 Introduction to AITO M9 Tail Lights
Introduction to AITO M9 Tail Lights
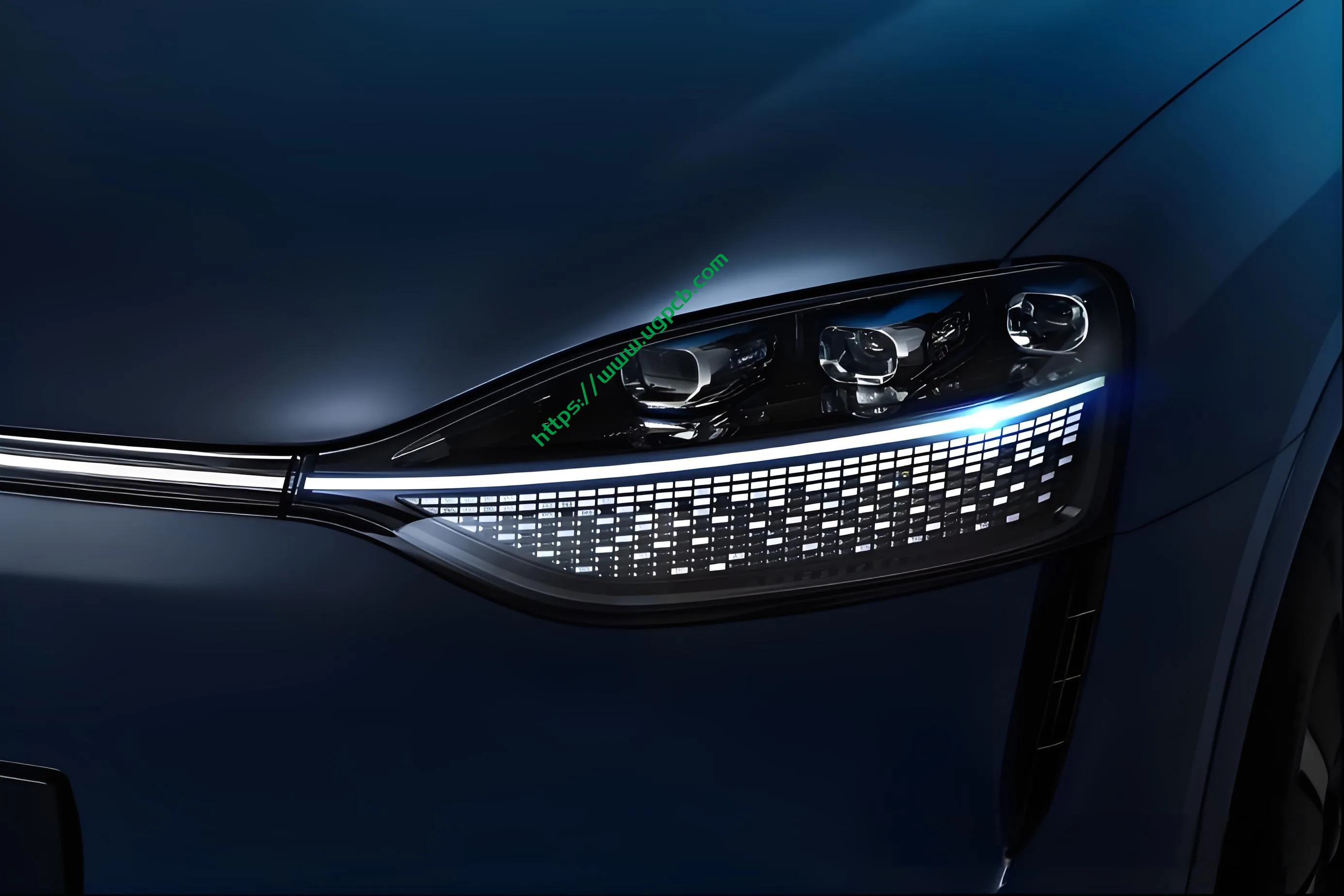

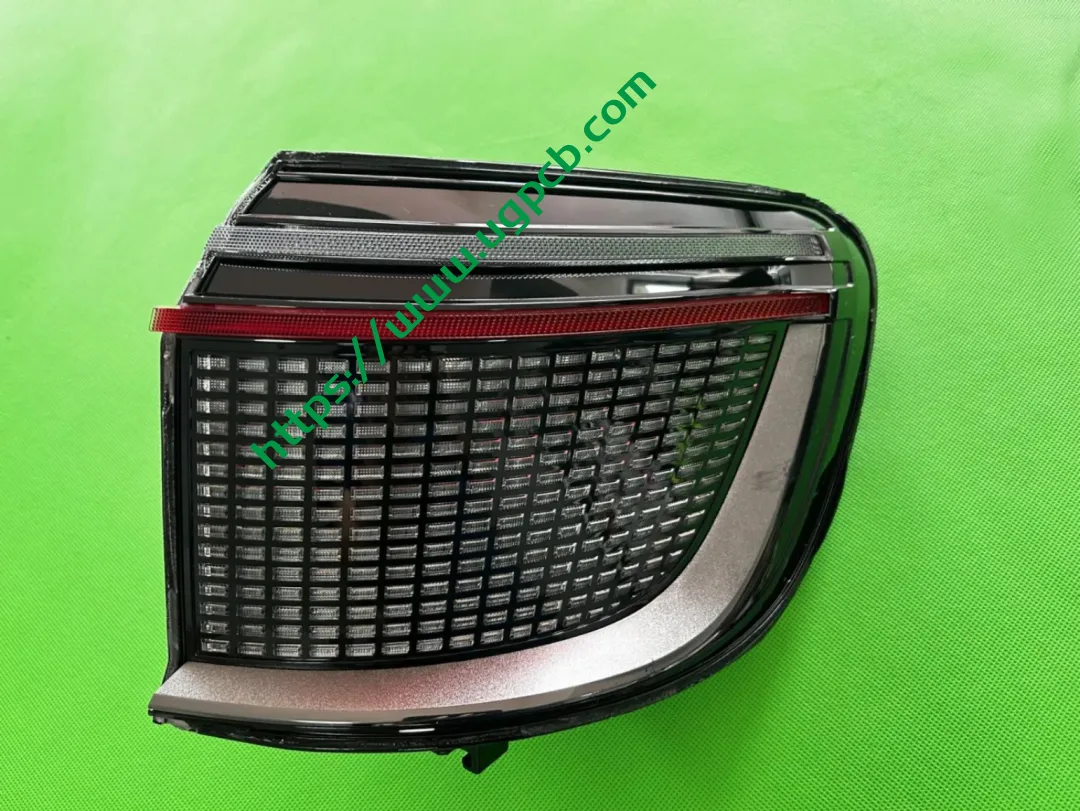
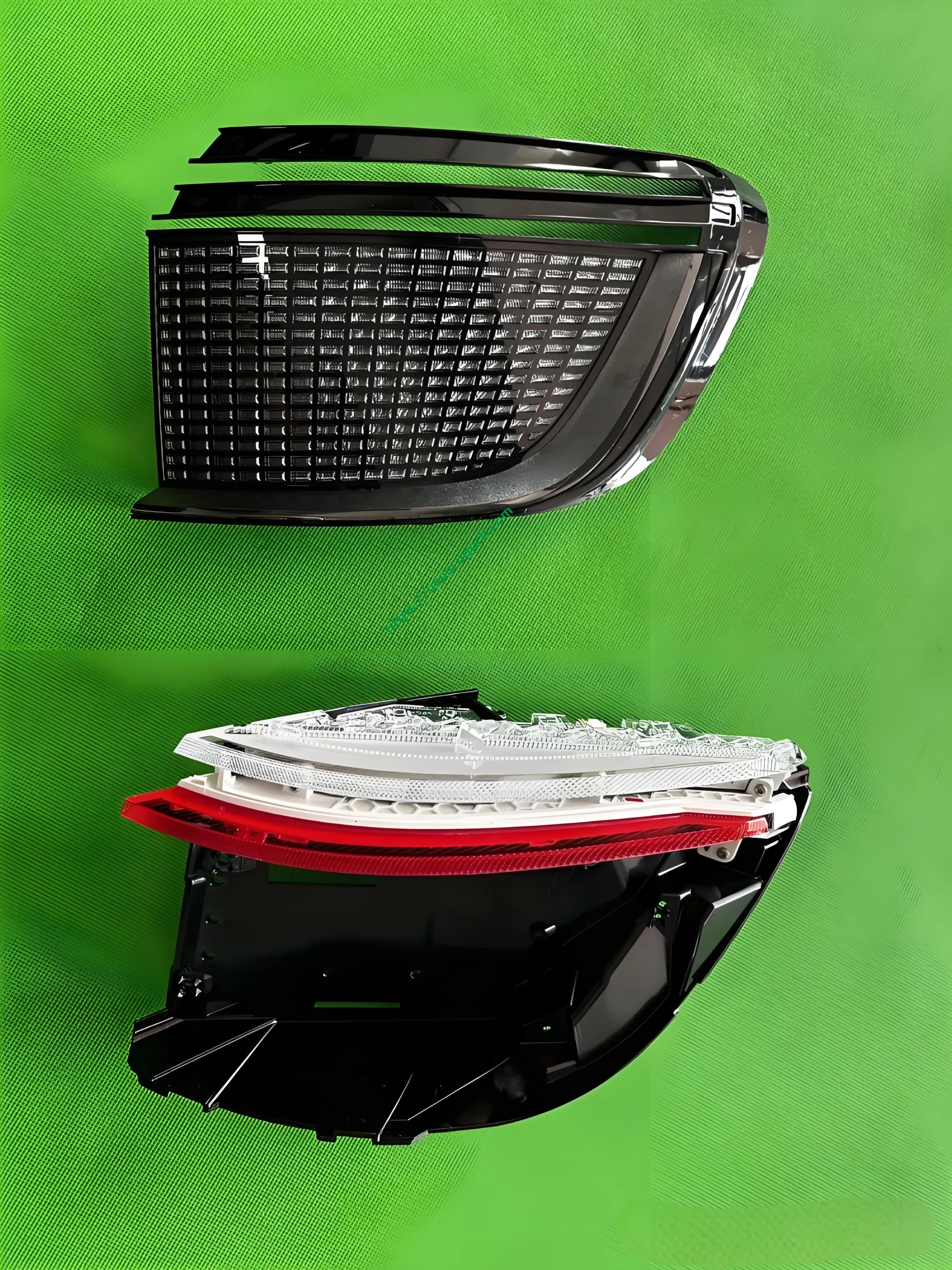
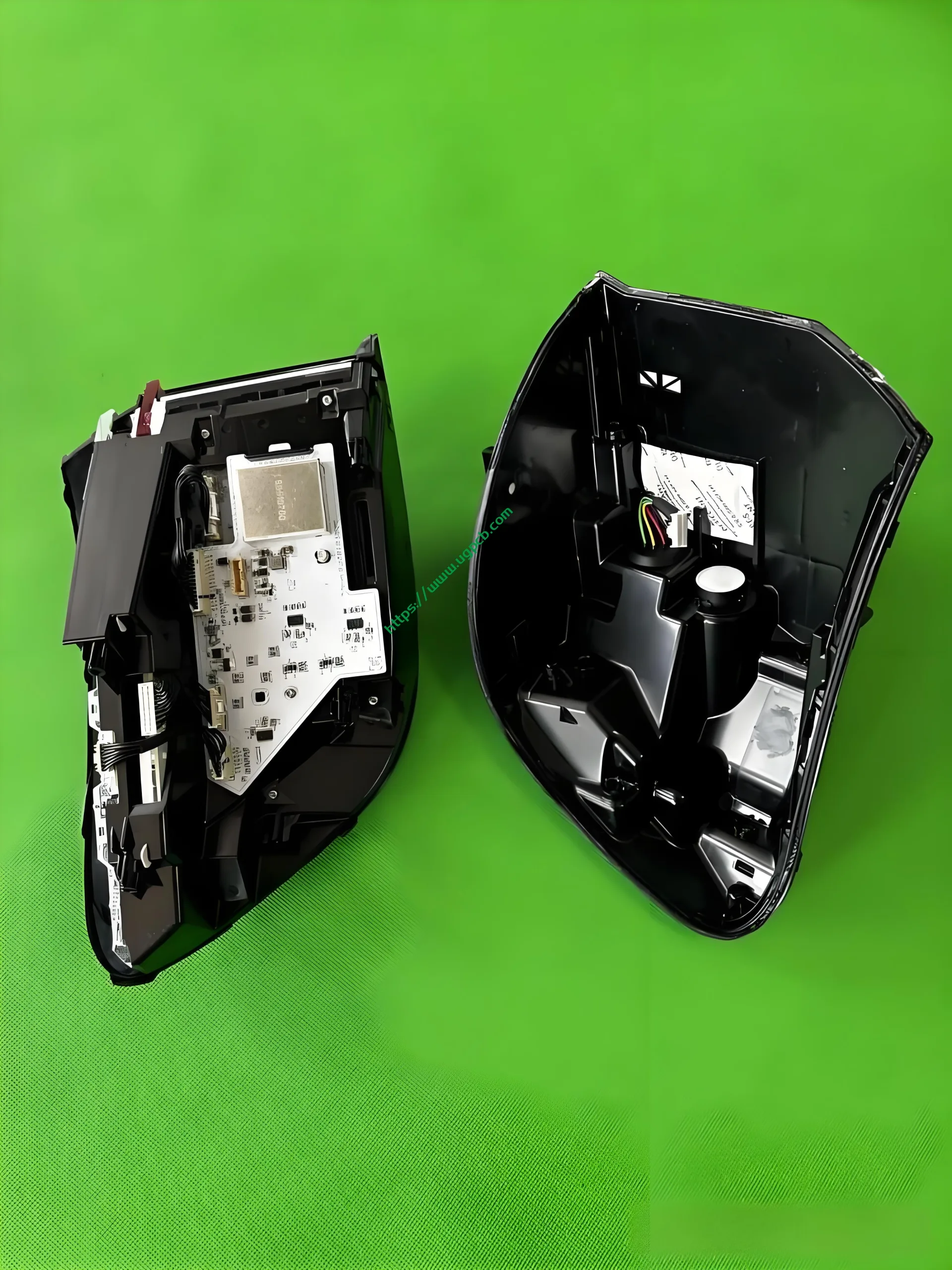
Recently, we obtained a high-configuration headlight and tail light set for the AITO M9. Due to the extensive disassembly required for the DLP headlight, we decided to present the tail light disassembly first. The tail light in question is the side tail light (A lamp), which serves functions such as positioning, braking, turning, and ISD interaction.
Disassembly of the Tail Light

