PCB impedance design
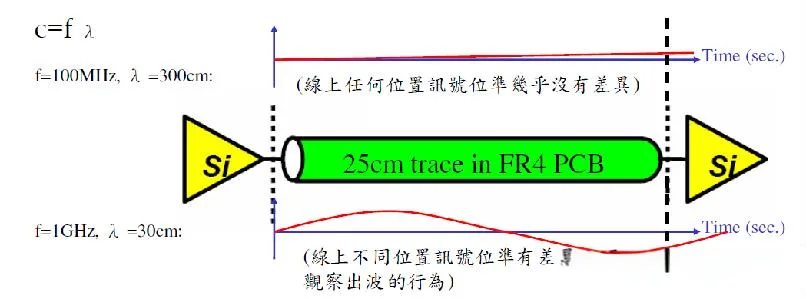
Impedance: A Crucial Concept in PCB Design, Especially for High-Frequency and High-Speed Signal Transmission
Below is a detailed analysis of PCB impedance knowledge:
ฉัน. What is Impedance
What is Impedance
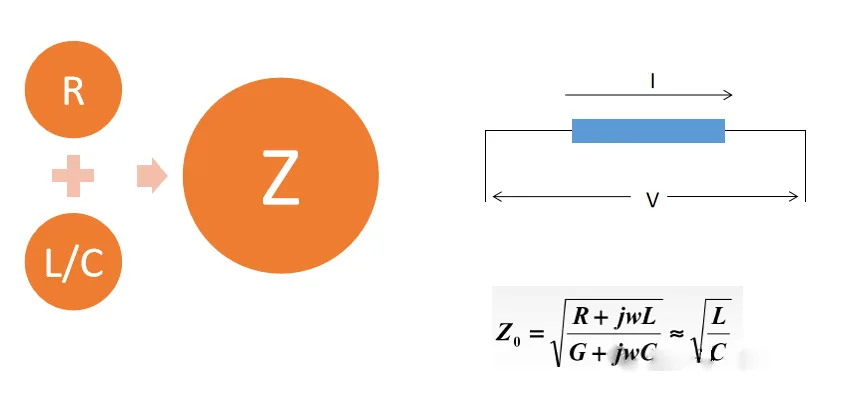
Impedance (Impedance) refers to the obstruction effect of a point in a circuit on alternating current. It includes resistance and reactance (caused by capacitance and inductance). In PCB design, impedance mainly refers to Characteristic Impedance (Characteristic Impedance), which is the ability of a transmission line to obstruct signal propagation. Impedance Z0, with the unit Ohm (Ω).
ครั้งที่สอง. The Importance of Impedance
- ความสมบูรณ์ของสัญญาณ: Impedance matching ensures that signals maintain their shape and intensity during transmission, reducing distortion and attenuation.
- Reduction of Reflections: If the impedance of the transmission line does not match the connected device, it can lead to signal reflections, affecting system performance.
- Improvement of System Performance: By controlling impedance, สัญญาณรบกวนแม่เหล็กไฟฟ้า (อีเอ็มไอ) and crosstalk can be reduced, enhancing system reliability and stability.
