In the vast universe of the electronics manufacturing industry, every star carries the brilliance of technology and the spark of innovation. Among them, SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is not only a rigorous process, but also a discipline that combines technology and art as a bridge between electronic components and printed circuit boards (PCBs). This article will take you to explore the professional terminology in the field of SMT and unveil the mystery of the precise language of the electronics manufacturing industry.
1. Basic SMT terminology: the cornerstone of building the electronic world
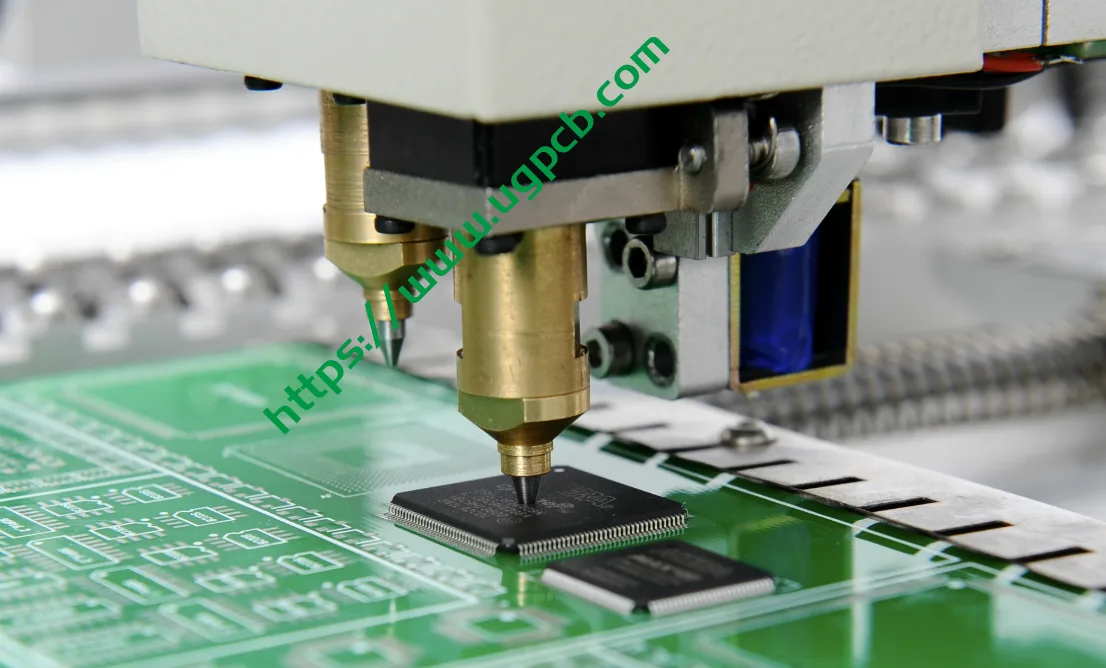

SMT: This technology mounts electronic components directly on the surface of the PCB, greatly improving the integration and production efficiency of the circuit board.
PCB: As the carrier of electronic components, the design, manufacturing and quality control of PCBs are the core of the entire electronic product manufacturing process.
SMD (Surface Mount Device) and DIP (Dual In-line Package): The two represent the mainstream packaging forms in the SMT and THT (Through Hole Technology) eras respectively.
2. Packaging and connection: the close embrace of components and circuit boards
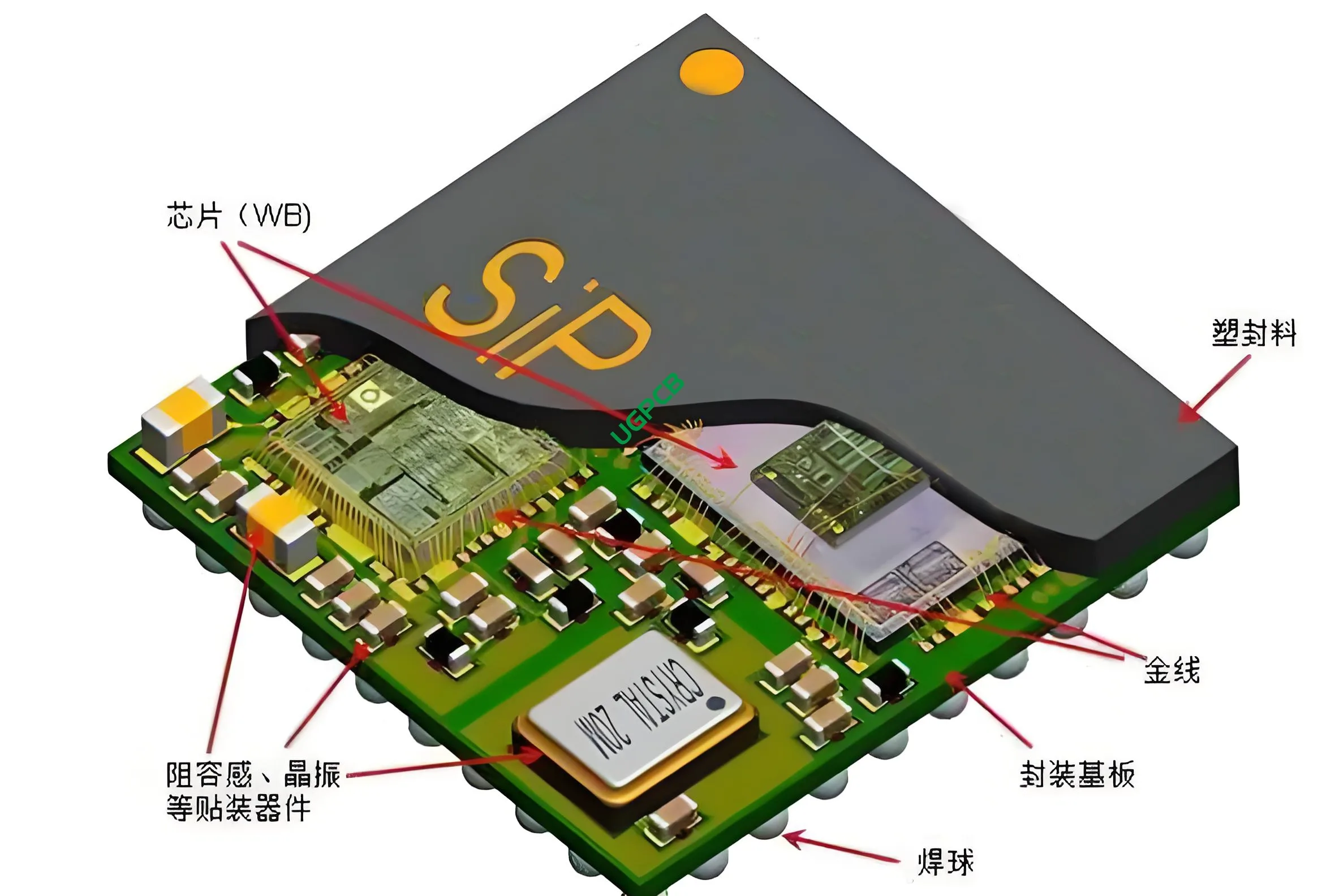
BGA (Ball Grid Array) and QFN (Quad Flat No-Lead): These high-density packaging technologies make electronic products more compact and efficient.
IC (Integrated Circuit): As the “brain” of modern electronic equipment, the integration and performance of IC are directly related to the competitiveness of products.
Reflow Soldering: By precisely controlling the temperature curve, the solder paste melts to achieve a firm connection between SMD components and PCBs.