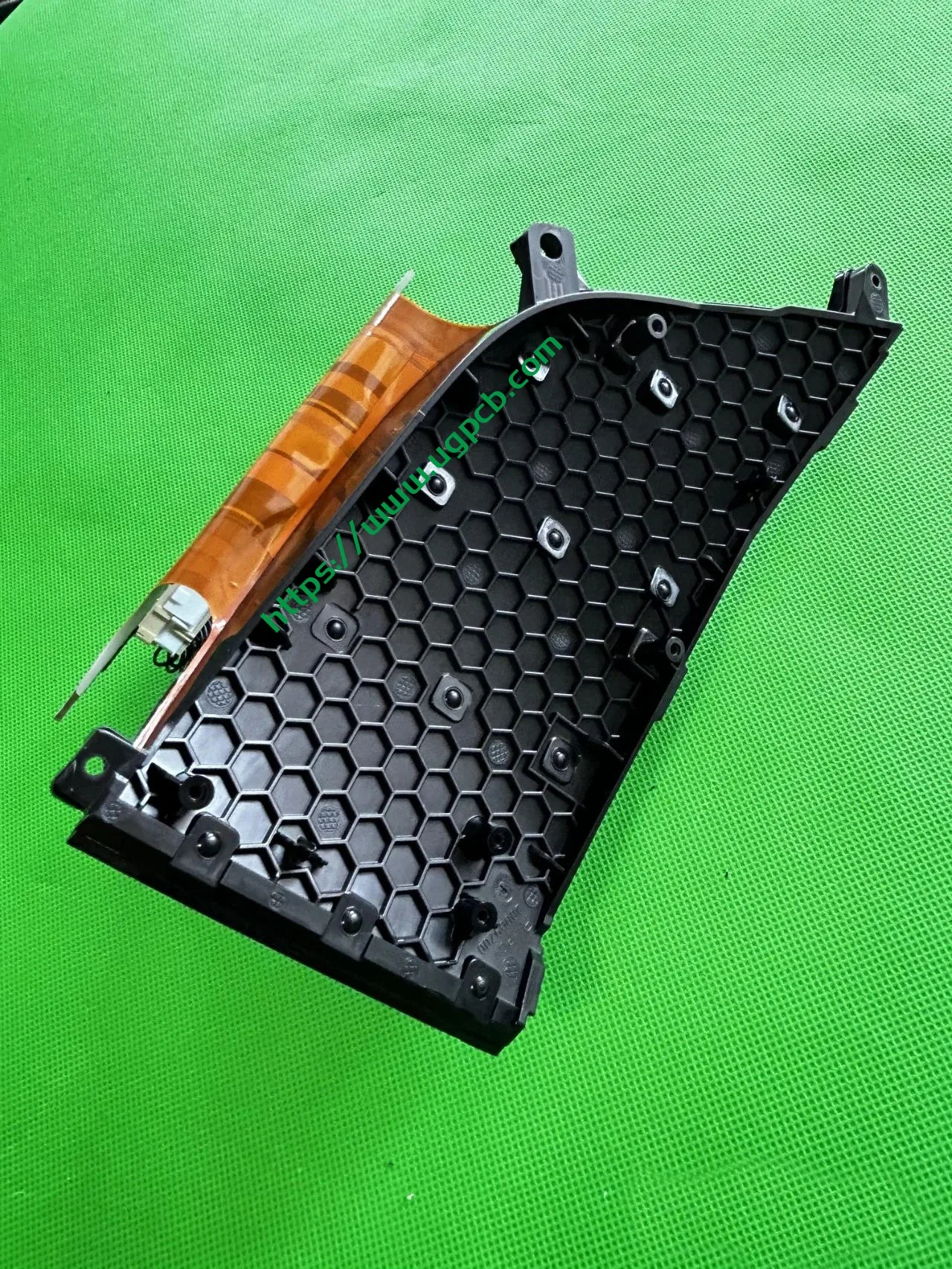
Starting with the separation of the housing, we found that desiccants have almost become a standard feature in car lights, reflecting the demanding nature of Chinese consumers. Manufacturers likely weigh the cost of incorporating desiccants—a mere ten-yuan investment—against reduced consumer complaints.
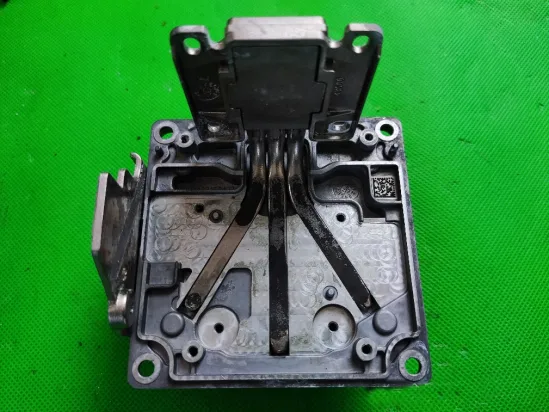
Components of the Tail Light
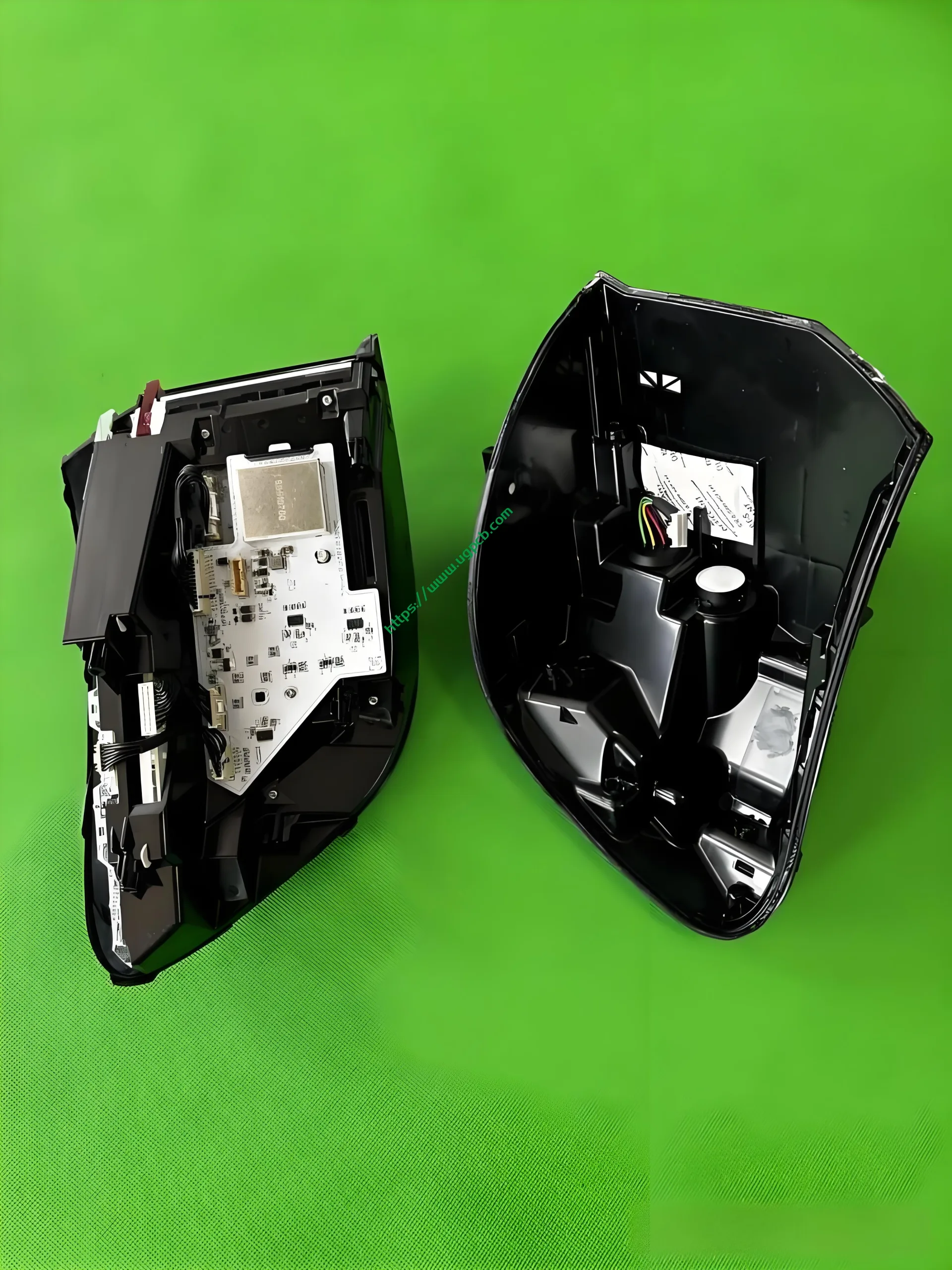

