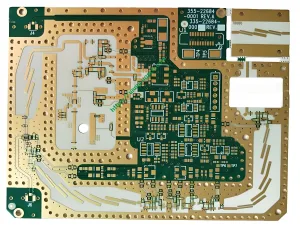
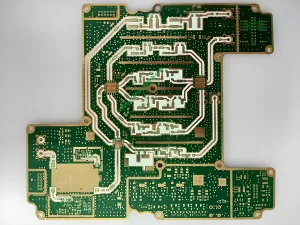
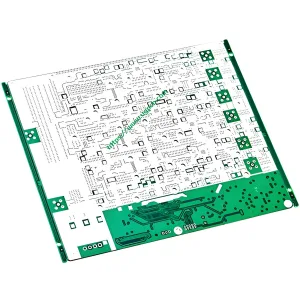
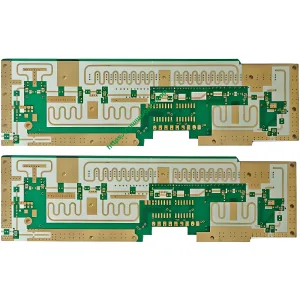
Overview of High Frequency PCB
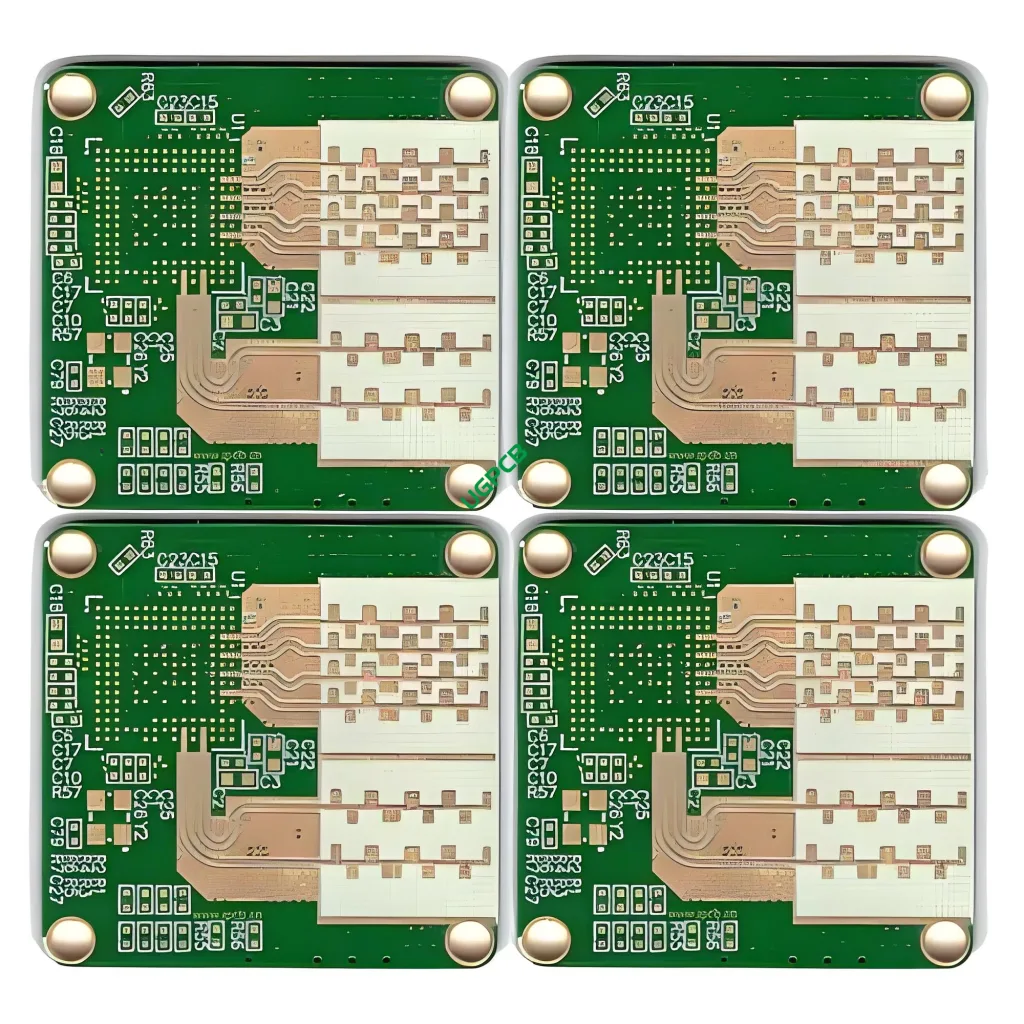
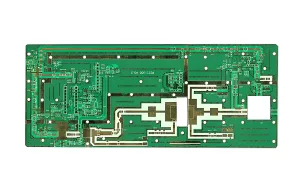
A high-frequency PCB is a specialized type of circuit board designed to operate at high frequencies, typically in the range of gigahertz (GHz). These PCBs are essential for applications that require precise signal transmission and minimal signal loss. They are widely used in industries such as telecommunications, systèmes radar, and satellite communications. The quality standard for high-frequency PCBs is IPC 6012 Class 2, ensuring high reliability and performance.