ที่สาม. Types of Impedance
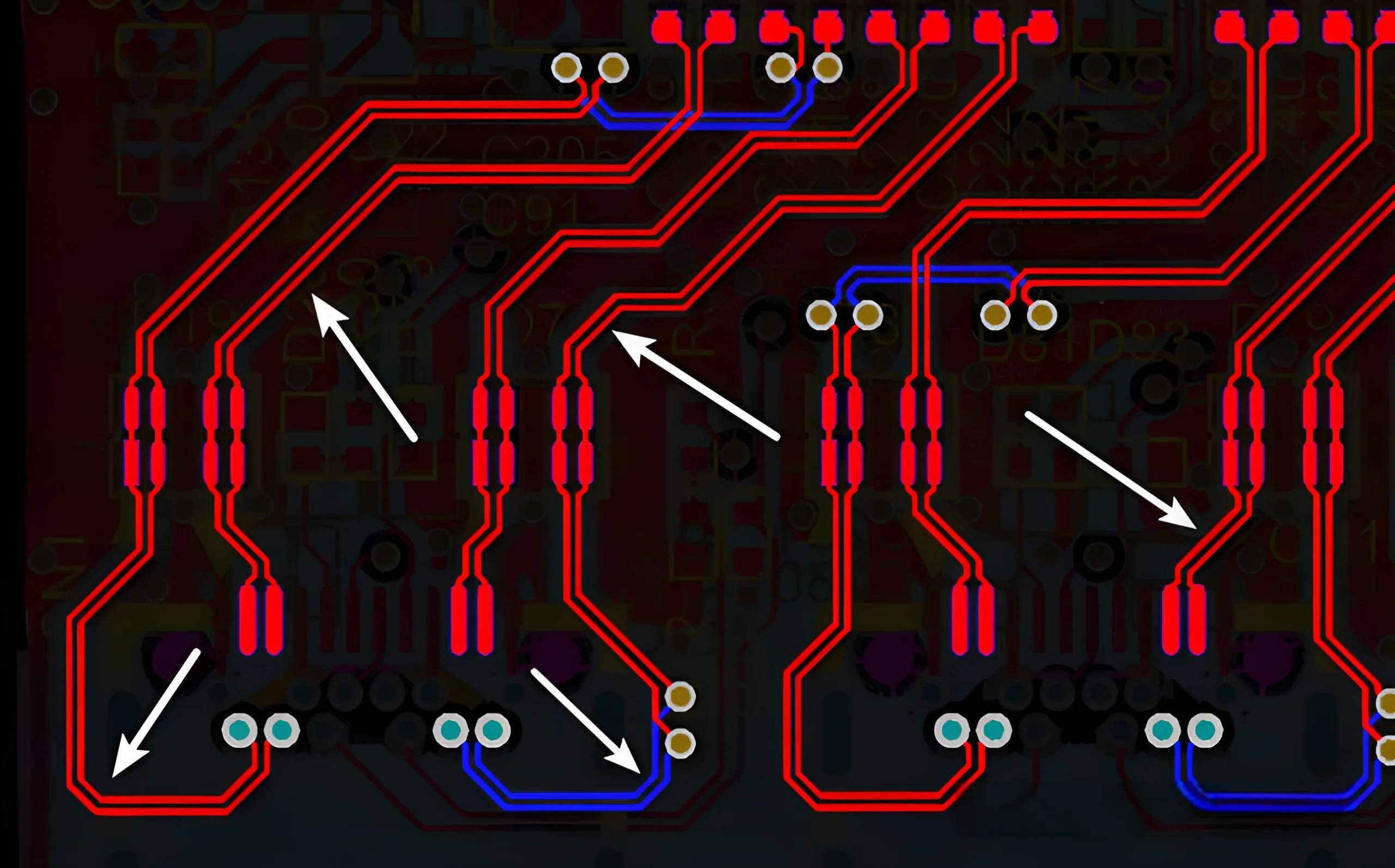
- Single-Ended Impedance: Impedance for a single conductor, such as Microstrip and Stripline. Below are examples of typical single-ended impedances:
Differential Impedance
- Differential Impedance: Impedance for a pair of differential signal lines, commonly used in high-speed interfaces like USB and HDMI. The impedance of two lines transmitted in parallel with a certain spacing is differential impedance.
- Coplanar Impedance: Includes coplanar single-ended and coplanar differential impedance, suitable for specific PCB layouts. Coplanar impedance refers to the impedance line surrounded by copper.
From these PCB impedance diagrams, it is not difficult to see that the transmission line of impedance is key to connecting impedances between conductors. How does the impedance of the transmission line transmit?
IV. Factors Affecting Impedance
- Line Width: The width of the trace directly affects the impedance value. Wider traces result in lower impedance.
- Line Spacing: The distance between traces also affects impedance. Larger spacings result in higher impedance.
- Dielectric Thickness: The thickness and dielectric constant (Dk value) of the PCB material significantly influence impedance.
- Laminate Structure: The laminate structure and material selection of the PCB affect the characteristic impedance of the transmission line.
- ความหนาของทองแดง: The thickness of the copper foil on the PCB also affects the impedance value. โดยทั่วไป, increasing copper thickness reduces impedance.