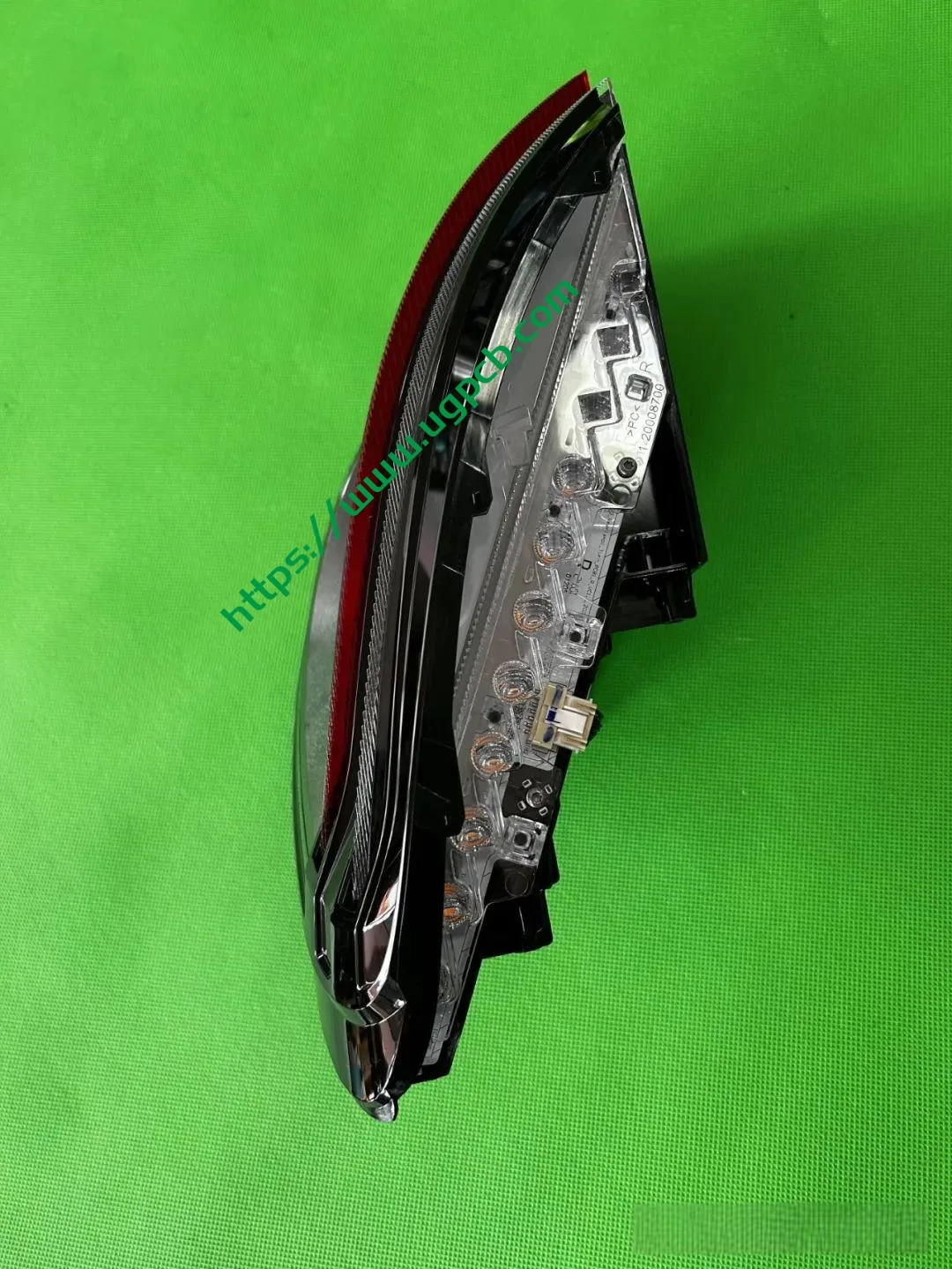
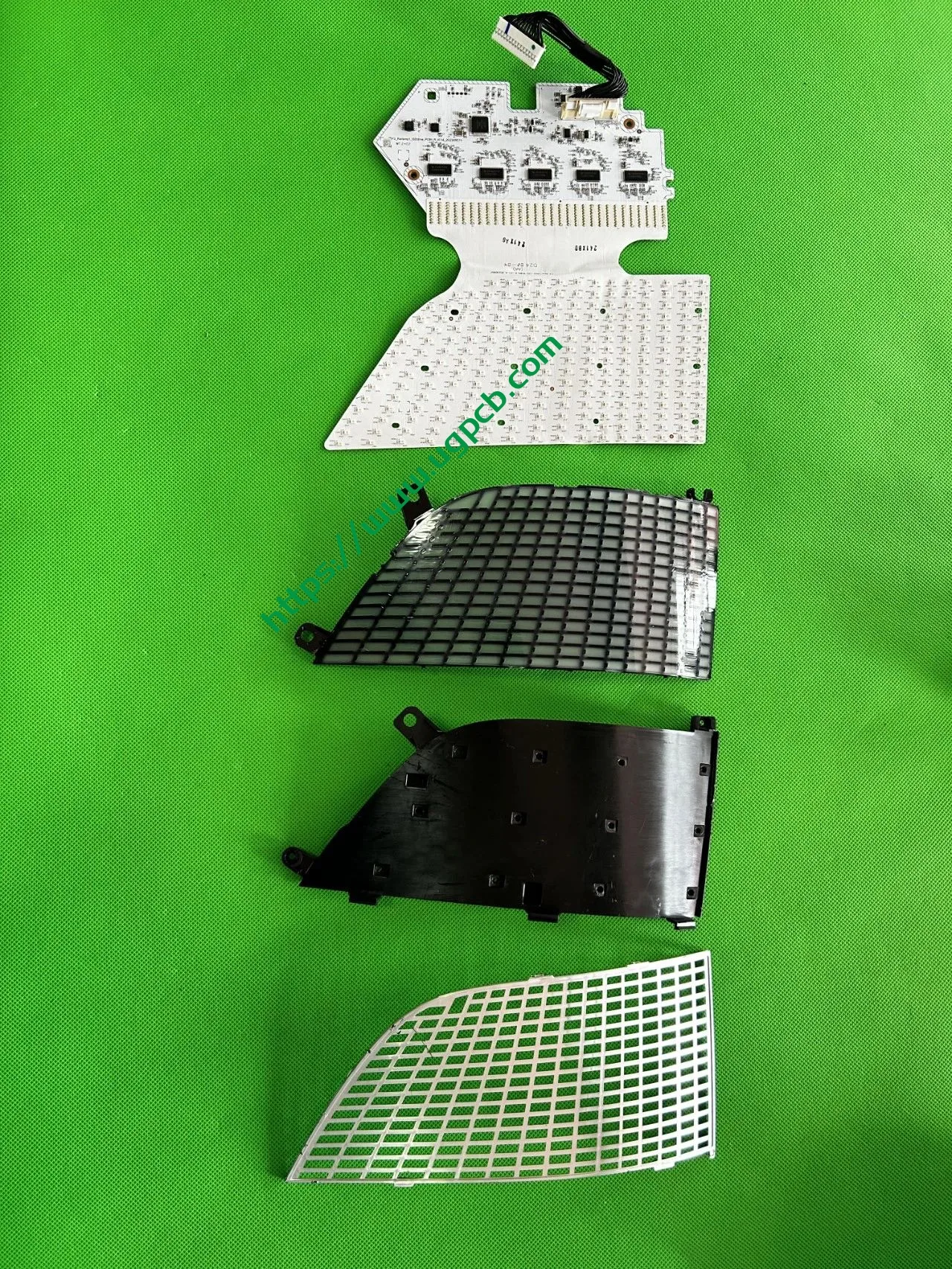
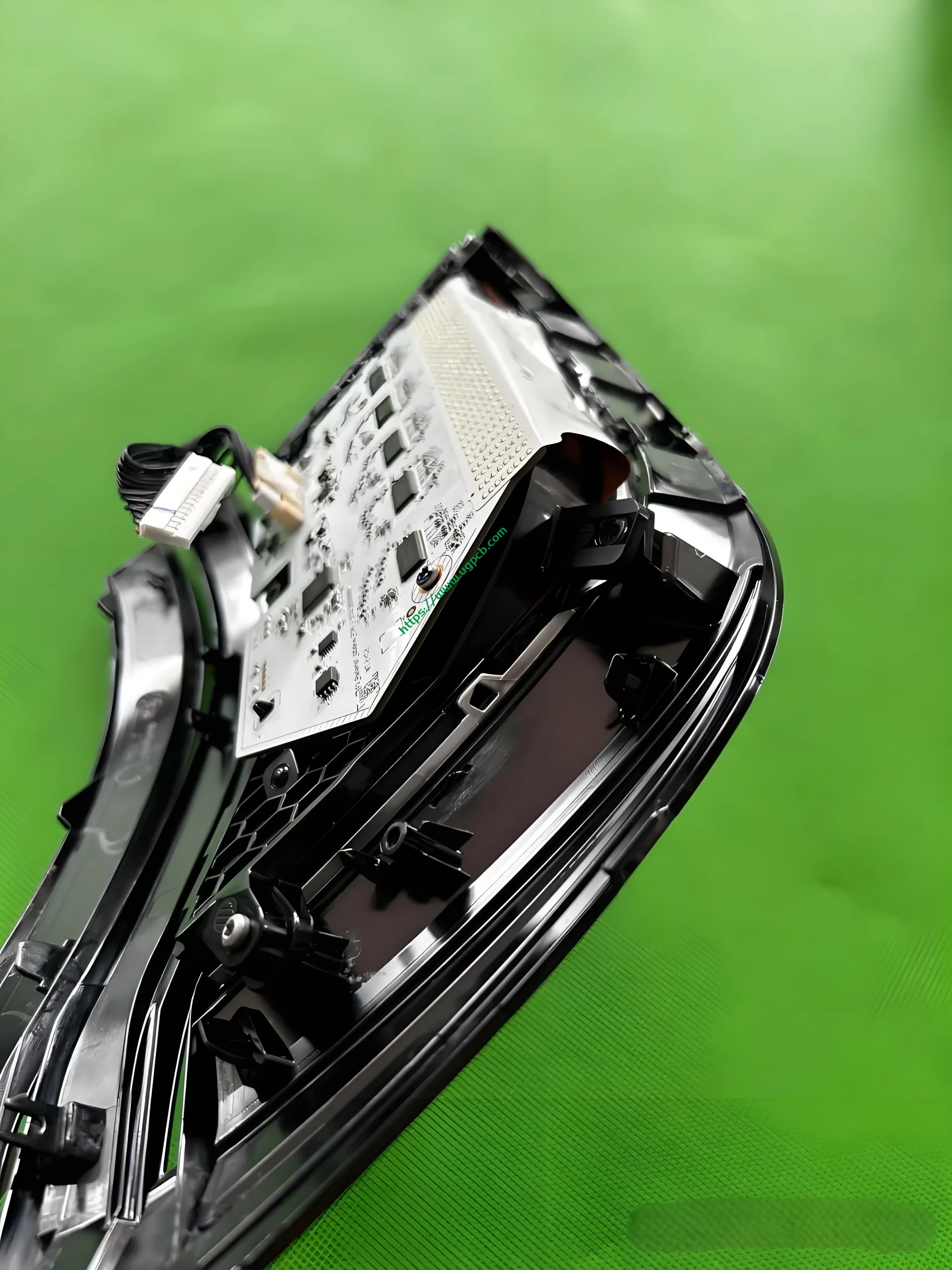
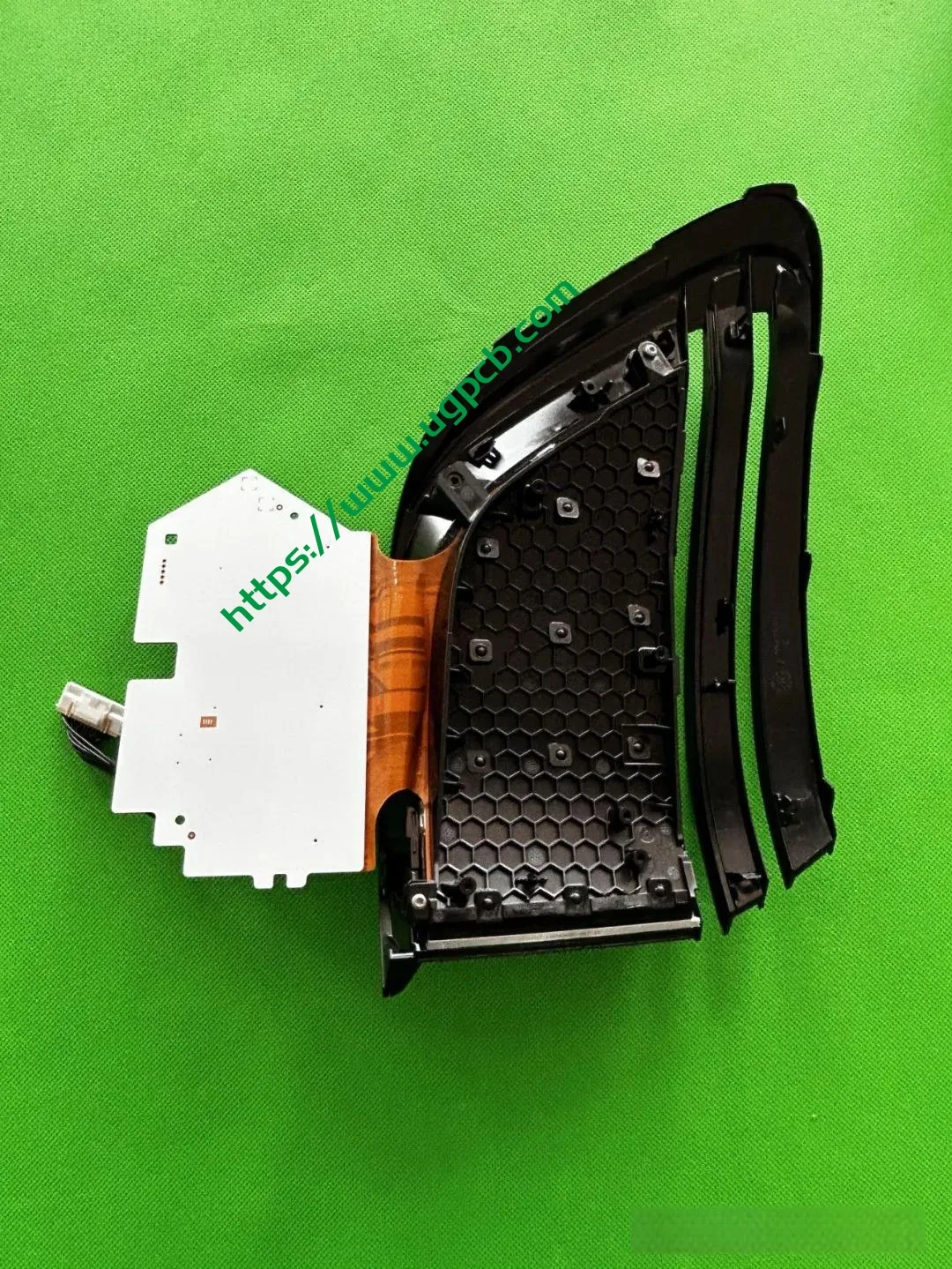
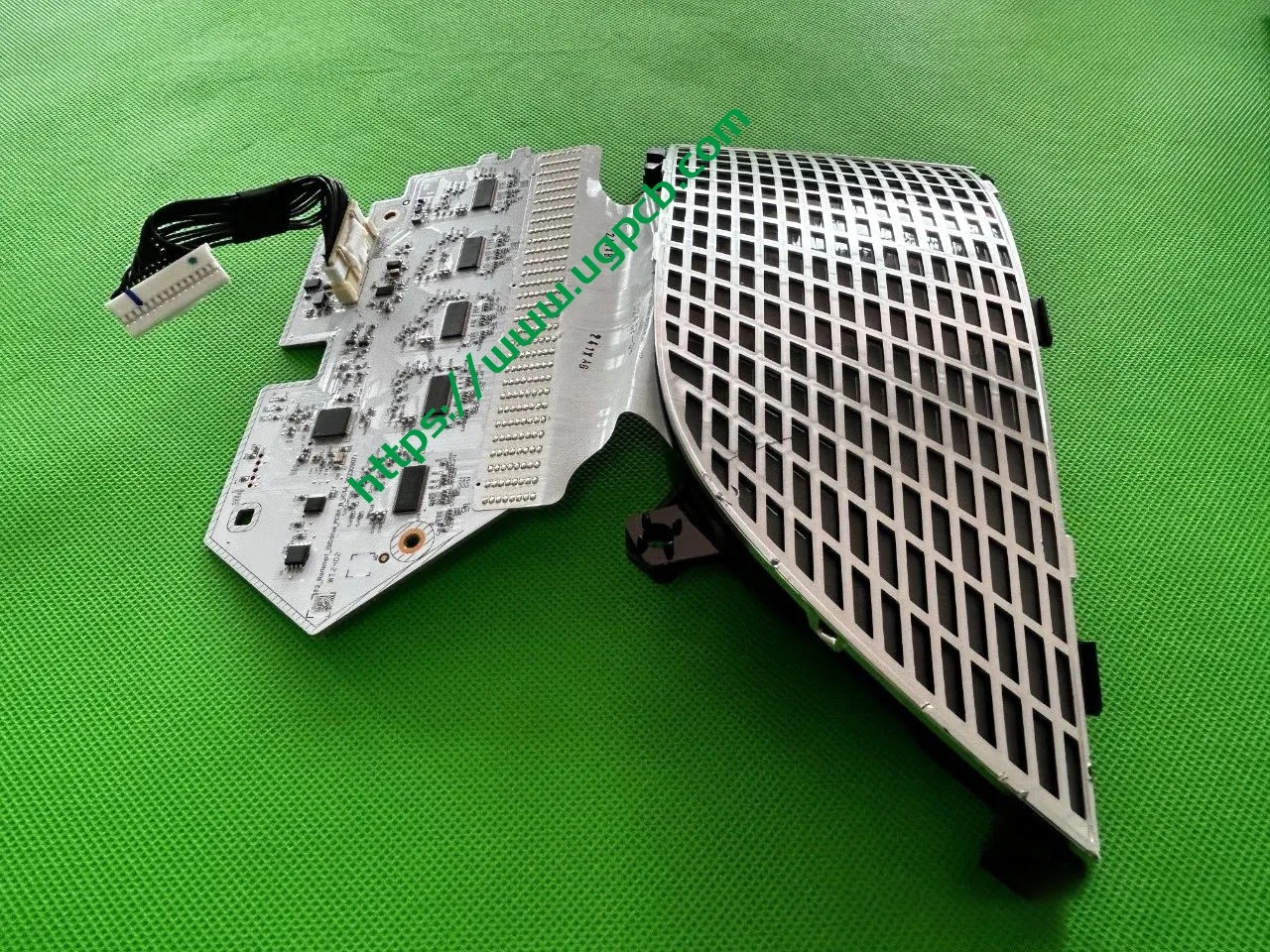
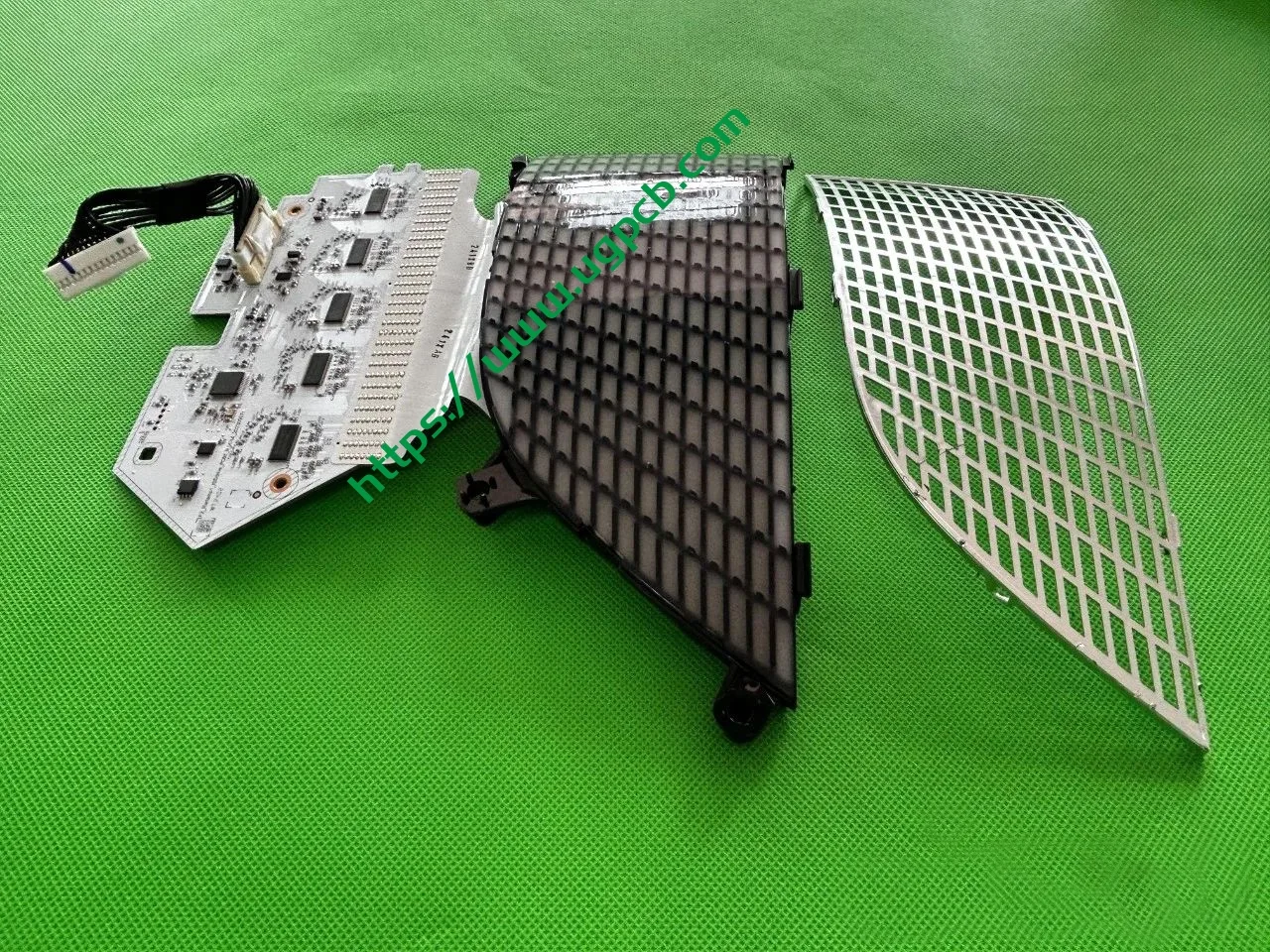
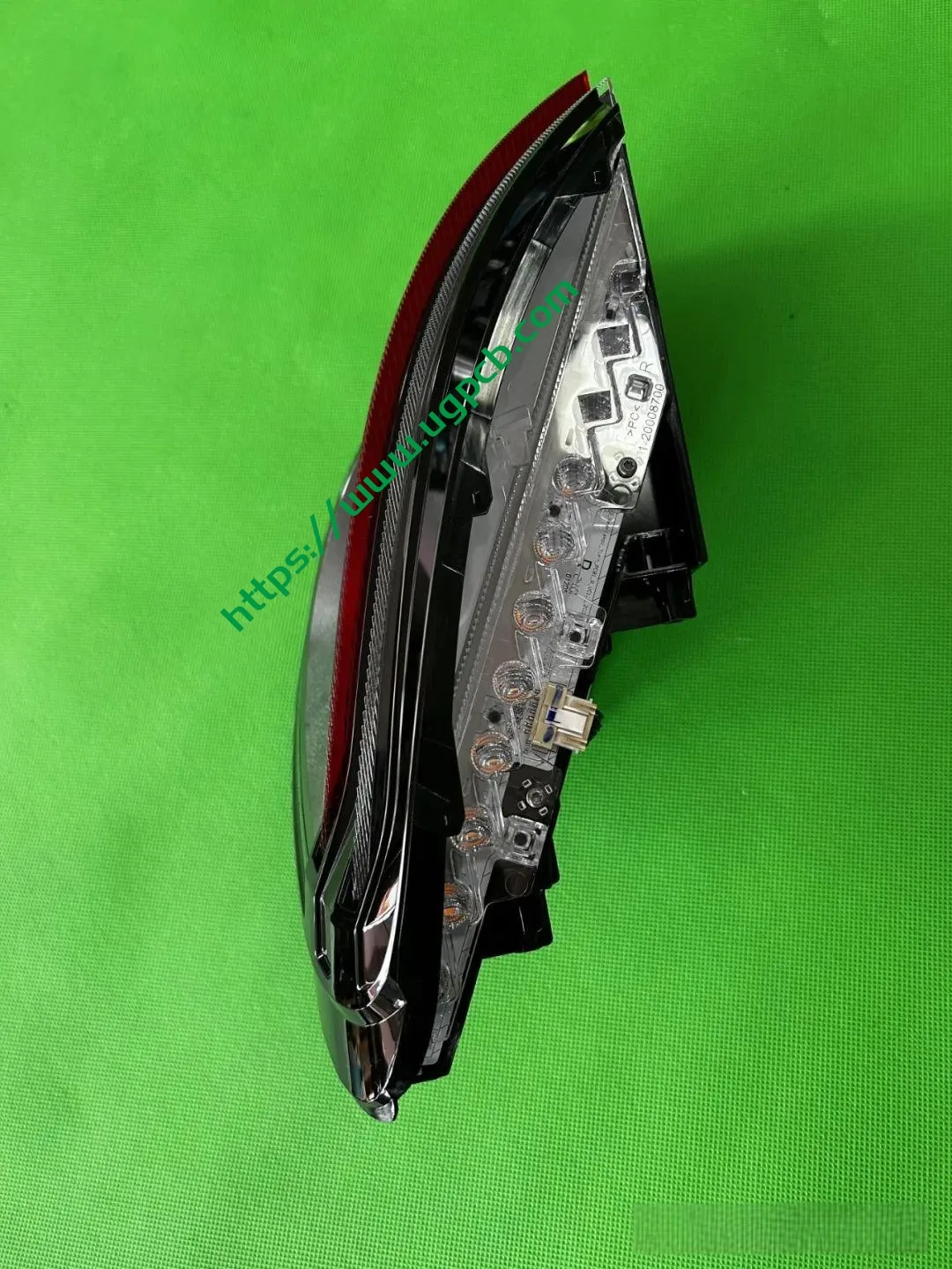
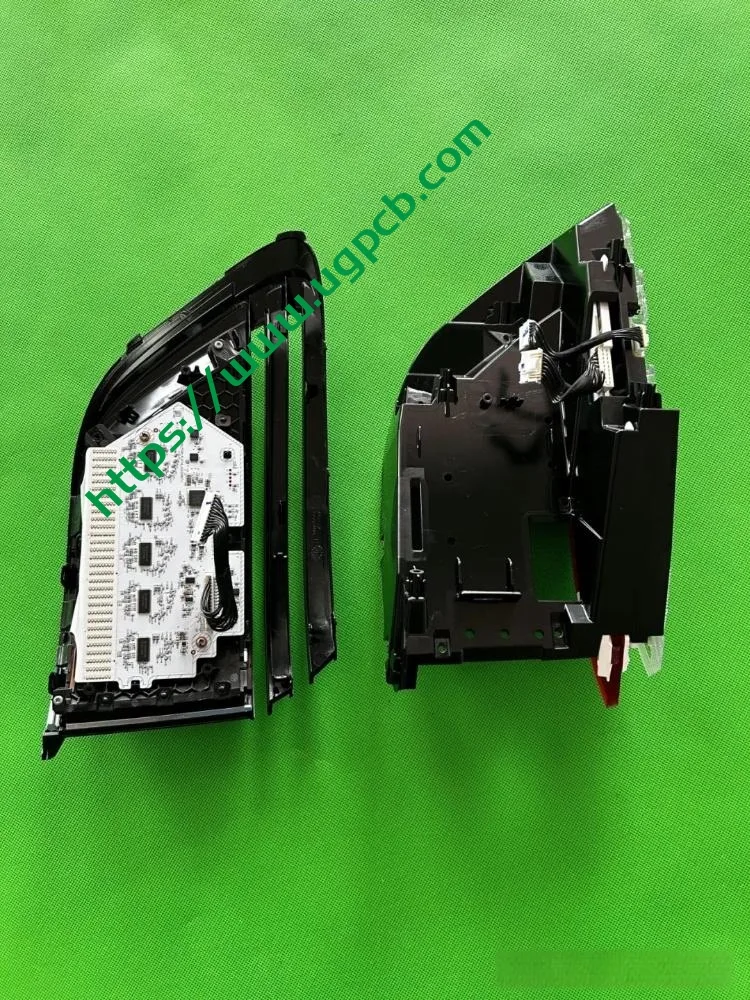
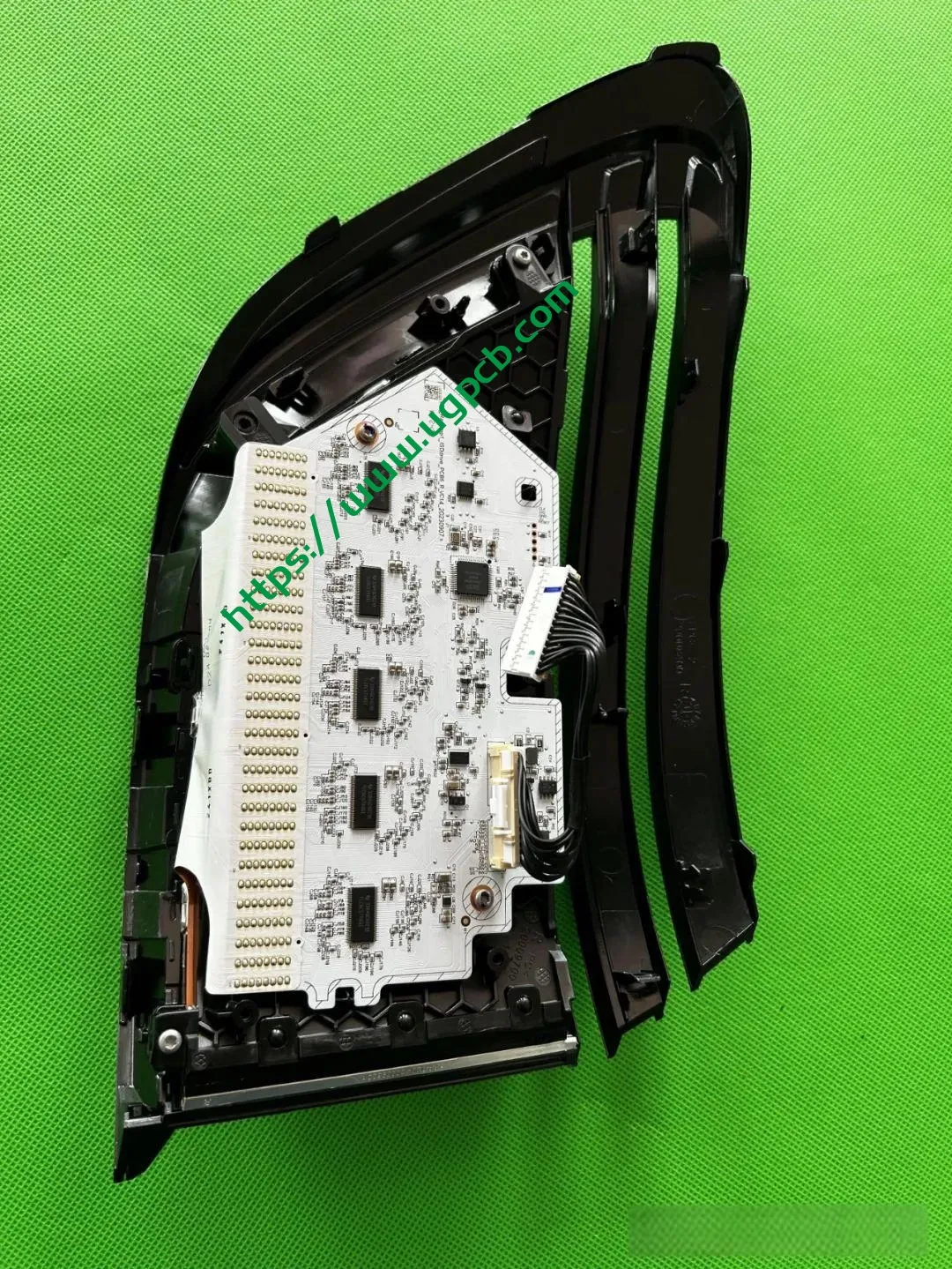