Définition et spécifications clés
A high-frequency PCB is defined by its ability to handle signals at very high frequencies while maintaining signal integrity. The dielectric constant (dk) of these PCBs ranges from 2.0 à 1.6, which is crucial for controlling signal speed and impedance. The number of layers can vary from 1 à 36, providing flexibility for different design requirements. The thickness of the PCB ranges from 0.254mm to 12mm, and the copper thickness can be either 0.5oz or 1oz. Surface technologies include Silver, Or, and OSP, each offering different benefits in terms of solderability and corrosion resistance. Special processes like mixed materials and stepped grooves further enhance the performance of high-frequency PCBs.
Considérations de conception
When designing a high-frequency PCB, several factors must be considered:
- Constante diélectrique (dk): The dk value between 2.0 et 1.6 is critical for maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies.
- Nombre de couches: The wide range of layer options (1 à 36) allows for customization based on specific application needs.
- Épaisseur: The thickness range from 0.254mm to 12mm provides flexibility in design, catering to different spatial and functional requirements.
- Épaisseur du cuivre: The choice between 0.5oz and 1oz base copper affects the current-carrying capacity and signal integrity.
- Technologie de surface: Options like Silver, Or, and OSP provide different levels of solderability and corrosion resistance.
- Processus spéciaux: Techniques like mixed materials and stepped grooves can significantly enhance the performance of high-frequency PCBs.
Principe de fonctionnement
High-frequency PCBs operate based on the principle of controlled impedance and minimal signal loss. The dielectric constant of the materials used ensures that signals travel with minimal delay and loss, maintenir leur intégrité. Le contrôle précis de l'épaisseur et du poids du cuivre permet une impédance constante, ce qui est essentiel pour la transmission des signaux haute fréquence. Surface technologies like Silver, Or, and OSP provide reliable connection points for components, Assurer un transfert de signal efficace.
Applications
High-frequency PCBs are used in a variety of applications that require high-speed data transmission and signal integrity:
- Télécommunications: Ensuring clear and reliable signal transmission in mobile phones, base stations, and other communication devices.
- Radar: Providing accurate and reliable signal processing in military and civilian radar systems.
- Communications par satellite: Facilitating rapid and reliable data transfer between ground stations and satellites.
Classification
High-frequency PCBs can be classified based on several criteria:
- Frequency Range: Typically operating at gigahertz (GHz) frequencies.
- Nombre de couches: Allant de 1 à 36 couches, en fonction de la complexité du circuit.
- Épaisseur: Options from 0.254mm to 12mm allow for customization based on specific application needs.
- Épaisseur du cuivre: Standard and heavy copper options (0.5oz and 1oz) cater to different current-carrying capacities.
- Technologie de surface: Choices like Silver, Or, and OSP provide different levels of solderability and corrosion resistance.
Propriétés des matériaux
The key properties of high-frequency PCB materials include:
- Faible constante diélectrique: Assure un délai et une perte de signal minimal, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
- Grande gamme d'épaisseur: Permet une flexibilité dans la conception, catering to different spatial and functional requirements.
- Excellent Signal Integrity: Maintient l'intégrité du signal même aux hautes fréquences, Assurer des performances fiables.
- Reliable Connection Points: Surface technologies like Silver, Or, and OSP provide strong and reliable connection points for components.
Processus de production
The production of a high-frequency PCB involves several steps:
- Sélection des matériaux: Choosing materials with a low dielectric constant and high signal fidelity.
- Conception de circuit: Création de la disposition du circuit avec des considérations pour les performances à haute fréquence et l'intégrité du signal.
- Gravure: Suppression du cuivre inutile pour créer le modèle de circuit souhaité.
- Laminage: Collage de plusieurs couches ensemble sous haute pression et température pour garantir une connexion solide et fiable.
- Finition des surfaces: Applying surface technologies like Silver, Or, or OSP to enhance solderability and corrosion resistance.
- Processus spéciaux: Utilizing techniques like mixed materials and stepped grooves to further enhance performance.
- Tests et contrôle qualité: S'assurer que le produit final répond à toutes les spécifications et normes.
Utiliser des scénarios
High-frequency PCBs are used in scenarios where high-speed data transmission and signal integrity are critical:
- Mobile Phones: Ensuring clear and reliable signal transmission in modern smartphones.
- Base Stations: Providing accurate and reliable signal processing in communication infrastructure.
- Radar: Enabling precise and reliable signal processing in military and civilian radar applications.
- Communications par satellite: Facilitating rapid and reliable data transfer between ground stations and satellites.
En résumé, high-frequency PCBs are specialized circuit boards designed for high-speed data transmission and signal integrity. Their low dielectric constant, grande gamme d'épaisseur, and excellent signal fidelity make them ideal for applications in telecommunications, systèmes radar, and satellite communications.
 LOGO UGPCB
LOGO UGPCB