Overview of Industrial Automation Control
Industrial control refers to industrial automation control, primarily realized through the integration of electronic, Elétrica, mecânico, and software components. This encompasses factory automation control, utilizing computer technology, microelectronic technology, and electrical methods to enhance the automation, eficiência, precision, controllability, and visibility of the production and manufacturing process within a factory.
Main Structure of Industrial Automation Control
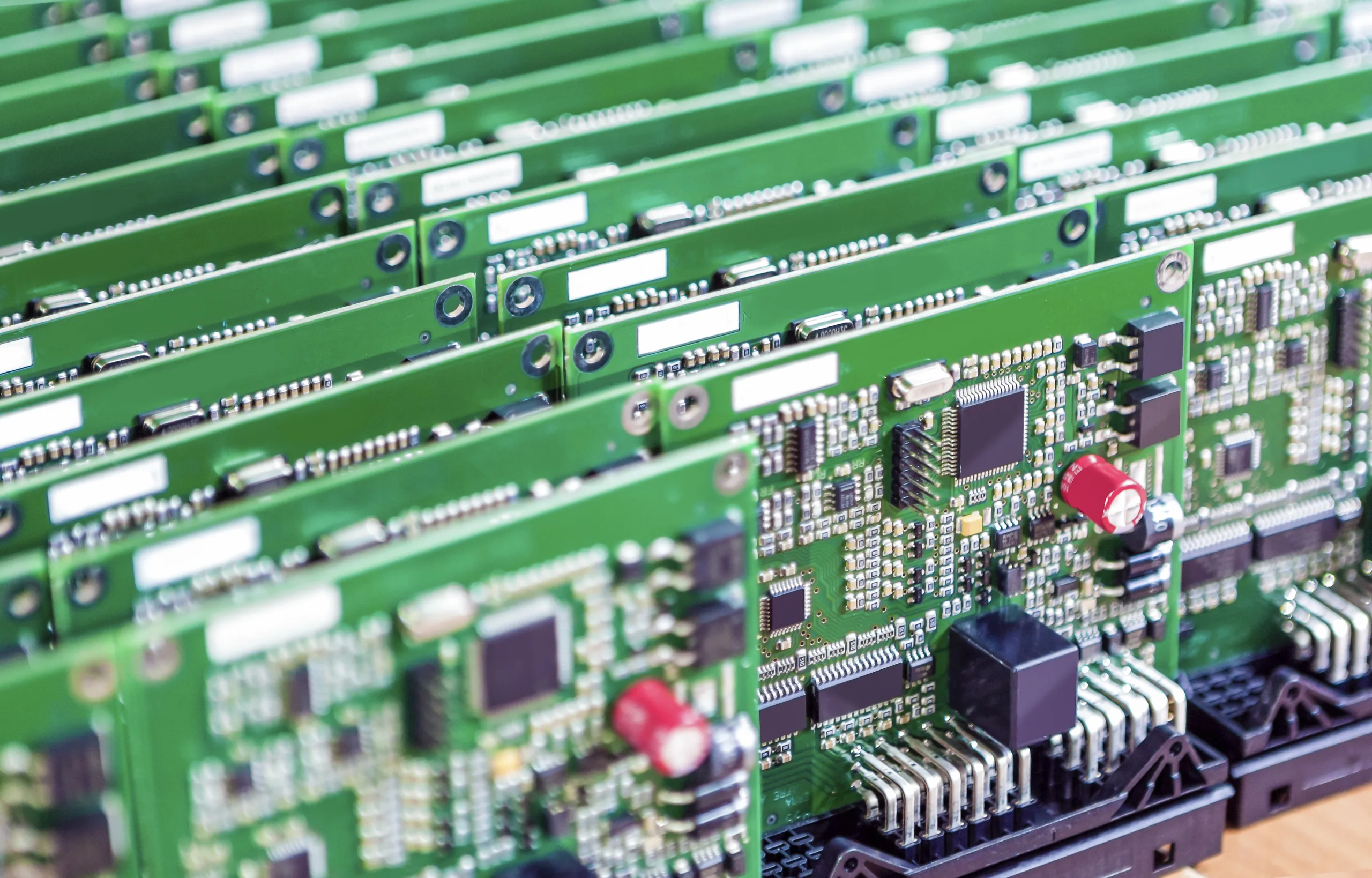
The main structure of industrial automation control consists of an all-steel chassis, passive backplane, industrial power supply, CPU card, and other accessories.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Industrial Computers
Advantages of Industrial Computers
- High Durability: The chassis adopts a steel structure, providing high anti-magnetic, dust-proof, and impact-proof capabilities.
- Modular Design: There is a special bottom plate in the chassis, featuring PCI and ISA slots for easy expansion.
- Robust Power Supply: The special power supply within the chassis boasts strong anti-interference abilities.
- Long-term Reliability: Industrial computers are designed to work continuously for extended periods.
- Ease of Installation: Tipicamente, a standard chassis that is easy to install is utilized.
Disadvantages of Industrial Computers
- Limited Storage: The configured hard disk capacity is generally small.
- Data Security Concerns: Lower data security compared to specialized systems.
- Limited Storage Options: Limited options for storage expansion.
- Higher Cost: The price of industrial computers is typically higher.
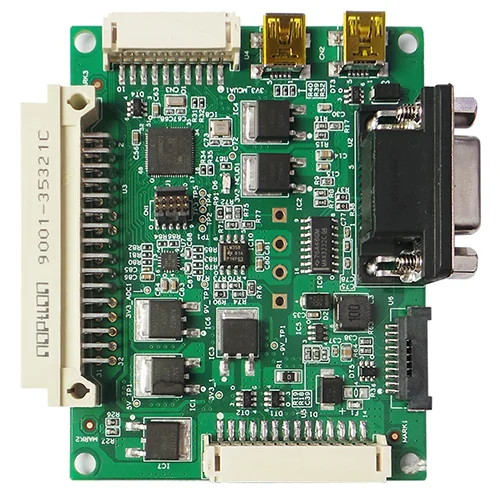
PCB Assembly Business for Industrial Control
We support Industrial Control Through Hole PCB Assembly business. UGPCB is a professional one-stop PCBA service factory. Welcome to inquire.
 LOGOTIPO UGPCB
LOGOTIPO UGPCB