The middle section of the tail light mainly consists of two parts: the signal light section and the ISD interactive display section. The signal light section employs two thick-walled lenses, one of which is red, which is relatively uncommon. The ISD section uses a drive control board and an LED board, connected by a flexible board, representing a relatively expensive solution.
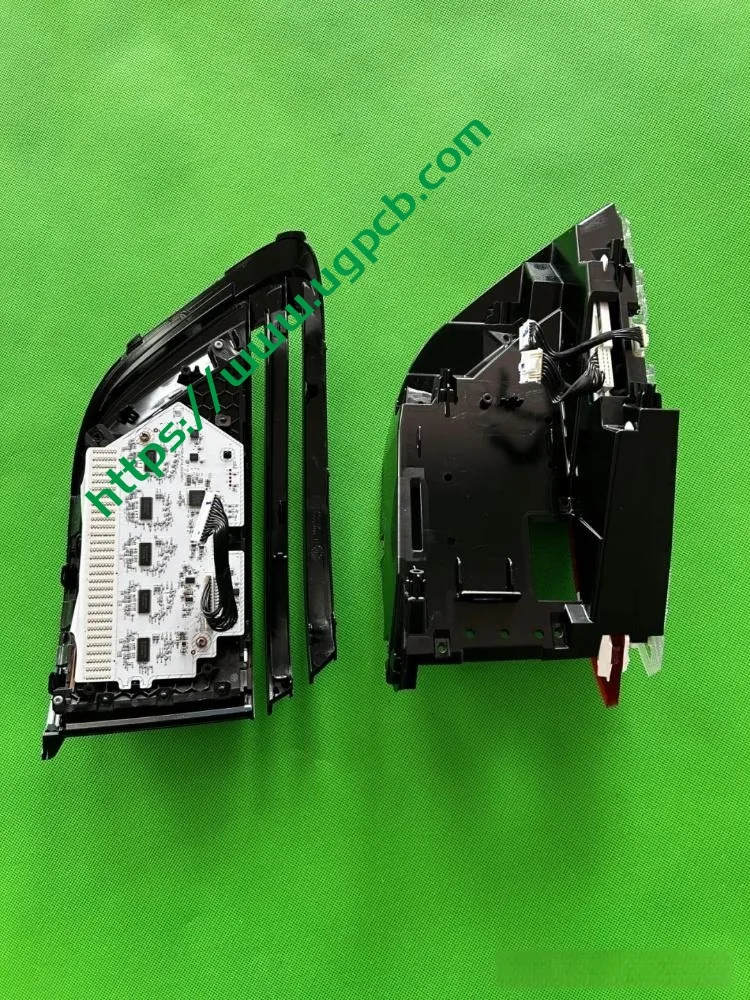


