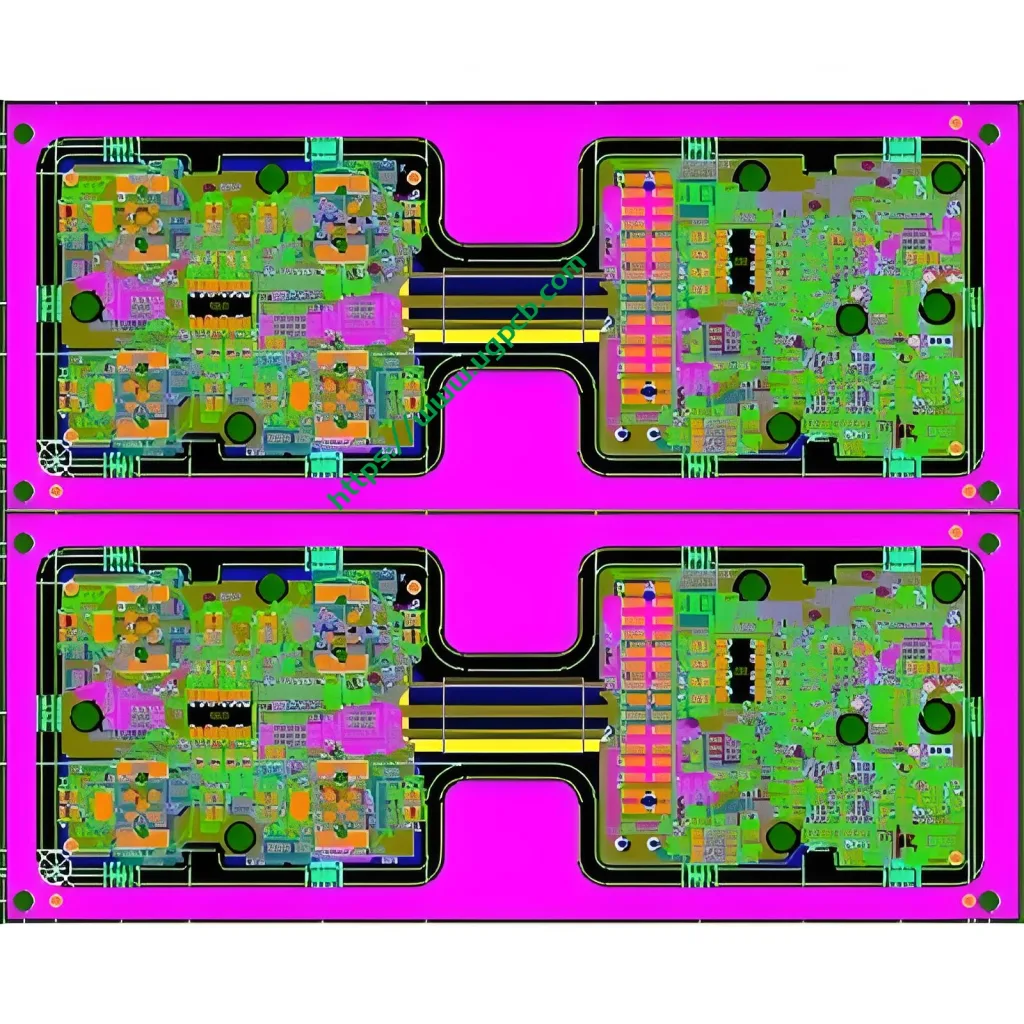
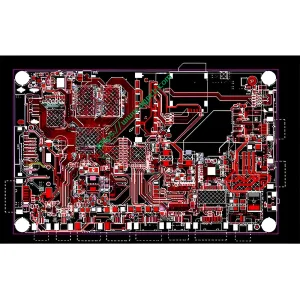
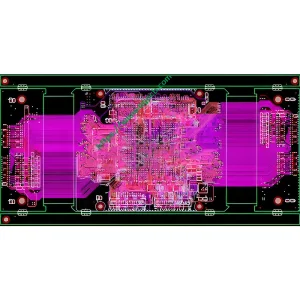
Définition du PCB HDI
Interconnexion à haute densité (IDH) est simplement un PCB avec un nombre plus élevé d'interconnexions dans la plus petite empreinte. Cela conduit à la miniaturisation de la carte de circuit imprimé. Les composants sont placés plus près les uns des autres et l'espace de la carte est considérablement réduit, Mais la fonctionnalité n'est pas compromise.
Plus précisément, un PCB avec une moyenne de 120 à 160 Les broches par pouce carré sont considérées comme un PCB HDI. Les conceptions HDI combinent le placement des composants dense et le routage polyvalent. HDI Technologie microporeuse popularisée en mettant en œuvre des microvias, vias enterrés, et vias aveugles. Le forage réduit du cuivre est une caractéristique des conceptions HDI.
Avantages du PCB HDI
Polyvalence extraordinaire
Les planches HDI sont idéales lorsque le poids, espace, fiabilité, et les performances sont les principales préoccupations.
Conception compacte
La combinaison de l'aveugle, enterré, et les micro vias réduisent les exigences de l'espace du conseil d'administration.
Meilleure intégrité du signal
HDI utilise via-pad et aveugle via la technologie. Cela aide à garder les composants proches les uns des autres, Réduction des longueurs du chemin du signal. La technologie HDI supprime les talons à travers, réduisant ainsi les réflexions du signal, améliorant ainsi la qualité du signal. Donc, Il améliore considérablement l'intégrité du signal en raison de chemins de signal plus courts.
Haute fiabilité
La mise en œuvre de vias empilés fait de ces conseils une super barrière contre les conditions environnementales extrêmes.
Rentable
La fonctionnalité d'une carte à trous de 8 couches standard (PCB standard) peut être réduit à une carte UGPCB à 6 couches sans compromettre la qualité.
 LOGO UGPCB
LOGO UGPCB