정의 및 기능
A ventilator is a medical device designed to assist individuals who are unable to breathe independently. It delivers oxygen to the lungs and removes carbon dioxide, crucial for patients with respiratory issues. The ventilator comprises a compressible air reservoir, an oxygen supply, a breathing tube, and multiple printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAS) that manage airflow and monitor the ventilator’s functions.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Ventilators are vital in modern medicine, playing a crucial role in preventing and treating respiratory failure, reducing complications, and saving lives. They are widely used in various respiratory conditions, anesthesia management during surgery, and emergency resuscitation.
Classification of Ventilators
By Type of Use or Application
(1) Controlled Mechanical Ventilation (CMV)
- 정의: Breathing is entirely controlled by the ventilator when spontaneous breathing is absent or weakened.
- Applicability: Diseases causing loss or weakening of spontaneous breathing.
(2) Assisted Mechanical Ventilation (AMV)
- 정의: Ventilator assists spontaneous breathing.
- Applicability: Weak spontaneous breathing requiring support.
By Route of Use
- (1) Intrathoracic or Airway Compression Type
- (2) Chest Appearance Type
By Switching Mode of Inhalation and Exhalation
- (1) Constant Pressure Type
- (2) Volume-Fixed Type
- (3) Timing Type
- (4) Mixed Type (Multifunctional Type)
By Ventilation Frequency
- (1) High-Frequency Ventilation: >60 times/min
- (2) Constant Frequency Ventilation: <60 times/min
By Synchronization Device
- (1) Synchronous Ventilator: Triggers with spontaneous breathing.
- (2) Asynchronous Ventilator: Used for controlled mechanical ventilation.
By Applicable Object
- (1) Baby Ventilator
- (2) Children Ventilator
- (3) Adult Ventilator
By Working Principle
- (1) Simple Ventilator
- (2) Membrane Lung Ventilator
Modes and Functions of Mechanical Ventilation
Primary Modes
(1) Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (IPPV)
- 작동 원리: Positive pressure during inhalation, zero pressure during exhalation.
- Clinical Application: Patients with respiratory failure.
(2) Intermittent Positive and Negative Pressure Ventilation (IPNPV)
- 작동 원리: Positive pressure during inhalation, negative pressure during exhalation.
- Clinical Application: Causes alveolar collapse.
(3) Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
- 작동 원리: Positive airway pressure throughout the respiratory cycle.
- 장점: Reduces inspiratory effort, prevents alveolar collapse.
- 단점: Disturbs circulation, causes barotrauma.
(4) Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation and Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (IMV/SIMV)
- IMV: No synchronization, time-based ventilation.
- SIMV: Synchronized ventilation with spontaneous breathing.
- 장점: Reduces ventilator dependence, better for weaning.
- 애플리케이션: Used during weaning.
(5) Mandatory Minute Ventilation (MMV)
- 작동 원리: Adjusts ventilation to meet preset minute ventilation.
(6) Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV)
- 정의: Pressure support during spontaneous inhalation.
- 작동 원리: Starts with inhalation, ends with exhalation.
- 애플리케이션: Used with SIMV for weaning.
(7) Volume Support Ventilation (VSV)
- 작동 원리: Patient-triggered, supports to achieve desired tidal volume.
(8) Biphasic or Bilevel Positive Pressure Ventilation
- 작동 원리: Different pressures for inhalation (P1) and exhalation (P2).
- Clinical Application: Versatile, can simulate IPPV, CPAP, and SIMV.
Secondary Functions
(1) End-Inspiratory Pause
- 기능: Holds breath at end of inspiration.
- Clinical Application: Enhances gas distribution and drug delivery.
(2) Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP)
- 기능: Maintains positive airway pressure at end of exhalation.
- Clinical Application: Treats hypoxemia due to intrapulmonary shunt.
Development and Applications
(1) Microcomputerization
- 특징: Self-test, alarm functions, special features like suction and atomization.
(2) Monitoring Function
- Key Aspects: Displays ventilation and lung mechanics parameters, trends, and logs.
(3) Ventilator Mode Developments
- Innovations: Autonomous pressure modes, closed-loop ventilation, BiPAP.
(4) Adjustment and Safety
- 특징: Single-knob adjustment, digital parameter setting, safety ranges.
(5) Purchasing Principles
- Considerations: Ventilator grade, hospital needs, user experience, and resource utilization.
Our Services
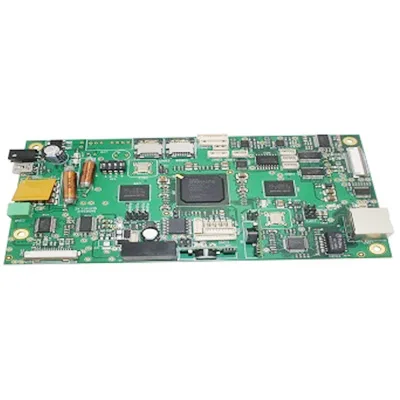

We provide Ventilator PCB Assembly and printed circuit board assemblies services. UGPCB is your one-stop Turnkey PCB Assembly factory.
 UGPCB 로고
UGPCB 로고