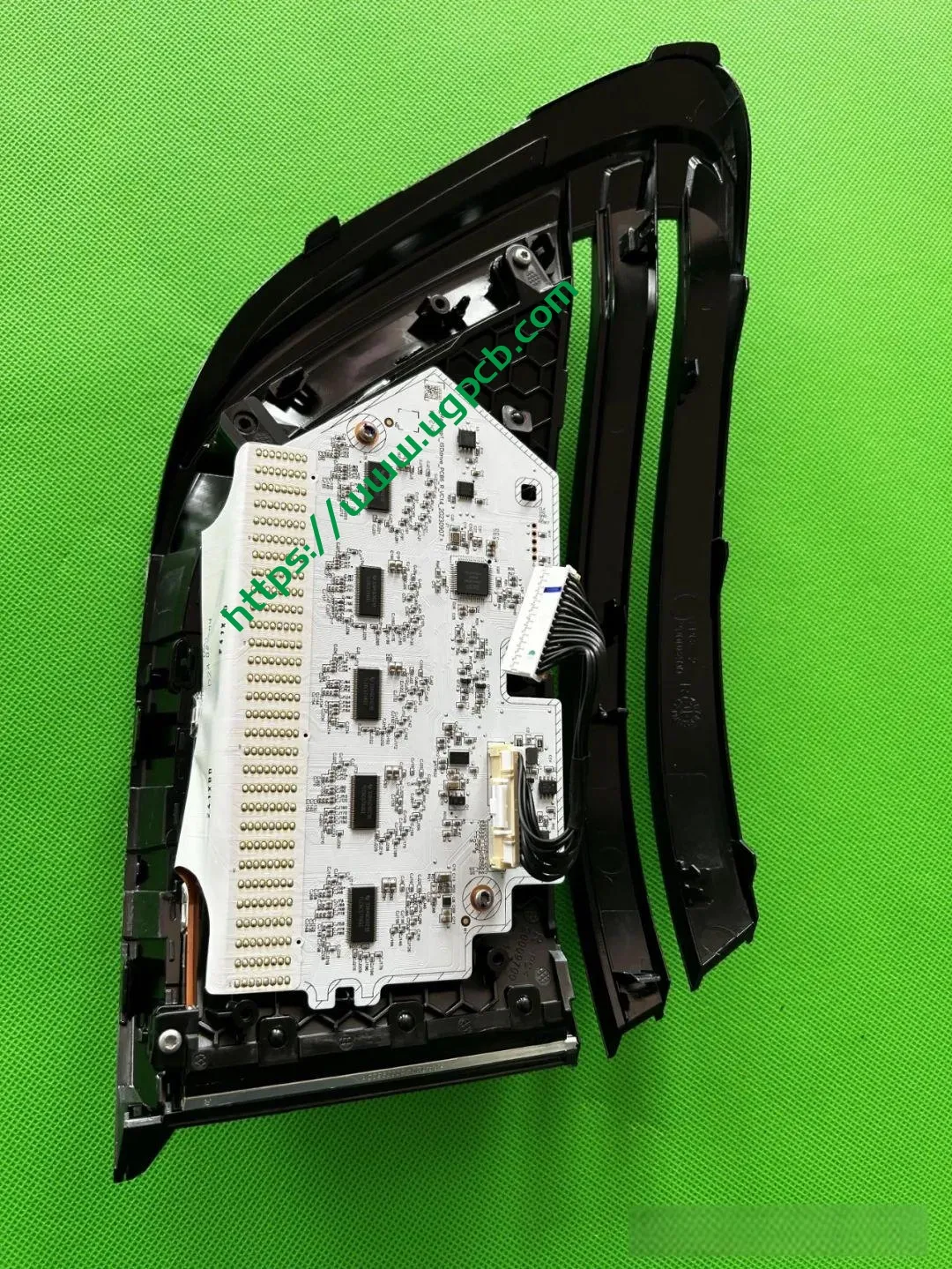
Clarity of the ISD Screen
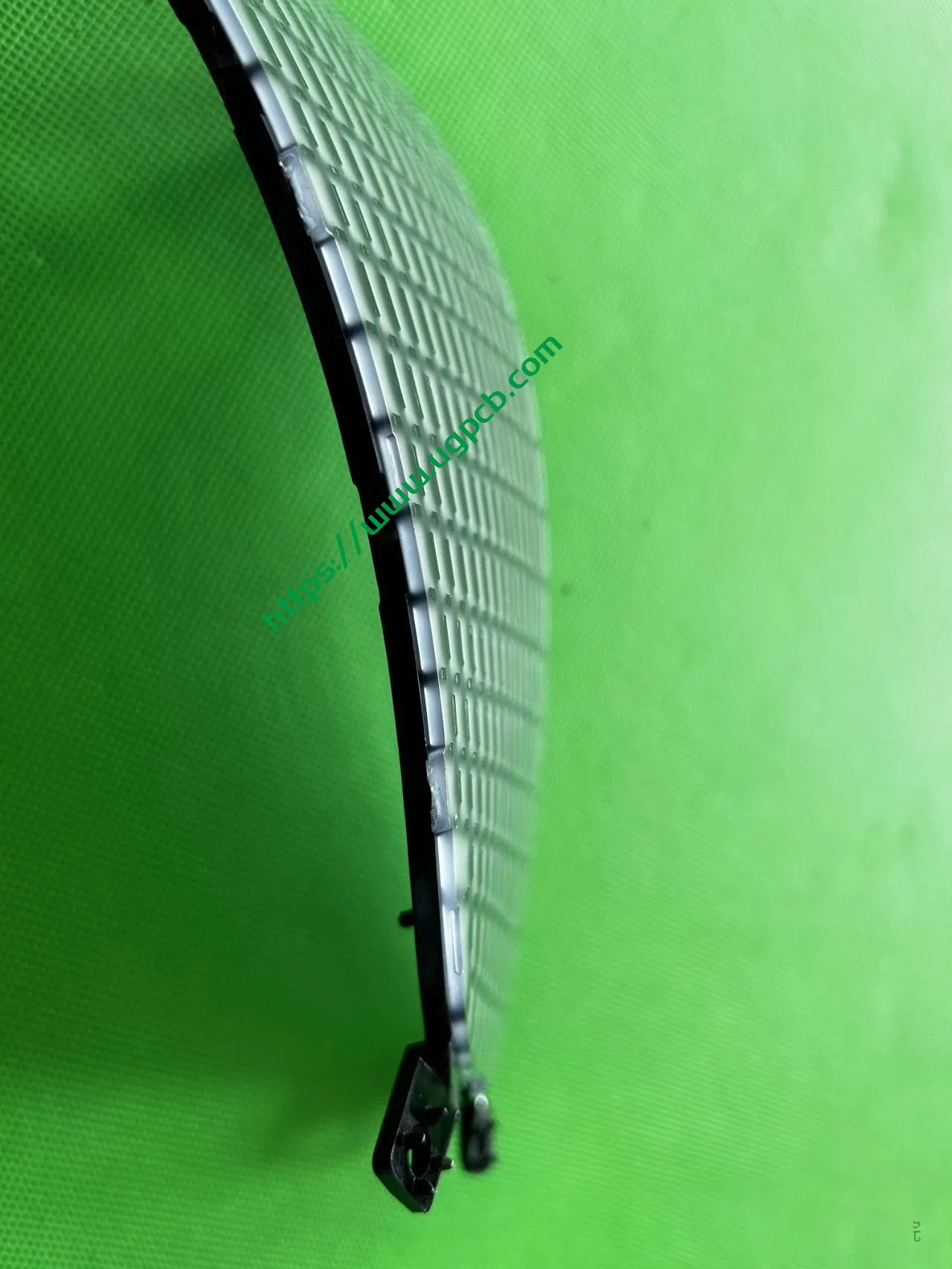
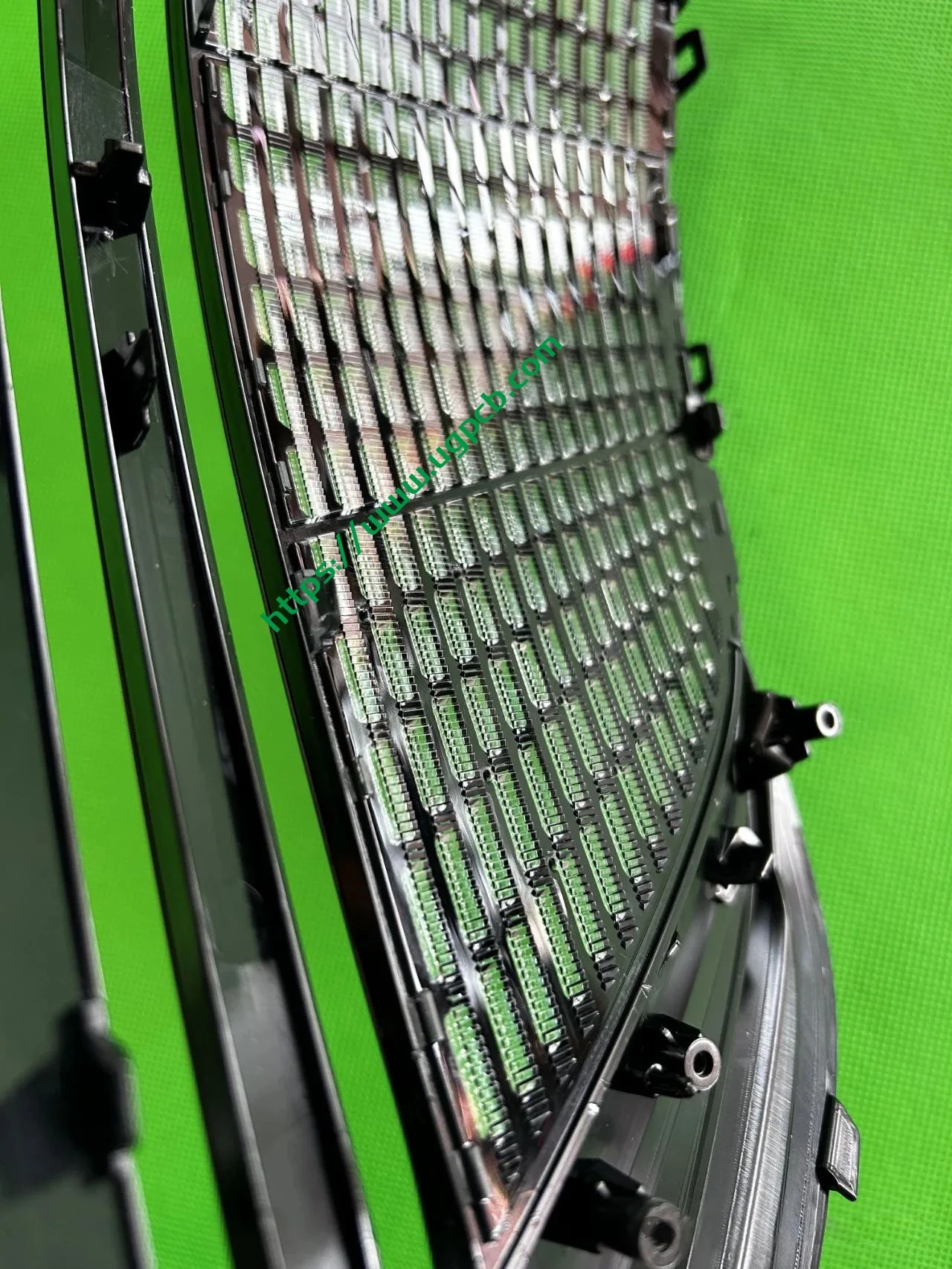
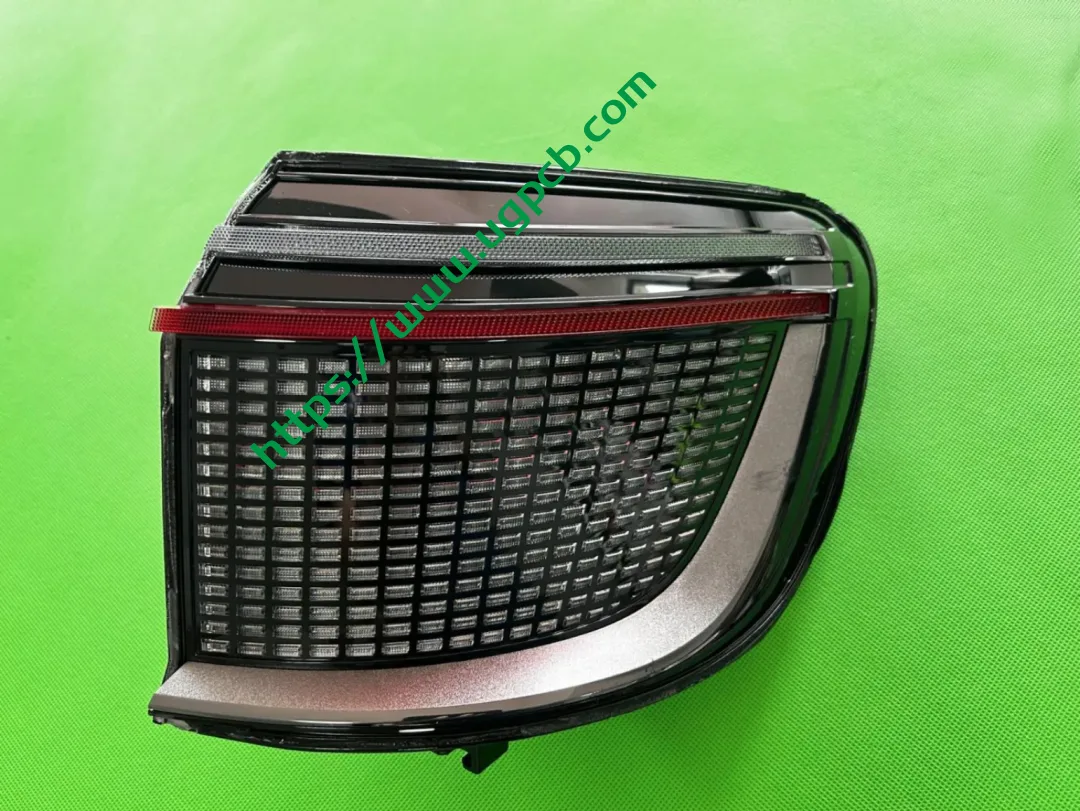
Despite having a limited number of pixels, the ISD screen of this tail light delivers high clarity without any light leakage. Structurally, the bottom features a base plate, above which is the LED board. The LED board is covered by a bicolor inner cover (black + diffuser material), followed by an aluminum-coated bracket to prevent light leakage. Outside is another bicolor inner cover (black + transparent). In total, there are three anti-leakage structural components, making light leakage highly unlikely.
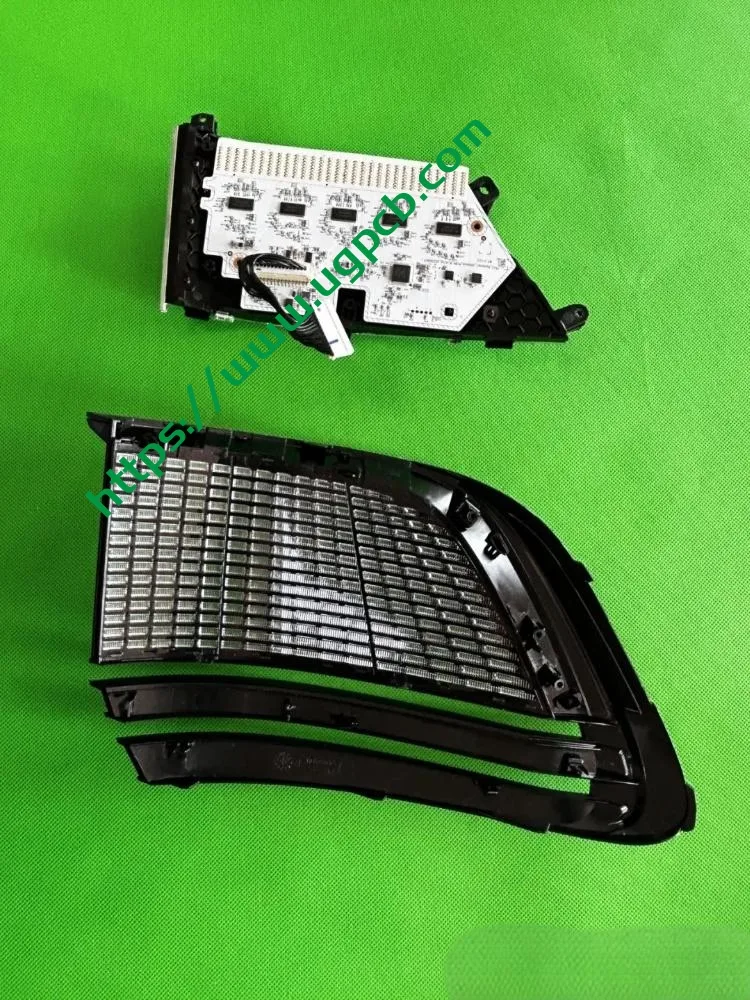
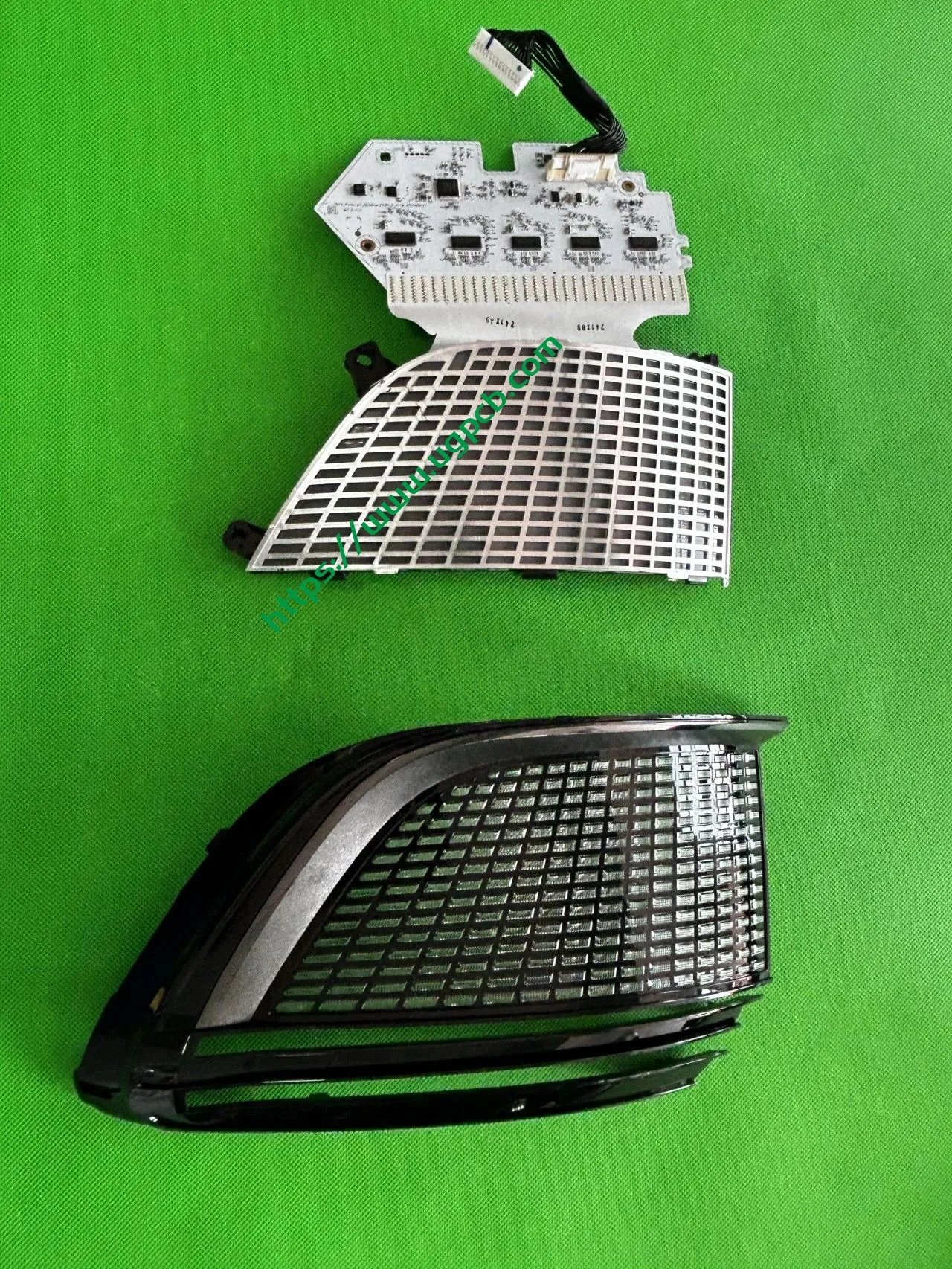
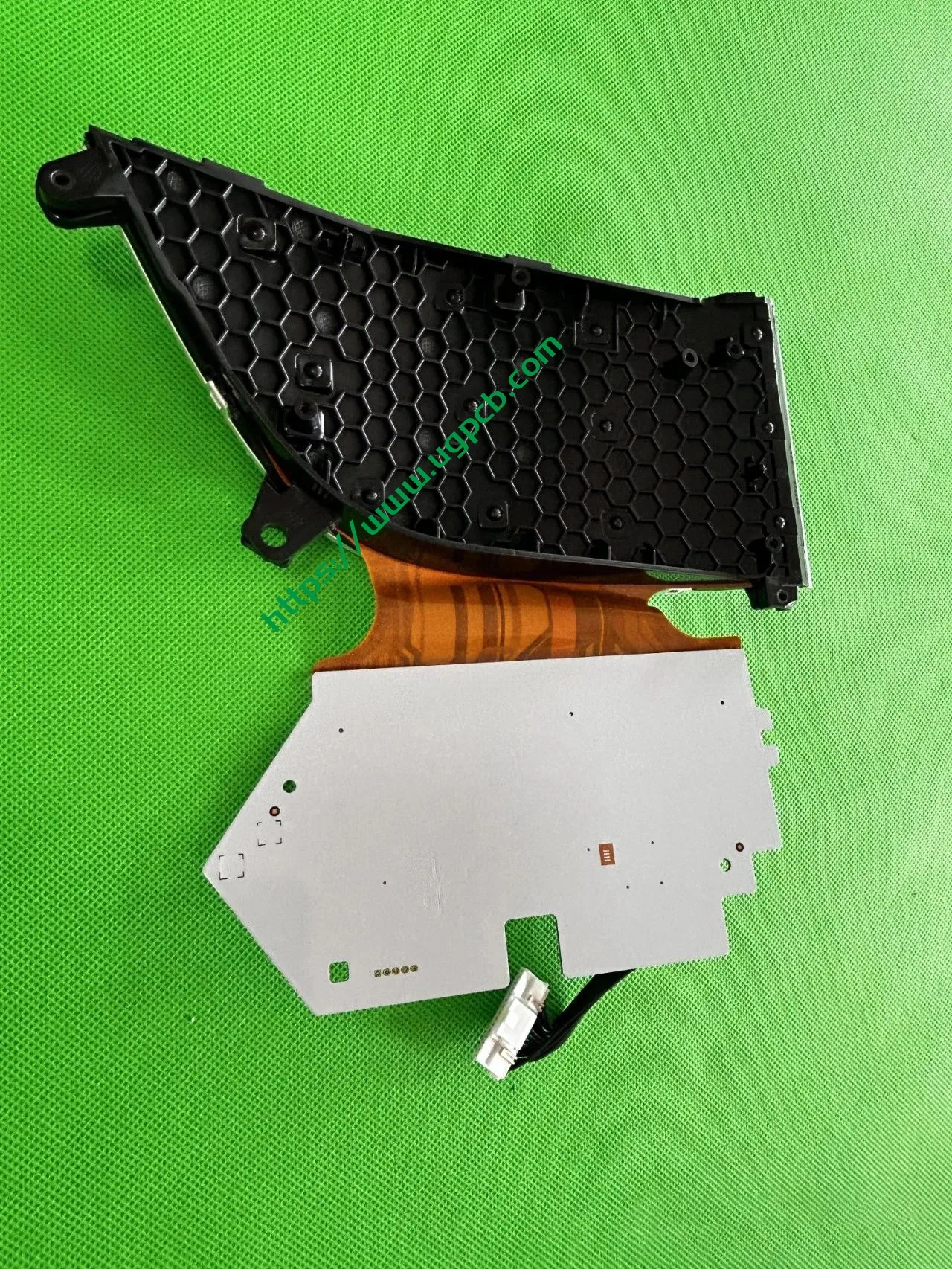
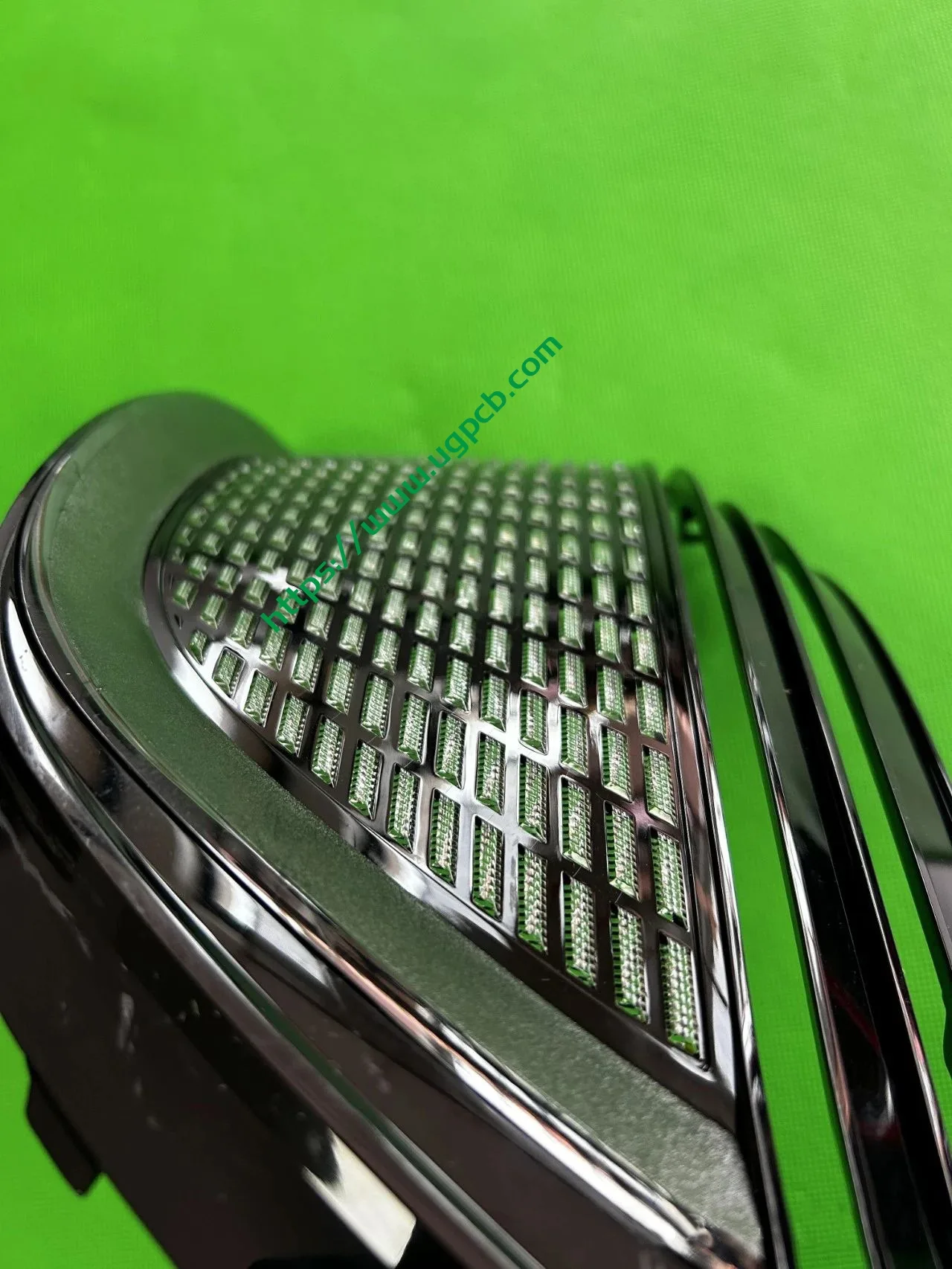





