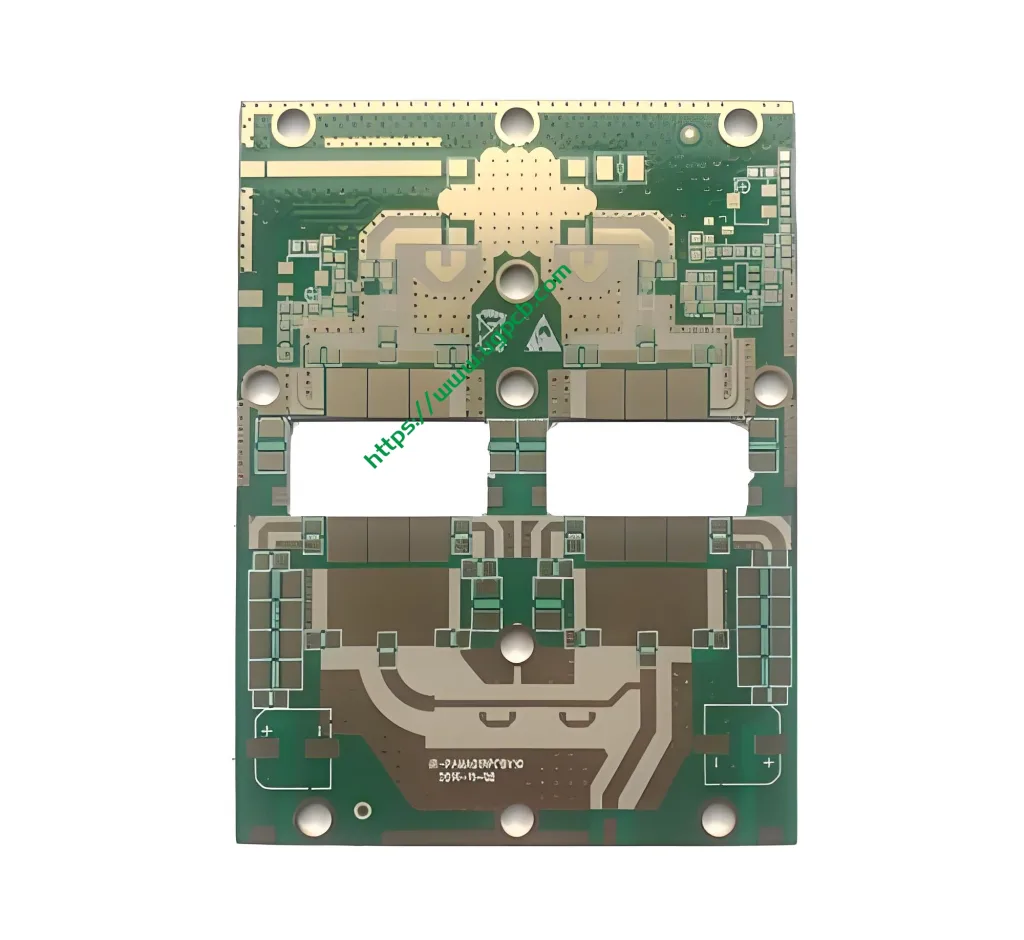
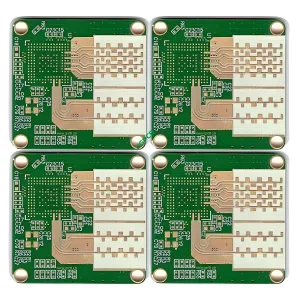
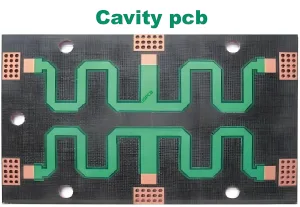
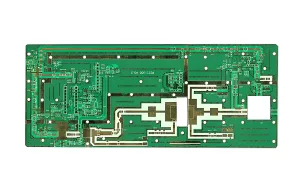
Overview of RF Circuit PCB
Radio Frequency (RF) Circuit Printed Circuit Boards, or RF PCBs, are specialized boards designed for high-frequency applications. They play a critical role in ensuring signal integrity and minimizing loss in devices operating at microwave frequencies. These boards are integral to the performance of antennas, instruments, and various communication equipment.
Definition and Design Considerations
An RF PCB is a type of circuit board specifically engineered to handle high-frequency signals, typically in the range of megahertz (MHZ) to gigahertz (GHz). Key design considerations include:
- Dielectric Material: The choice of material affects signal propagation speed and loss.
- Grosime de cupru: Determines current-carrying capacity and thermal management.
- Layer Stack-Up: Influences impedance control and crosstalk.
Working Principle and Applications
RF PCBs operate based on the principles of electromagnetic wave propagation. At high frequencies, even minor imperfections can significantly impact signal quality. Prin urmare, these boards are designed with precision to maintain controlled impedance and minimize insertion loss. Applications include:
- Antennas: Ensuring efficient transmission and reception of signals.
- Instruments: Providing accurate measurements in test and measurement equipment.
- Communication Equipment: Facilitating reliable data transfer in wireless systems.
Classification and Materials
Types:
- Single-Sided and Double-Sided RF PCBs: Suitable for simpler designs with fewer layers.
- Multilayer RF PCBs: Offer more complexity and better performance for advanced applications.
Core Materials:
- FR-4: A common material known for its cost-effectiveness and reliability.
- Teflon/PTFE: Offers low dielectric constant and loss tangent, ideal for high-frequency applications.
- Ceramic/Hydrocarbon: Provides excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength.
Performance and Structure
Key performance indicators for RF PCBs include:
- Dielectric Constant (DK): Ranges from 2.0 to 1.6, affecting signal speed and impedance.
- Grosime: Varies from 0.254mm to 12mm, influencing the board’s mechanical stability and layer count.
- Grosime de cupru: Typically ranges from 0.5oz to 2oz, impacting current handling and heat dissipation.
The structure of an RF PCB includes multiple layers of conductive pathways embedded within the dielectric material, often with precise impedance control and strict tolerances to ensure optimal signal integrity.
Characteristics and Production Process
RF PCBs are characterized by:
- Strict Tolerance Control: Ensuring consistent electrical performance across all units.
- High-Quality Standards: Adhering to IPC Class 2 or Class 3 Standarde.
The production process involves several stages:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right substrate and copper foil based on application requirements.
- Circuit Patterning: Using photolithography to create precise circuit patterns.
- Gravură: Removing unwanted copper to form the desired circuitry.
- Plating: Applying surface finishes like silver, gold, or OSP for corrosion resistance and better solderability.
- Quality Assurance: Conducting rigorous testing to ensure compliance with specifications.
Use Scenarios
RF PCBs are essential in scenarios where signal quality and integrity are paramount. Some examples include:
- Wireless Communications: Enabling clear and reliable transmission in mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers, and other wireless devices.
- Radar Systems: Providing precise signal handling for detection and ranging.
- Medical Devices: Ensuring accurate data collection and analysis in diagnostic equipment.
În concluzie, RF Circuit PCBs are specialized boards designed for high-frequency applications, requiring meticulous attention to detail in their design and manufacturing. They offer superior performance in terms of signal integrity and are crucial in various industries, including telecommunications, aerospace, and medical technology.
 LOGO UGPCB
LOGO UGPCB