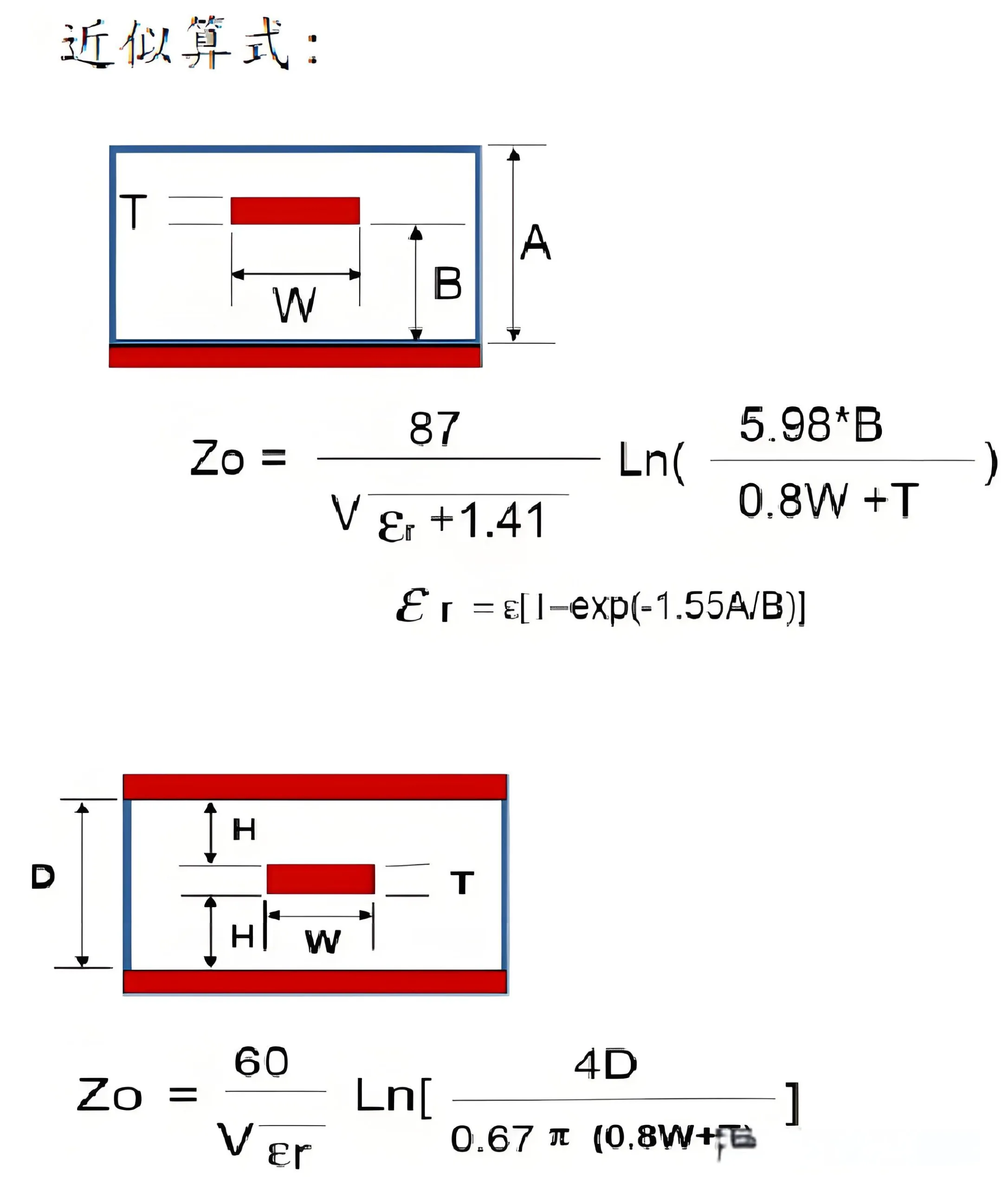
วี. Impedance Calculation Methods
Impedance calculation is typically performed using specific formulas or software tools. ตัวอย่างเช่น, for microstrip lines, the characteristic impedance can be calculated using the following formula:
Z_0 = \frac{87}{\sqrt{\epsilon_r + 1.41}} \cdot \ln\left(\frac{5.98h}{0.8w + t}\right)
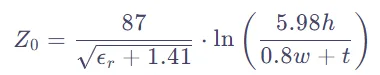
Where Z_0 is the characteristic impedance, Er is the relative dielectric constant, hh is the thickness of the dielectric substrate, ww is the width of the conductor strip, and tt is the thickness of the conductor strip.