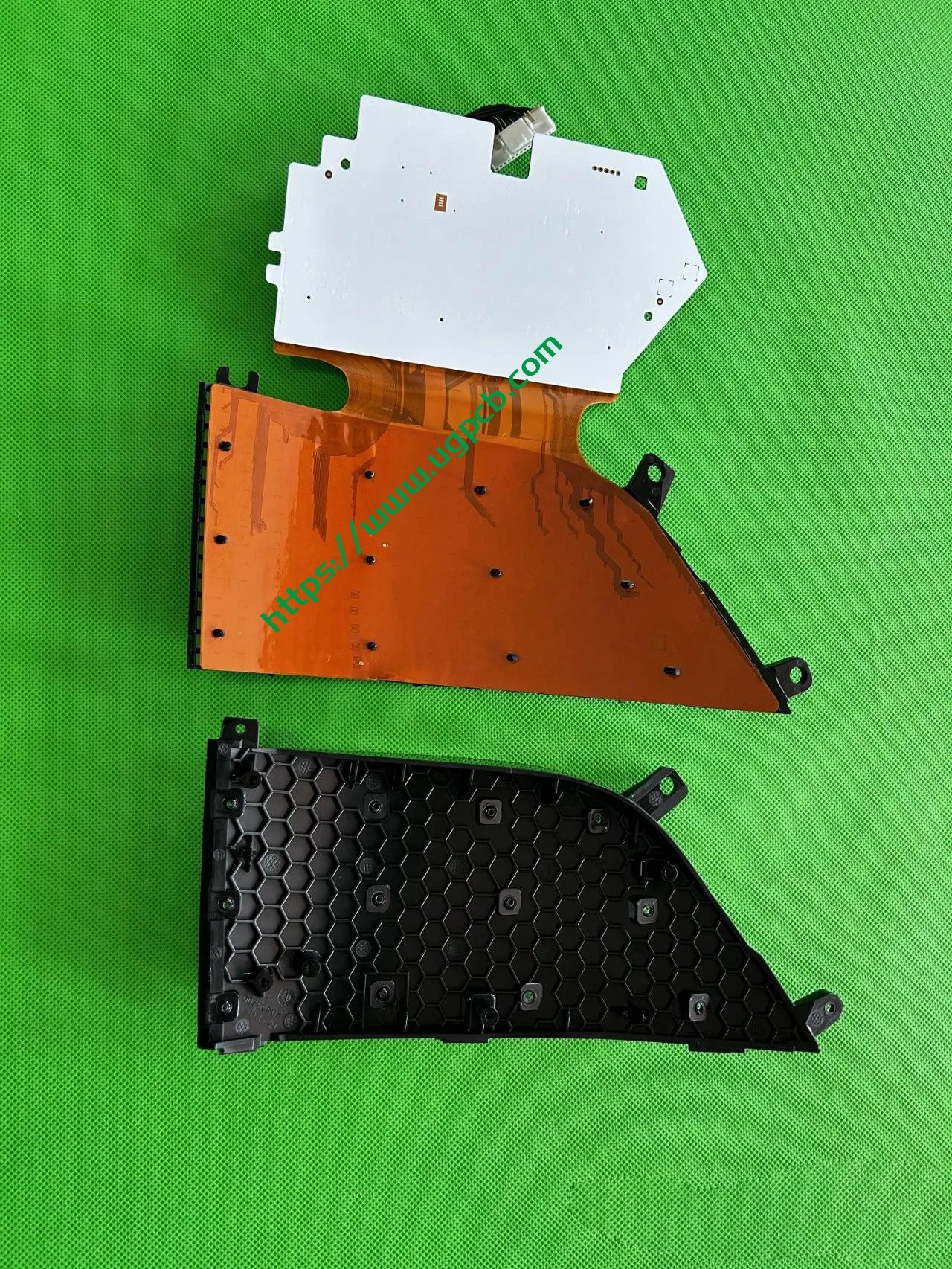







Manufacturer Information
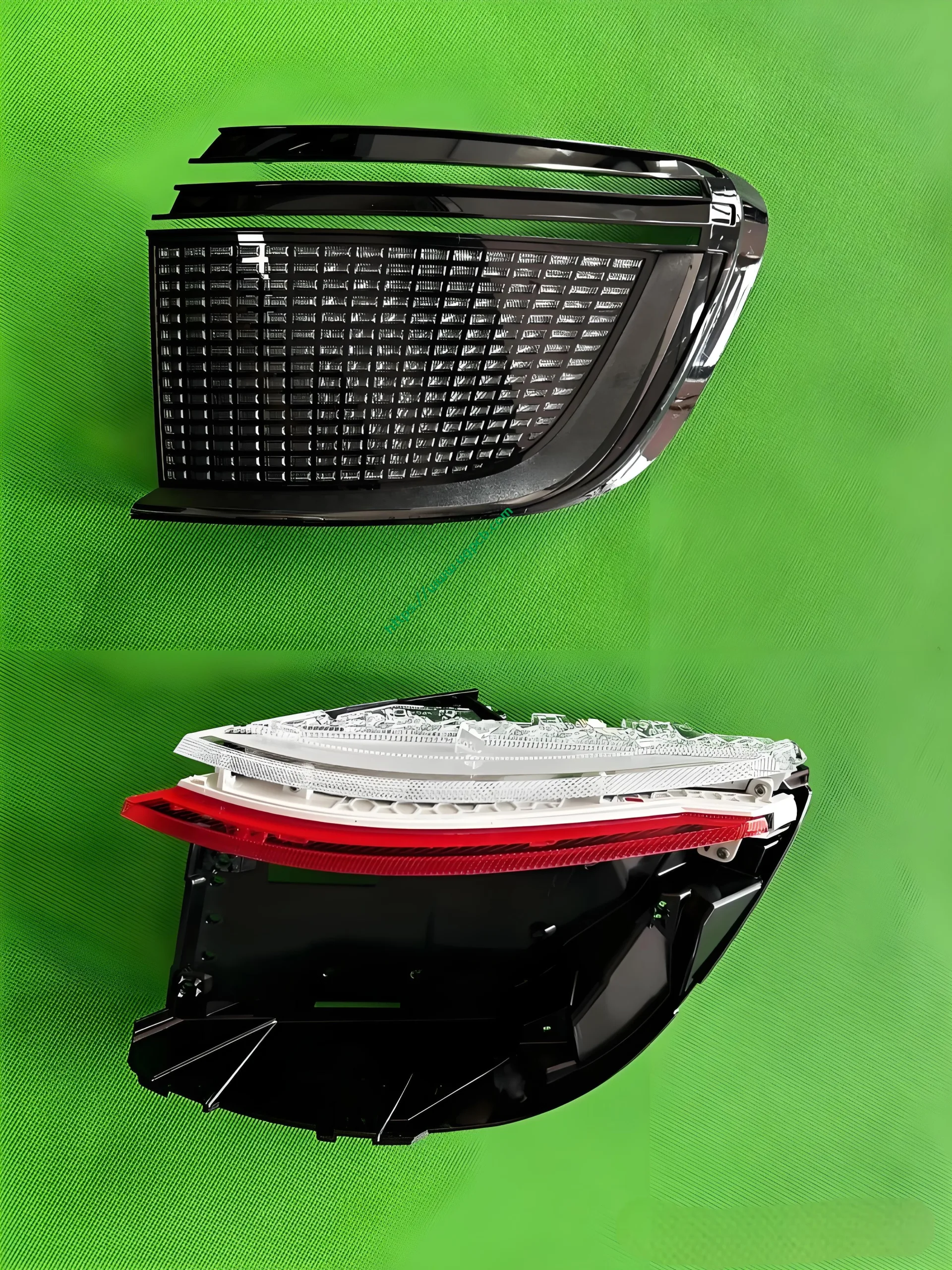






This tail light is manufactured by Xingyu.
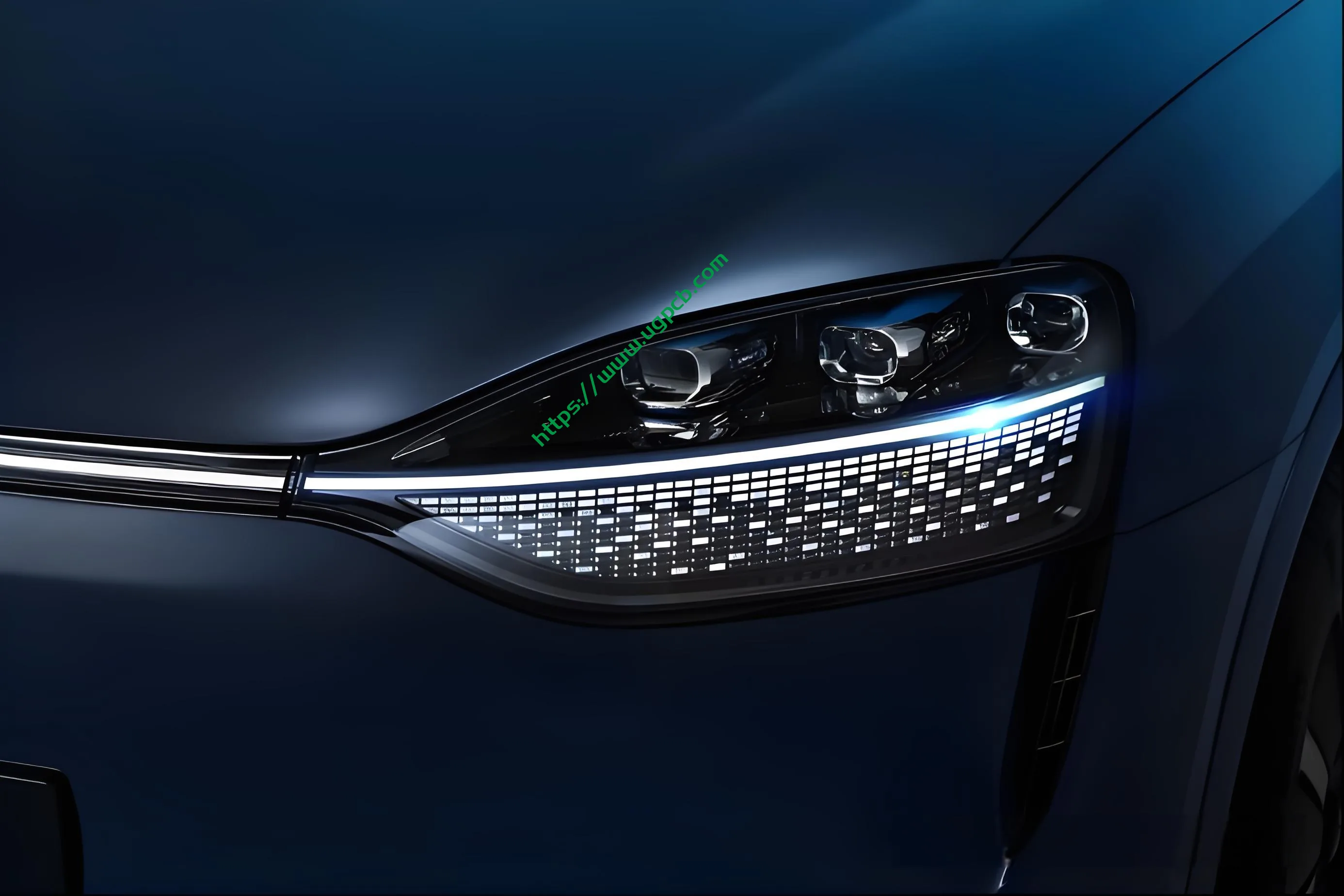
Introduction to AITO M9 DLP Headlights

DLP Projection Headlights are not new, having been used by luxury brands such as Mercedes-Benz, Audi, and Land Rover, as well as domestic automakers like HiPhi and IM Motors. However, with Huawei’s involvement, this technology has gained significant attention, prompting domestic automakers to switch from HD to DLP solutions. Today, we will dismantle Huawei’s DLP projection headlights after previously dissecting HiPhi X’s projection headlights.
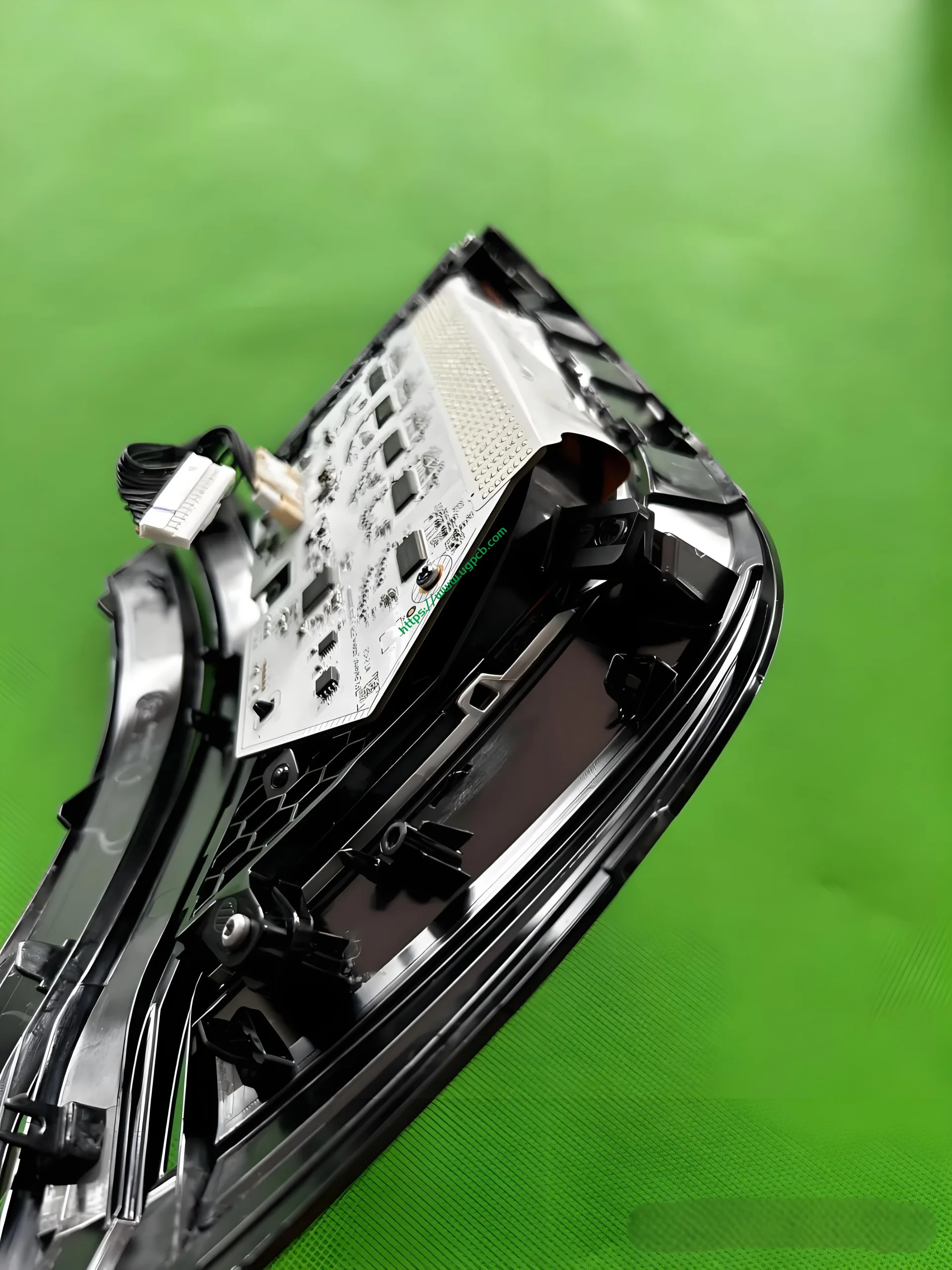
Components of the DLP Headlights


Here is a functional diagram of the headlights, showcasing a luxurious configuration. From the fender to the grille, there are low beam lenses, 84-pixel ADB lenses, and DLP projection lenses, separated by a thick-walled light guide. Below is the ISD interactive light. In this article, we will focus on the ISD interactive light and signal light sections.
Design of the ISD Scheme
Although this light is not the first to use the ISD concept, it has unique advantages in detailed design. Let’s look at an exploded view: bracket + FPC + inner lens (bicolor – black + diffuser) + aluminum-coated light-blocking bracket + second inner lens (bicolor – black + transparent) + main frame.




