Definition of CTI
CTI is the relative leakage tracking index. The maximum voltage value, expressed in V, that a material surface can withstand 50 drops of electrolyte without forming leakage traces. CTI 600 refers to 600V.
IEC Standard for CTI
Resistance to electric leakage traces is generally expressed by comparative tracking index (CTI). The definition of CTI index in IEC 112 standard is the maximum voltage value (usually expressed in volts) when the material is subjected to 50 drops of electrolyte (โดยทั่วไป 0.1% ammonium chloride aqueous solution) without leakage trace during the experiment. IEC950 also defines and classifies three CTI grades of substrate materials according to the different voltage values withstood by the substrate under the above experimental conditions. They are grade I (CTI ≥ 600V), grade II (600V ≥ CTI ≥ 400V), and grade III (400วี > CTI ≥ 175V). โดยทั่วไป, the lower the CTI level of the substrate material is, the higher the leakage resistance of the substrate material is.
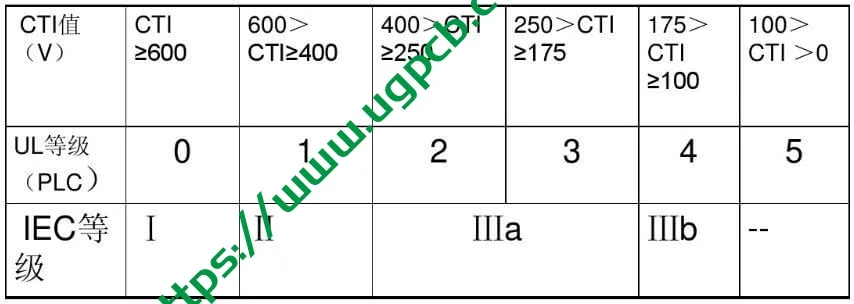
PCB CTI Grade
As the carrier of various components and the hub of circuit signal transmission, UGPCB has become the most important and key part of electronic information products. The quality and reliability level of UGPCB determine the quality and reliability of the whole equipment. Due to the development trend of high density UGPCB and the environmental requirements of lead-free and halogen-free, more and more UGPCBs appear poor wetting, board explosion, delamination, คาเฟ่, and other failure problems. The acquisition of UGPCB failure mechanism and reason will be beneficial to the quality control of UGPCB in the future, so as to avoid the recurrence of similar problems.
Electric Tracking and CTI
The relative tracking index (CTI) of a material is designed for electrical insulating materials. The index is defined as the voltage value when the tracking is caused. Electric tracking is a process that produces a part of the conductive path that is partially depleted on the surface of the insulating material. This is caused by the radiation of electric charges on or close to the insulator. In some cases, surface contamination can accelerate electrical tracking, so CTI refers to the voltage experienced after fifty drops of contaminated liquid are dropped.
CTI Testing and Usage
Comparative Tracking Index (CTI): The highest voltage value at which the surface of the material can withstand 50 drops of electrolyte (0.1% ammonium chloride aqueous solution) without forming a trace of leakage, unit For V. It can be found in the UL file. If there is no accident, the general UGPCB factory does not require UL to test this index. If there is a customer’s request, you can find a sheet supplier to get it and tell the customer all the actual situation. The client does not necessarily insist on verifying this indicator, it is probably also for document requirements, and document requirements can be negotiated. ในปัจจุบัน, the CTI index is not commonly used in the UGPCB industry. ดังนั้น, many UGPCB manufacturers, including well-known domestic manufacturers, no longer test this item in their UL files. CTI refers to the anti-leakage index. โดยทั่วไป, the CTI value of FR-4 sheet is about 175.
 โลโก้ UGPCB
โลโก้ UGPCB