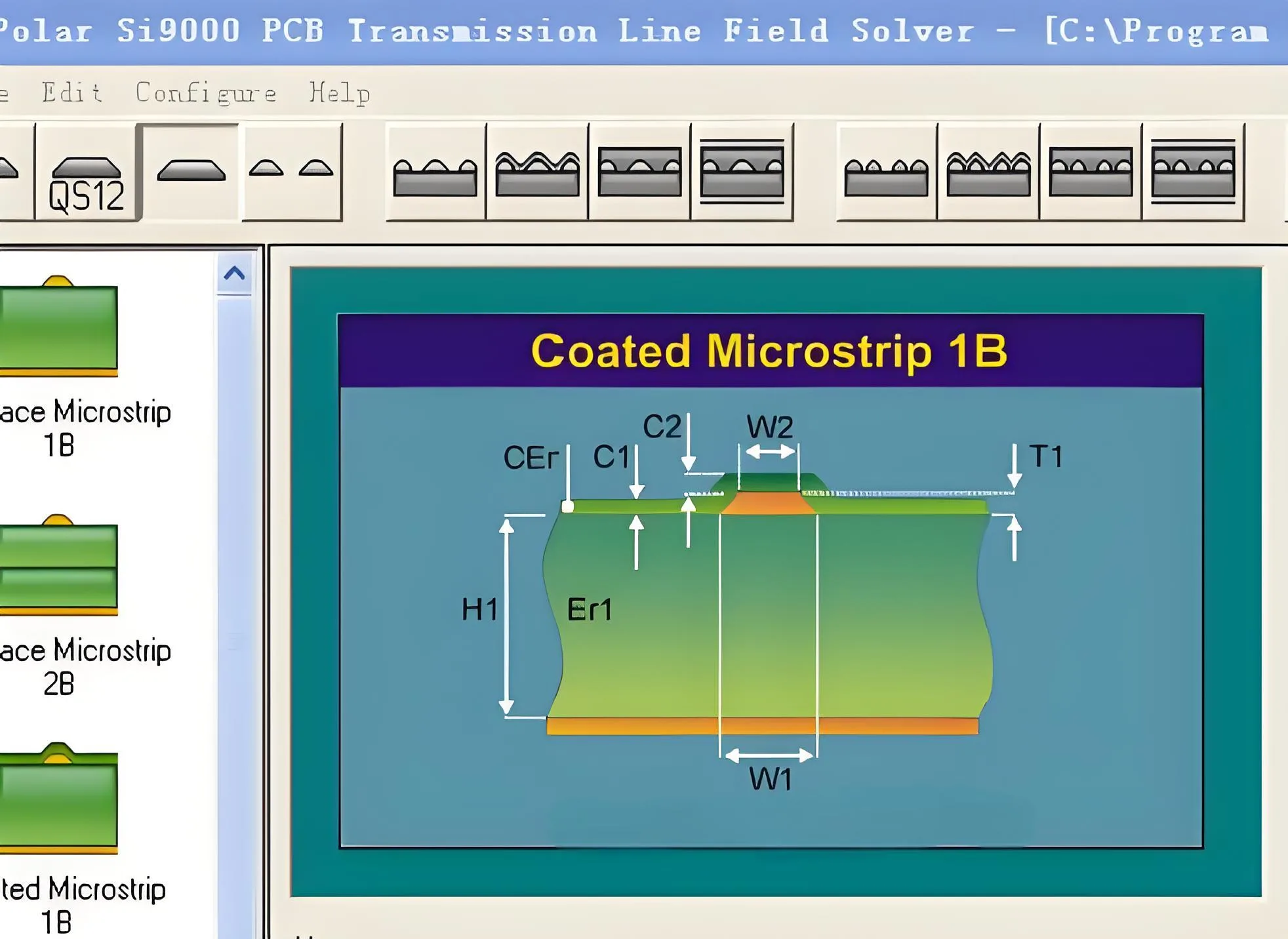
นอกจากนี้, there are many professional PCB impedance calculation tools, such as Polar SI9000, which can conveniently calculate the characteristic impedance of different types of transmission lines.