The manufacturing process involves two sub-assemblies: the first consisting of a bracket, FPC, and inner lens (using thermal riveting), and the second consisting of an aluminum-coated light-blocking bracket, second inner lens, and main frame (using thermal riveting and laser welding).
Design Details of the ISD Scheme
This ISD solution considers pixel leakage across three stacked components. Let’s dive into some notable details. The aluminum-coated light-blocking bracket between the first and second inner lenses uses PP-TD20 material coated with aluminum, which is soft and thin-walled, effectively bridging gaps between the inner and outer lenses and enhancing brightness in static conditions.


Static Effects Comparison
Below are comparisons of static effects with and without the aluminum-coated light-blocking bracket (the physical difference is significant).

Signal Light Section
The daytime running light, turn signal, and position light share a common light-emitting area using bicolor LEDs. The optical component is an assembly connected by clips, and for clarity, we’ve provided a hand-drawn cross-section.



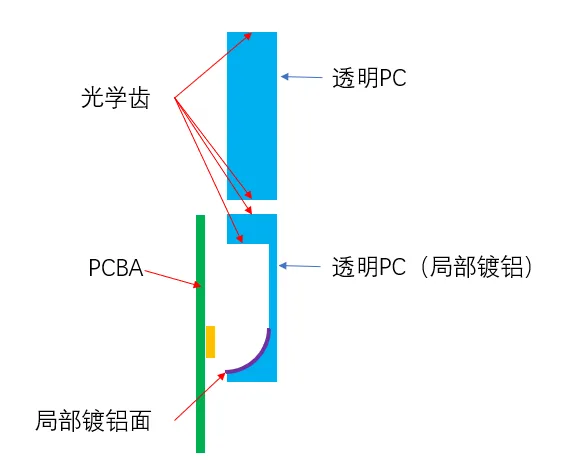
PCBA and Mounting
The PCBA and black bracket are fixed to the optical component with screws. An interesting design choice is that the installation screws and positioning pins for the PCBA are distributed on both sides of the LED. We welcome your thoughts on this design in the comments.


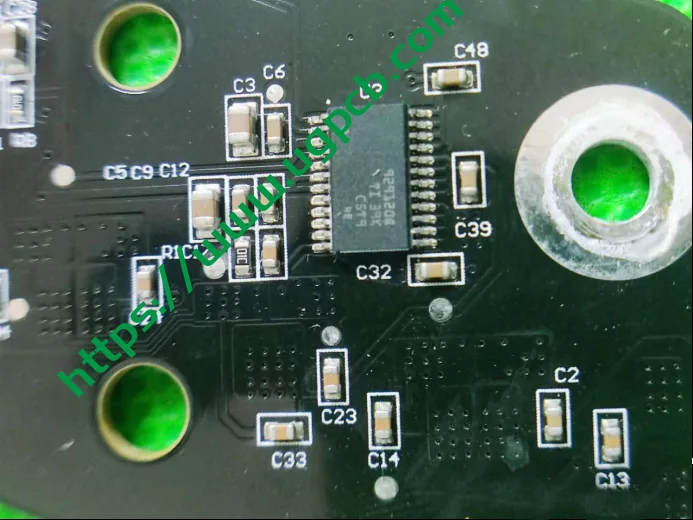
Components of the Signal Light Board
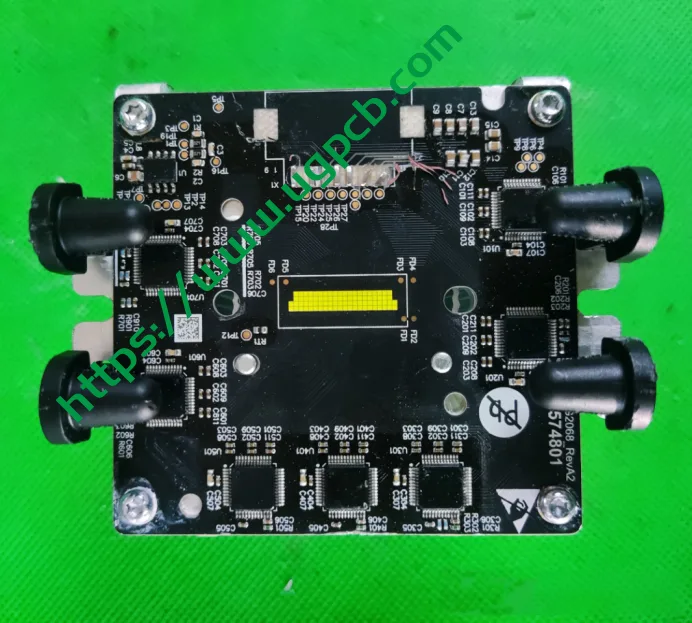
The signal light board uses a TI 1044 CAN transceiver chip, seven 12-channel TPS929120Q LED direct drive chips, and 40 bicolor LEDs.
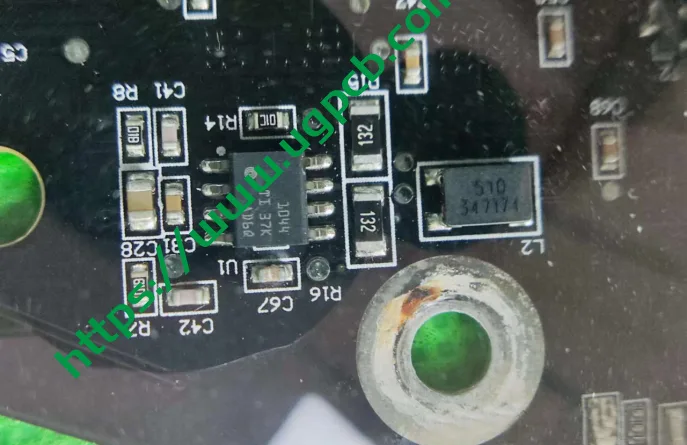

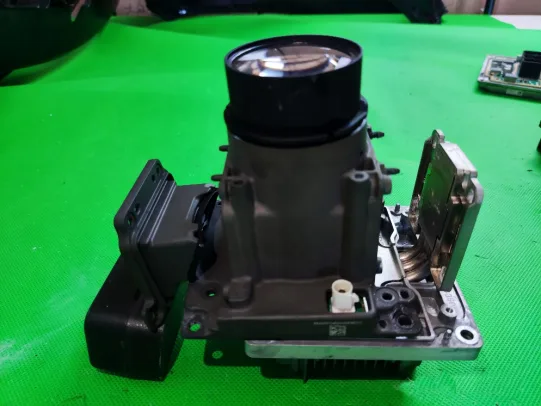
Disassembly of the Main Light Source and DLP Module
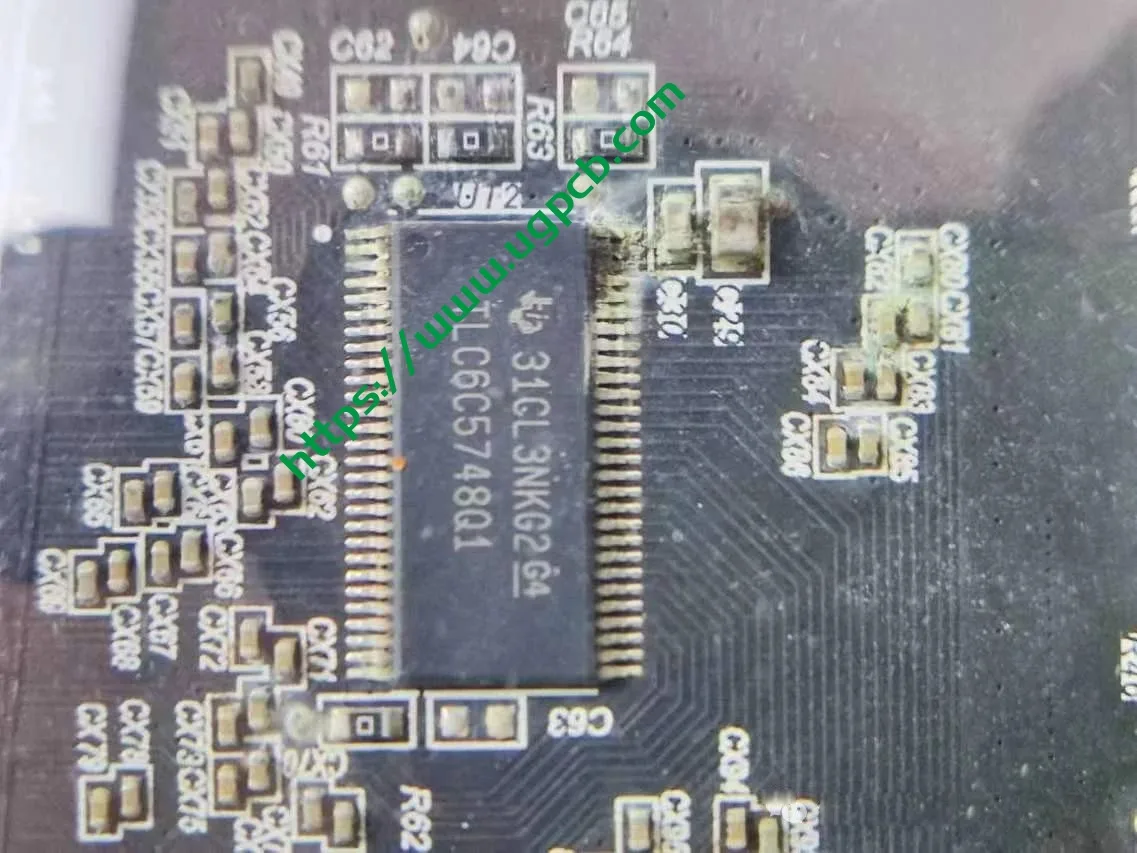
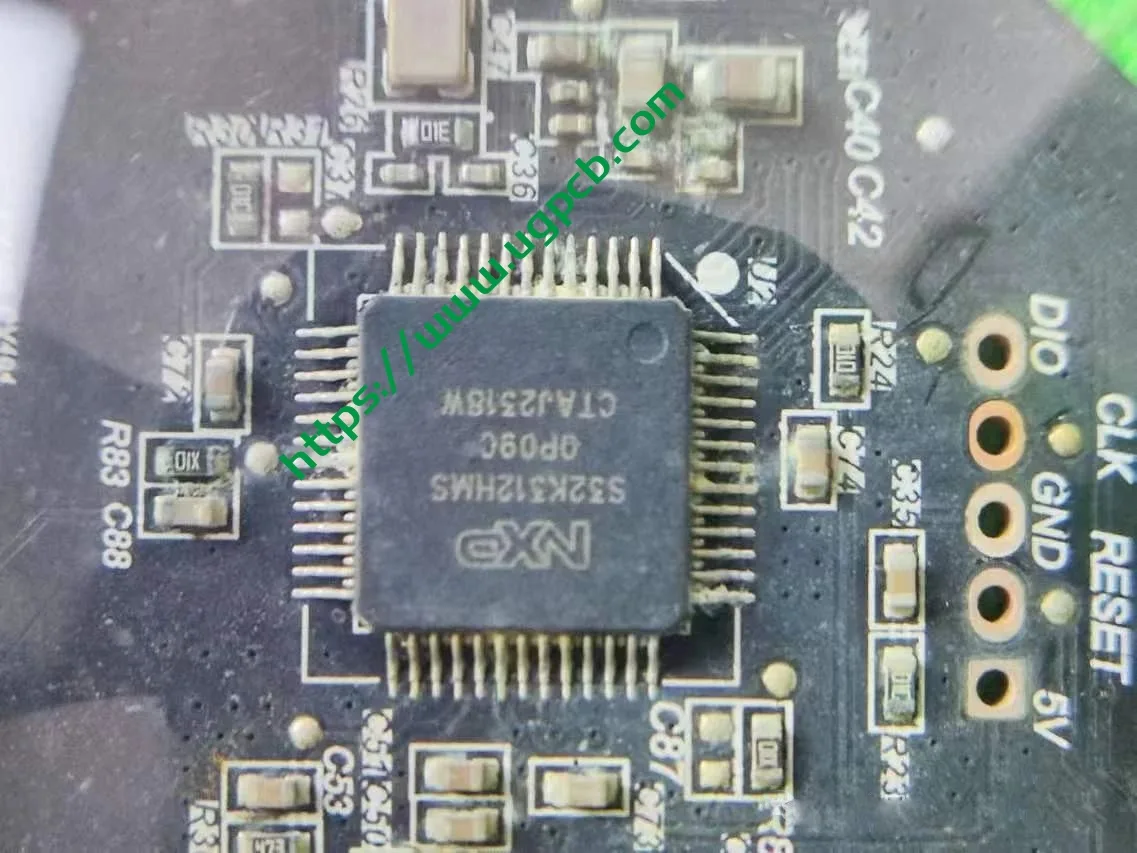
Now, let’s move to the main light source and Huawei’s DLP module. We will provide details on the 1.3-megapixel module. First, to answer a question from our previous audience, the ISD LEDs are driven by specific chips, as shown in the diagram below.
Review of Lens Functions
Recall the functions of the three lenses in the headlights: the innermost is DLP, the middle is 84-pixel, and the outermost is the low beam lens.

Low Beam Module
The low beam module has no particularly outstanding design except for a low-cost solution for the cut-off line achieved through features on the radiator.
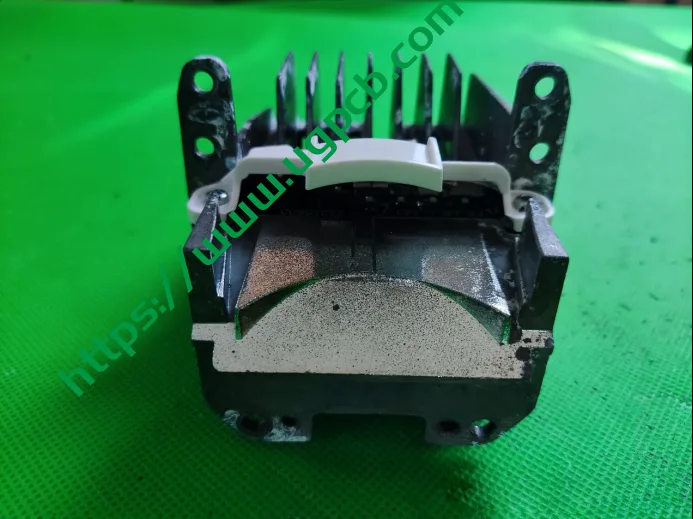



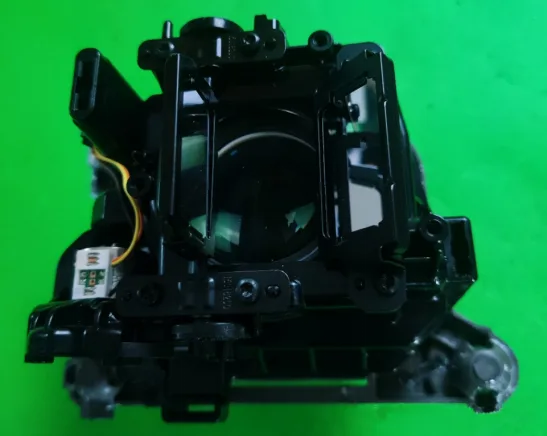
84-Pixel Lens
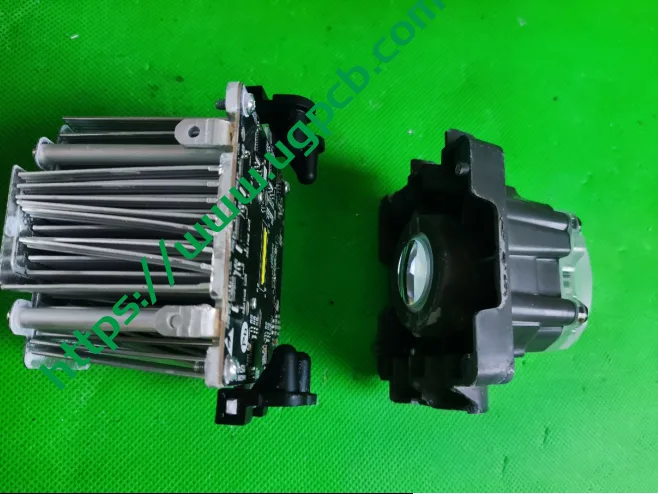
This lens employs a direct imaging method using the light source. The light source is directly followed by an imaging lens, designed with three pieces: glass, PMMI, and PC. The precise arrangement of light source pixels is likely key to adopting this imaging solution.
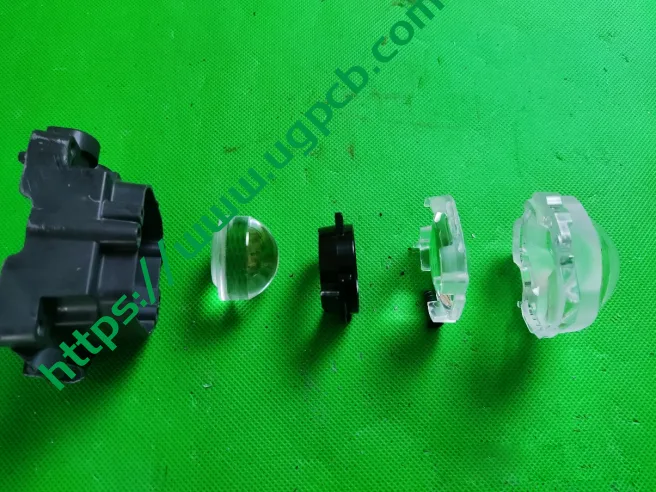


Additional Lens for Effect

Another costly design choice is the addition of an extra lens in front of the module for overall lighting effect.