3. Quality Inspection and Reliability: Guarding the Lifeline of Electronic Products
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) and X-Ray Inspection: They are like “microscopes” in the electronics manufacturing industry, ensuring that every solder joint and every component meets quality standards.
ICT (In-Circuit Test) and FCT (Functional Test): Together, they constitute the “physical examination” of electronic products before they leave the factory, ensuring that the product functions normally and has stable performance.
4. Production Line and Process: The Art of Precision Manufacturing
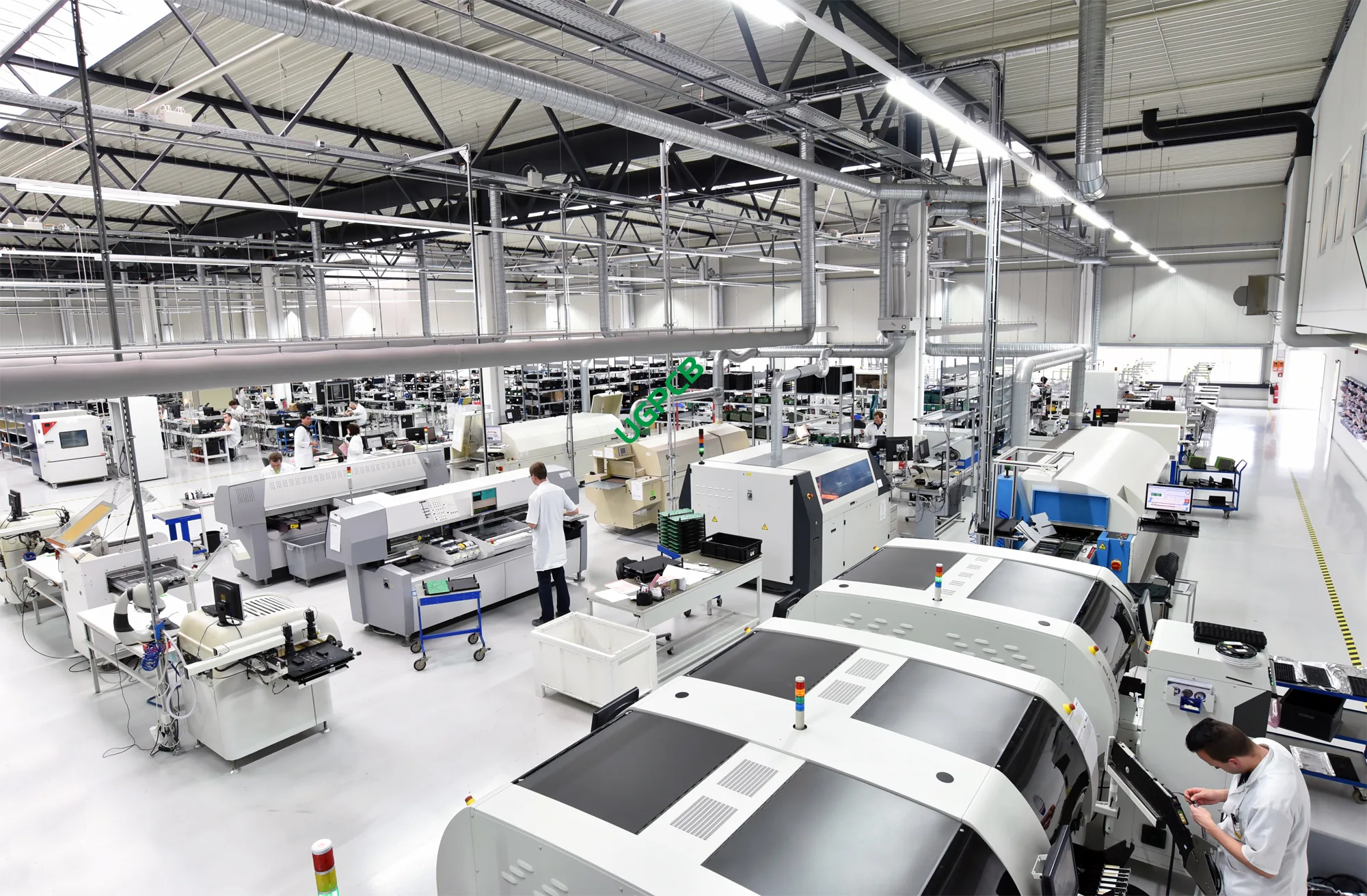

SMT Line: From printer to SMT machine, and then to reflow oven, each process embodies the wisdom and sweat of engineers.
Stencil Printing and Pick and Place: These seemingly simple actions are the key steps to achieve high-precision placement.
Lead-Free Solder: The improvement of environmental awareness has promoted the widespread application of lead-free solder, bringing a greener and more sustainable future to the electronics manufacturing industry.
5. PCB Design and Manufacturing: Blueprint and Cornerstone of the Electronic World

PCB Thickness and Copper Thickness: These parameters directly affect the electrical performance and mechanical strength of PCB.
Impedance Control: Ensuring the integrity of signal transmission on PCB is an important part of high-speed circuit design.
Microvia, Blind Via and Buried Via: The introduction of these special structures makes PCB design more flexible and efficient.
6. Management and efficiency: the smart engine of the electronics manufacturing industry
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and MES (Manufacturing Execution System): They are like the “brain” of the electronics manufacturing industry, monitoring and optimizing the production process in real time to improve production efficiency.

JIT (Just-in-Time) and kanban: The application of these management concepts makes the electronics manufacturing industry more flexible and efficient, reduces inventory costs, and improves market response speed.
7. The evolution and innovation of packaging technology: exploring the infinite possibilities of the future
COB (Chip-on-Board), Flip Chip and Underfill: These advanced packaging technologies not only improve the integration and heat dissipation performance of chips, but also provide infinite possibilities for the innovation of electronic products.
Six Sigma: The application of this quality management method allows the electronics manufacturing industry to continue to move forward on the road of pursuing zero defects.
Conclusion: A journey of terminology in the electronics manufacturing industry, a symphony of exploration and innovation
From SMT to PCB, from packaging technology to quality inspection, from production line technology to management efficiency, every term in the electronics manufacturing industry carries the wisdom of technology and the spark of innovation. Together, they constitute the precise language and art of the electronics world, allowing us to keep moving forward on the road of exploration and innovation. In this era full of challenges and opportunities, let us work together to write a glorious chapter in the electronics manufacturing industry with wisdom and sweat!
 UGPCB LOGO
UGPCB LOGO