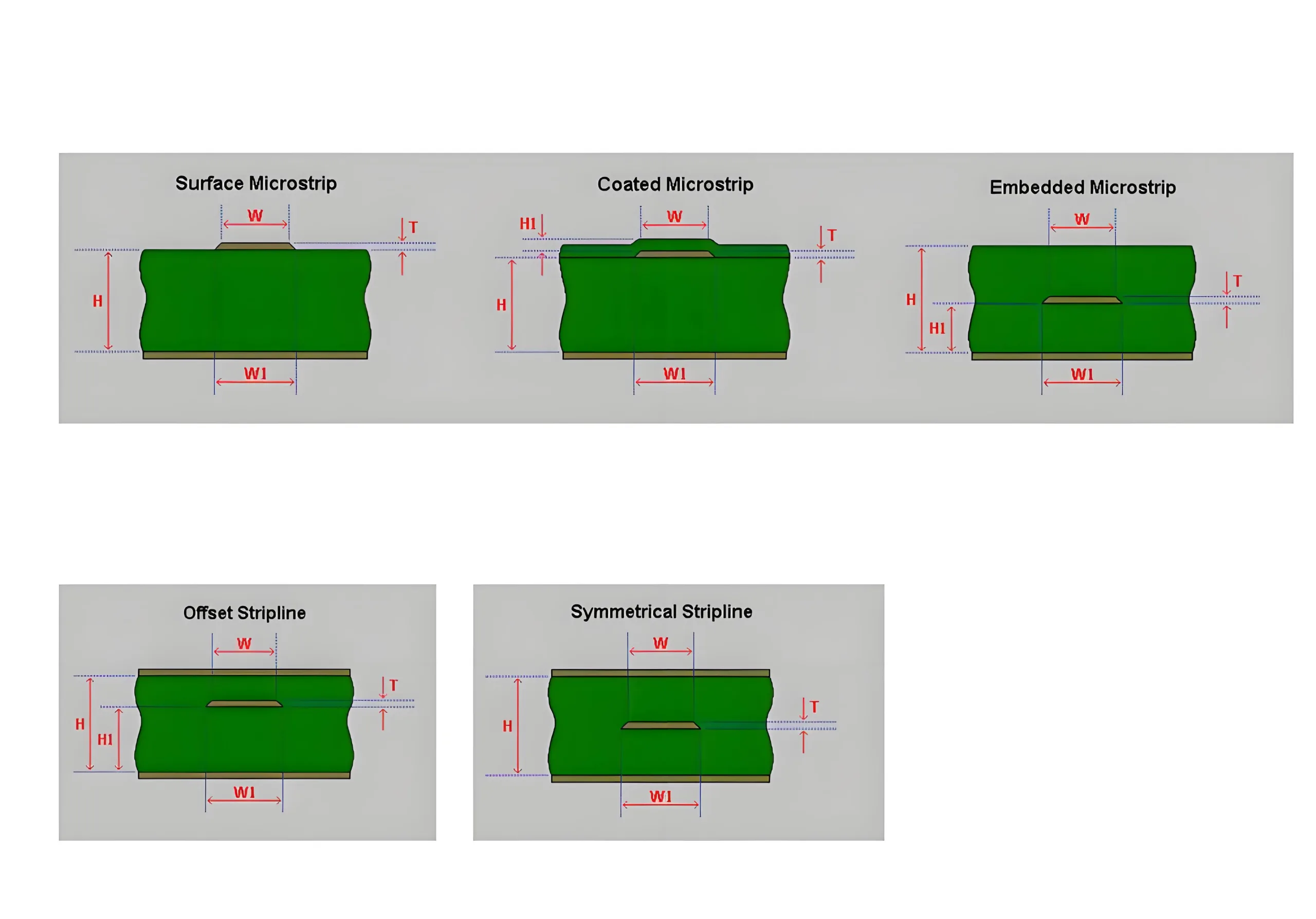
Common PCB transmission line structures
VI. Practical Applications of Impedance Control
In PCB design, appropriate impedance control strategies need to be selected based on specific applications.
ตัวอย่างเช่น, in fields such as high-speed digital signal processing and radio frequency communication, impedance must be strictly controlled to ensure signal integrity and system performance.
ดังนั้น, how is impedance controlled in actual PCB production? This topic will be discussed in our next article.
สรุปแล้ว, impedance is a significant factor that cannot be ignored in PCB design. Understanding and mastering the basic principles, calculation methods, and practical applications of impedance is crucial for improving the performance and reliability of electronic products.
 โลโก้ UGPCB
โลโก้ UGPCB