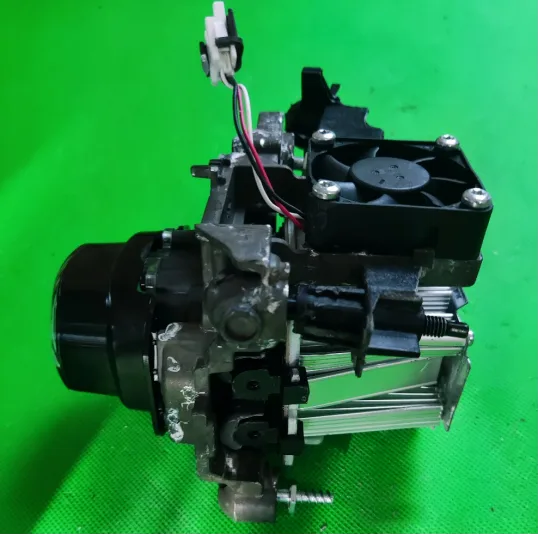
DLP Module Design
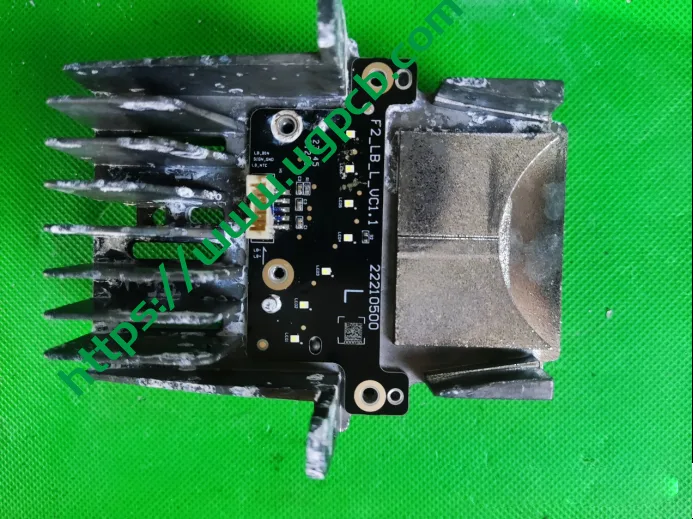
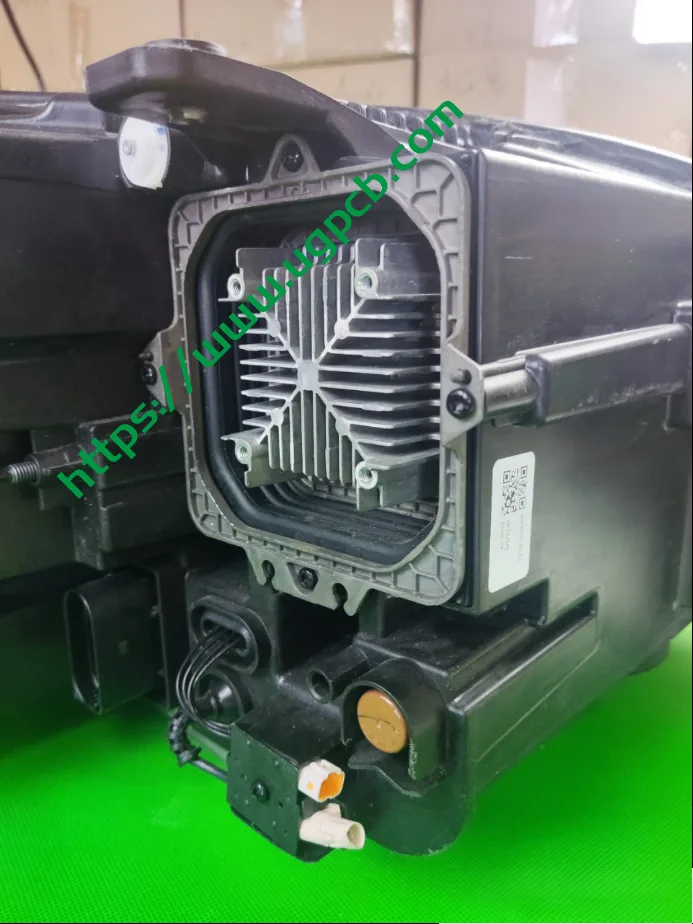
The DLP module has two interesting design features: an external fan design and a design for ultra-near-field projection. The DLP module (16*95*100) radiator is externally mounted, with the cooling fan directly assembled to the back of the radiator. This design offers better cooling than内置 designs. However, it remains to be seen whether this externally mounted fan can withstand harsh vehicle environments without additional protection.

Module Sealing
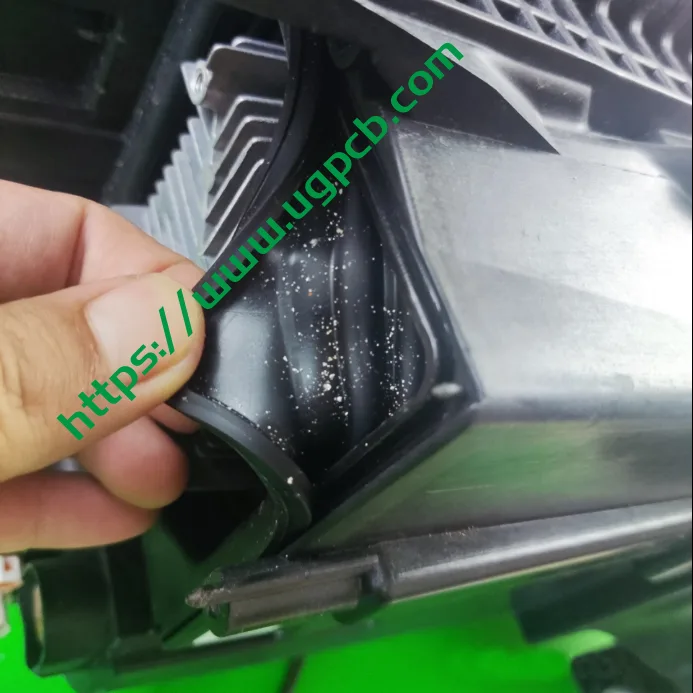

The module and the entire lamp are sealed with soft glue to ensure both sealing and adjustability after installation. The soft glue is fixed to the lamp housing and module radiator through two metal pressure plates.
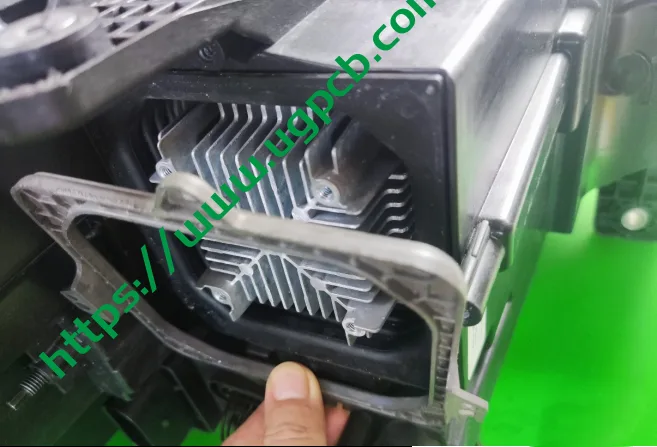
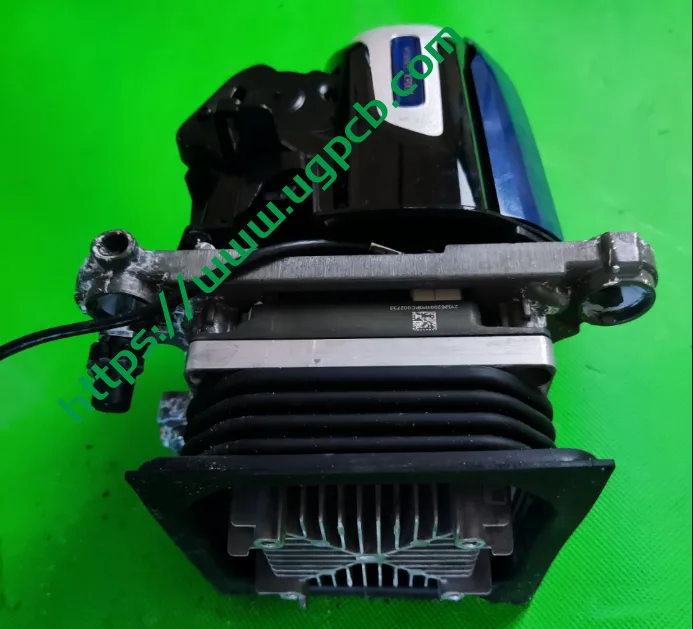


Ultra-Near-Field Projection

For DLP projection modules, the field of view for projection clarity is not set to be very large. Therefore, special designs are required to balance low beam functionality and ultra-near-field projection. The light path is as follows: a reflective mirror can change angles to enable ultra-near-field projection.
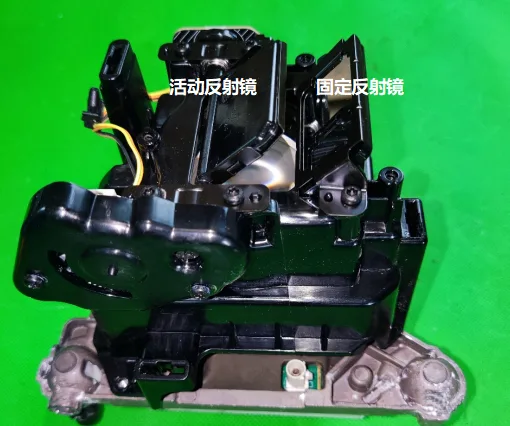
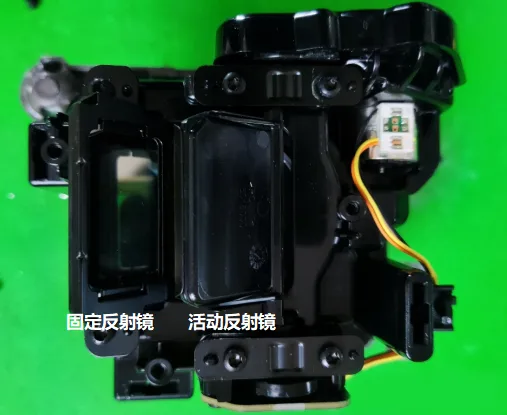
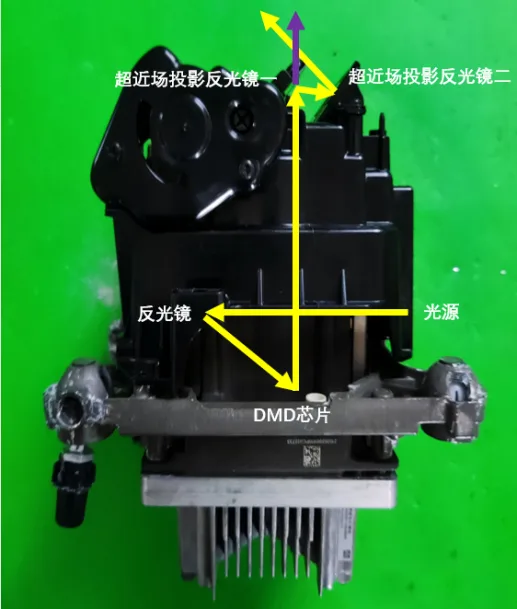
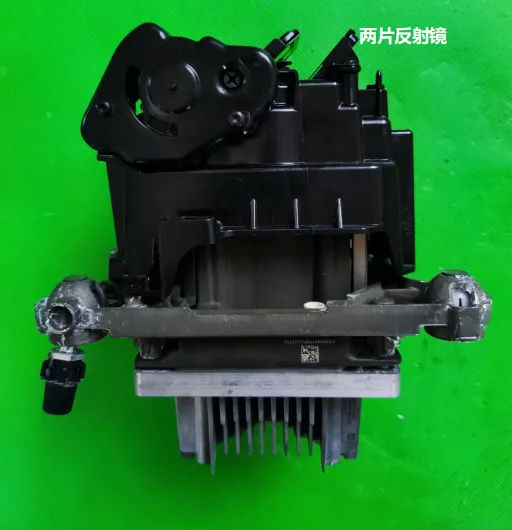



Reflective Mirror and Radiator
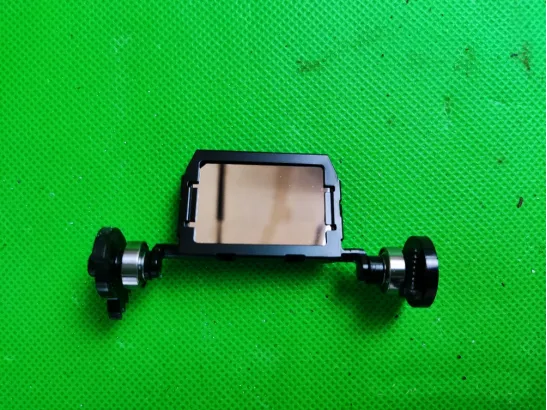
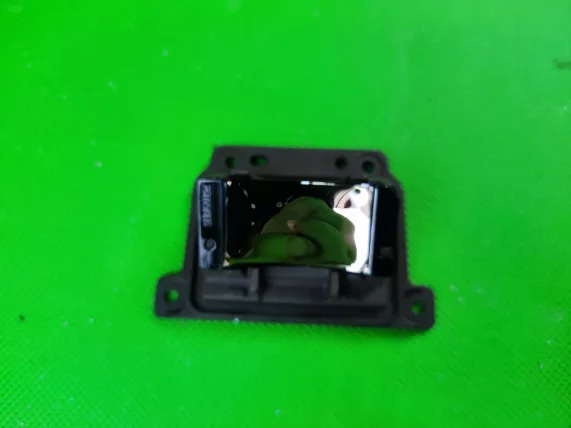
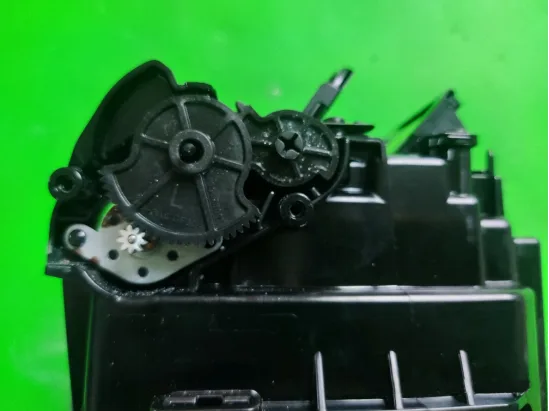


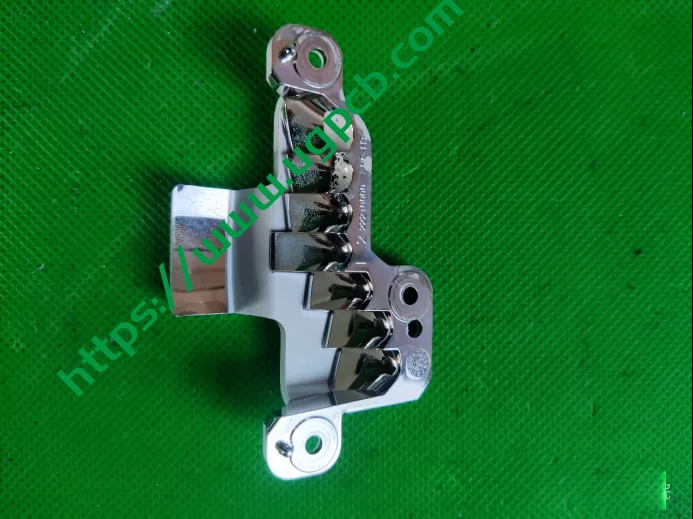
The reflective mirror changes angles through a motor and is connected to the bracket via bearings pressed by a metal clip. The radiator features three heat pipes.
Conclusion
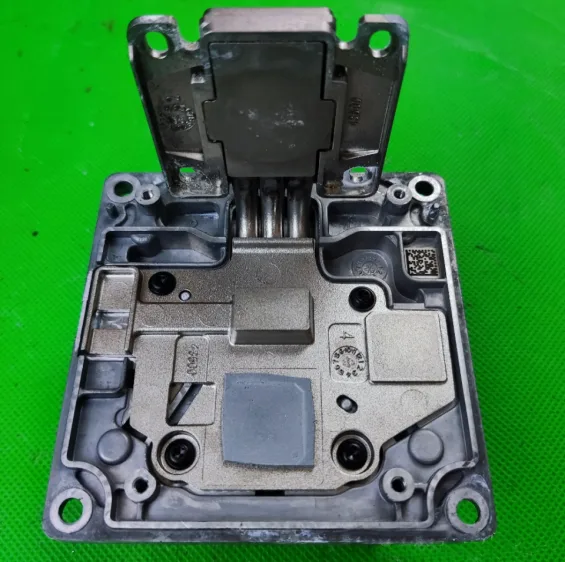

This concludes our disassembly of the AITO M9 headlights. Finally, these headlights are manufactured by Xingyu.
 UGPCB LOGO
UGPCB LOGO

